Chapter 4 - The Structure of the Atom Atomic Models PIONEERS OF
... substance that cannot be broken down by ordinary chemical means. - It was also believed that elements combined to form compounds that have different physical and chemical properties than those of the elements that formed them. - However, there was controversy as to whether elements always combined i ...
... substance that cannot be broken down by ordinary chemical means. - It was also believed that elements combined to form compounds that have different physical and chemical properties than those of the elements that formed them. - However, there was controversy as to whether elements always combined i ...
PowerPoint
... 1- How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in an atom of chlorine-37? Chlorine has an atomic number of 17. Protons = 17 (atomic number) Electron = 17 (atomic number) Neutrons = 20 (neutrons = mass number (37)—atomic number (17) 2- How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in an atom of Br ...
... 1- How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in an atom of chlorine-37? Chlorine has an atomic number of 17. Protons = 17 (atomic number) Electron = 17 (atomic number) Neutrons = 20 (neutrons = mass number (37)—atomic number (17) 2- How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in an atom of Br ...
isotopes and atomic mass
... 1. Which of the data in the table must be measured and which must be calculated? 2. In all except step 11, the “Total” is calculated by adding the numbers across each row. Step 11 is an exception because it does not take into account the fact that there are different numbers of each isotope. Rather ...
... 1. Which of the data in the table must be measured and which must be calculated? 2. In all except step 11, the “Total” is calculated by adding the numbers across each row. Step 11 is an exception because it does not take into account the fact that there are different numbers of each isotope. Rather ...
Unit 10: Structure and Bonding
... Radioactive and Non radioactive isotopes Do NOT assume the word isotope means the atom it is radioactive, this depends on the stability of the nucleus i.e. unstable atoms (radioactive) might be referred to as radioisotopes. Many isotopes are extremely stable in the nuclear sense and NOT radioactive ...
... Radioactive and Non radioactive isotopes Do NOT assume the word isotope means the atom it is radioactive, this depends on the stability of the nucleus i.e. unstable atoms (radioactive) might be referred to as radioisotopes. Many isotopes are extremely stable in the nuclear sense and NOT radioactive ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE
... to a maximum of five at 3d5, then decreases as further electrons are added........ ...
... to a maximum of five at 3d5, then decreases as further electrons are added........ ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2006-2007
... Which of the following elements has the same number of valence electrons as the element sodium? a. Ar b. Cs c. Ca d. Mg Which of the following elements has the same number of valence electrons as the element selenium? a. Fe b. K c. P d. O Which of the following elements will have similar physical an ...
... Which of the following elements has the same number of valence electrons as the element sodium? a. Ar b. Cs c. Ca d. Mg Which of the following elements has the same number of valence electrons as the element selenium? a. Fe b. K c. P d. O Which of the following elements will have similar physical an ...
Chapter 2 power point
... Filtration: Separates components of a mixture based upon differences in particle size. Filtration usually involves separating a precipitate from solution. Crystallization: Separation is based upon differences in solubility of the components in a mixture. Distillation: Separation is based upon differ ...
... Filtration: Separates components of a mixture based upon differences in particle size. Filtration usually involves separating a precipitate from solution. Crystallization: Separation is based upon differences in solubility of the components in a mixture. Distillation: Separation is based upon differ ...
Chapter 3
... Using Aufbau principle or periodic table a. Potassium: 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 4s1 b. Phosphorus: 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p3 Problem: Examine the electron configurations below, and name the element. 1s2 2s2 1s2 2s2 2p3 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1 Answer: Going through the periodic table. 1s2 2s2 (He) 1s2 2s2 ...
... Using Aufbau principle or periodic table a. Potassium: 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 4s1 b. Phosphorus: 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p3 Problem: Examine the electron configurations below, and name the element. 1s2 2s2 1s2 2s2 2p3 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1 Answer: Going through the periodic table. 1s2 2s2 (He) 1s2 2s2 ...
The Origin of the Sigma, Pi, Delta Notation for Chemical Bonds
... spectroscopists in the form of a printed flyer. Though it is unclear from his published accounts how much of the final consensus was based on Mulliken’s original suggestions and how much on the suggestions of others, the final result was, in any case, submitted for presentation at a meeting of the Fara ...
... spectroscopists in the form of a printed flyer. Though it is unclear from his published accounts how much of the final consensus was based on Mulliken’s original suggestions and how much on the suggestions of others, the final result was, in any case, submitted for presentation at a meeting of the Fara ...
Chapter 18: Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... number would be too cumbersome to use. Considering the scale of the building, you would more likely give the height in a smaller unit, meters. When thinking about the small masses of atoms, scientists found that even grams were not small enough to use for measurement. Scientists need a unit that res ...
... number would be too cumbersome to use. Considering the scale of the building, you would more likely give the height in a smaller unit, meters. When thinking about the small masses of atoms, scientists found that even grams were not small enough to use for measurement. Scientists need a unit that res ...
Topic 5 - Holy Cross Collegiate
... or periodic, intervals. The eighth element in his arrangