Test Objectives: Unit 1 – Measurement
... Determine the percent composition of the elements in a compound, given the formula of the compound o determine the percent composition of elements in a compound from measured elemental mass data Determine the percent water in a hydrate, given the formula of the hydrate Determine the number of atoms ...
... Determine the percent composition of the elements in a compound, given the formula of the compound o determine the percent composition of elements in a compound from measured elemental mass data Determine the percent water in a hydrate, given the formula of the hydrate Determine the number of atoms ...
Chapter 4 Atoms and Elements
... • The properties of atoms determine the properties of matter. • An atom is the smallest identifiable unit of an element. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances. • There are about 91 different elements in nature, and consequently about 91 different kinds of ato ...
... • The properties of atoms determine the properties of matter. • An atom is the smallest identifiable unit of an element. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances. • There are about 91 different elements in nature, and consequently about 91 different kinds of ato ...
6.022 X 10 23 atoms - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... He also called the elements pure substances because all atoms of an element were identical and that in particular they had the same mass. ...
... He also called the elements pure substances because all atoms of an element were identical and that in particular they had the same mass. ...
Help us improve Wikipedia by supporting it financially
... The lightest elements are hydrogen and helium, both theoretically created by Big Bang nucleosynthesis during the first 20 minutes of the universe[10] in a ratio of around 3:1 by mass (approximately 12:1 by number of atoms). Almost all other elements found in nature, including some further hydrogen a ...
... The lightest elements are hydrogen and helium, both theoretically created by Big Bang nucleosynthesis during the first 20 minutes of the universe[10] in a ratio of around 3:1 by mass (approximately 12:1 by number of atoms). Almost all other elements found in nature, including some further hydrogen a ...
TEST-Periodic Table
... b. mixture of aluminum and an unknown element. c. unknown element he predicted would have properties similar to those of aluminum. d. rare isotope of aluminum. ...
... b. mixture of aluminum and an unknown element. c. unknown element he predicted would have properties similar to those of aluminum. d. rare isotope of aluminum. ...
ch3 - Otterville R-VI School District
... Thomson (English 1897) did more experiments to actually make the discovery he found ratio of charge of this particle to this mass of the particle since the ratio stayed constant for any metal that contained it, it must be the same in all of the metals ...
... Thomson (English 1897) did more experiments to actually make the discovery he found ratio of charge of this particle to this mass of the particle since the ratio stayed constant for any metal that contained it, it must be the same in all of the metals ...
File
... combine to form compounds. A particular compound is always made up of the same kinds of atoms and the same number of each kind of atom. 4. A chemical reaction involves the rearrangement, separation, or combination of atoms. Atoms are never created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. © 2014 Pearson ...
... combine to form compounds. A particular compound is always made up of the same kinds of atoms and the same number of each kind of atom. 4. A chemical reaction involves the rearrangement, separation, or combination of atoms. Atoms are never created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. © 2014 Pearson ...
g - Porterville College Home
... prefixes. Do not allow other instances of Greek or similar prefixes to confuse use in naming some of the oxyanions. For example, Cr2O72- is named dichromate. This has nothing to do with the naming of binary molecular compounds. There are a few instances of oxyanions series for a non-metal with two ...
... prefixes. Do not allow other instances of Greek or similar prefixes to confuse use in naming some of the oxyanions. For example, Cr2O72- is named dichromate. This has nothing to do with the naming of binary molecular compounds. There are a few instances of oxyanions series for a non-metal with two ...
3 The Atom GOB Structures
... • are tiny particles of matter. • of an element are similar to each other and different from those of other elements. • of two or more different elements combine to form compounds. • are rearranged to form new combinations in a chemical reaction. Atoms are never created or destroyed during a chemica ...
... • are tiny particles of matter. • of an element are similar to each other and different from those of other elements. • of two or more different elements combine to form compounds. • are rearranged to form new combinations in a chemical reaction. Atoms are never created or destroyed during a chemica ...
The Periodic Table
... The atomic number (Z) is the number of protons in the nucleus. Atoms are neutral, so it’s also the number of electrons. Protons determine the identity of an element. For example, nitrogen’s atomic number is 7, so every nitrogen has 7 protons. The mass number (A) is the total number of protons and ...
... The atomic number (Z) is the number of protons in the nucleus. Atoms are neutral, so it’s also the number of electrons. Protons determine the identity of an element. For example, nitrogen’s atomic number is 7, so every nitrogen has 7 protons. The mass number (A) is the total number of protons and ...
Unit 3 Lesson 1
... • In 1808, John Dalton published an atomic theory, stating that all matter is made up of atoms that cannot be created, divided, or destroyed. • This theory also stated that all atoms of a certain element are identical, but they differ from atoms of all other elements. • Every substance is made up of ...
... • In 1808, John Dalton published an atomic theory, stating that all matter is made up of atoms that cannot be created, divided, or destroyed. • This theory also stated that all atoms of a certain element are identical, but they differ from atoms of all other elements. • Every substance is made up of ...
Chapter 03
... orbital, and 6 in three 2p orbitals. ► The third shell can hold 18 electrons, 2 in a 3s orbital, 6 in three 3p orbitals, and 10 in five 3d orbitals, and so on. Prentice Hall © 2007 ...
... orbital, and 6 in three 2p orbitals. ► The third shell can hold 18 electrons, 2 in a 3s orbital, 6 in three 3p orbitals, and 10 in five 3d orbitals, and so on. Prentice Hall © 2007 ...
- Orangefield ISD
... • 6(D) Use isotopic composition to calculate average atomic mass of an element. • 2(G) Express and manipulate chemical quantities using scientific conventions and mathematical procedures, including dimensional analysis, scientific notation, and significant figures. • 2(I) Communicate valid conclusi ...
... • 6(D) Use isotopic composition to calculate average atomic mass of an element. • 2(G) Express and manipulate chemical quantities using scientific conventions and mathematical procedures, including dimensional analysis, scientific notation, and significant figures. • 2(I) Communicate valid conclusi ...
Chemistry
... 1) The smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element is the: a) cell b) proton c) electron d) neutron e) none of the above 2) Which of the following is not a part of Dalton’s atomic theory? a) All elements are composed of atoms. b) The positive charge of the atom is loc ...
... 1) The smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element is the: a) cell b) proton c) electron d) neutron e) none of the above 2) Which of the following is not a part of Dalton’s atomic theory? a) All elements are composed of atoms. b) The positive charge of the atom is loc ...
Chapter 11
... Atomic Weight: It’s all in the Nucleus • Since electrons weigh virtually nothing, the mass of an atom is concentrated in its nucleus. • Each atom can be described by its atomic weight (or mass), which is the sum of the protons and neutrons. ...
... Atomic Weight: It’s all in the Nucleus • Since electrons weigh virtually nothing, the mass of an atom is concentrated in its nucleus. • Each atom can be described by its atomic weight (or mass), which is the sum of the protons and neutrons. ...
Chapter2
... Coordination number • Coordination number is the number of adjacent ions (or atoms) surrounding a reference ion (or atom) • Depends directly on the relative sizes of the ...
... Coordination number • Coordination number is the number of adjacent ions (or atoms) surrounding a reference ion (or atom) • Depends directly on the relative sizes of the ...
Inorganic Chemistry Lesson 3
... (i.e. a chemical formula of water) means there are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom in each water molecule. Is the composition of molecules arbitrary, or there is some law that defines it? If such a law does exists, then is it possible to predict composition of molecules? Yes, it is possible ...
... (i.e. a chemical formula of water) means there are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom in each water molecule. Is the composition of molecules arbitrary, or there is some law that defines it? If such a law does exists, then is it possible to predict composition of molecules? Yes, it is possible ...
Step 1 Lesson Plan
... At this point we will come back together and discuss the important elements and things that the students absolutely MUST take away from the lesson. On Day 1 I will mostly be interested in knowing that they understand what an isotope is and that they have at least been introduced to the symbols that ...
... At this point we will come back together and discuss the important elements and things that the students absolutely MUST take away from the lesson. On Day 1 I will mostly be interested in knowing that they understand what an isotope is and that they have at least been introduced to the symbols that ...
9/6/12 - Note: Once it is downloaded, click SET
... Energy and Change Endothermic and Exothermic Processes - Any change in matter in which energy is absorbed from the surrounding in an Endothermic process o The melting of ice and boiling of water are examples of physical changes that are Endothermic o As the chemicals react, energy is absorbed. Energ ...
... Energy and Change Endothermic and Exothermic Processes - Any change in matter in which energy is absorbed from the surrounding in an Endothermic process o The melting of ice and boiling of water are examples of physical changes that are Endothermic o As the chemicals react, energy is absorbed. Energ ...
File
... Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Chemistry is the study of the properties of matter and how matter and how matter changes. In chemistry, a substance is a single kind of matter that is pure. Every form of matter has two kinds of properties - physical and chemical properties. A phy ...
... Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Chemistry is the study of the properties of matter and how matter and how matter changes. In chemistry, a substance is a single kind of matter that is pure. Every form of matter has two kinds of properties - physical and chemical properties. A phy ...
Atomic structure Atomic masses
... Relative atomic mass, Ar: the weighted mean mass of an atom of an element compared with 1/12 of the the mass of an atom of carbon-12 The term ‘weighted mean mass’ is used to account for the contribution made by each isotope to the overall mass of an element. The contribution made by an isotope to th ...
... Relative atomic mass, Ar: the weighted mean mass of an atom of an element compared with 1/12 of the the mass of an atom of carbon-12 The term ‘weighted mean mass’ is used to account for the contribution made by each isotope to the overall mass of an element. The contribution made by an isotope to th ...
6-2 Notes: The Atom
... The charges or protons and electrons are opposite but _________, so the charges cancel out. If the numbers of electrons and protons become unequal, the atom becomes a charged particle called an ______. An atom that loses one or more electrons becomes a _______________ charged ion. An atom that gains ...
... The charges or protons and electrons are opposite but _________, so the charges cancel out. If the numbers of electrons and protons become unequal, the atom becomes a charged particle called an ______. An atom that loses one or more electrons becomes a _______________ charged ion. An atom that gains ...
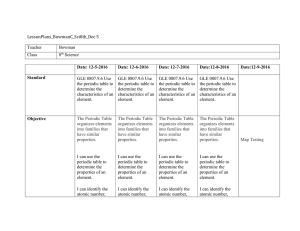
LessonPlans_BowmanC_Sci8th_Dec 5 Teacher Bowman Class 8th
... organizes elements into families that have similar properties. ...
... organizes elements into families that have similar properties. ...
Chapter 07 and 08 Chemical Bonding and Molecular
... • Pure substance • Made of 2 or more elements in a definite proportion by mass • Physically and chemically different from the elements that make up the compound • All elements (except Noble gases) react to gain a stable octet. (duet-for H through B) • Compounds form to gain a stable valence shell wh ...
... • Pure substance • Made of 2 or more elements in a definite proportion by mass • Physically and chemically different from the elements that make up the compound • All elements (except Noble gases) react to gain a stable octet. (duet-for H through B) • Compounds form to gain a stable valence shell wh ...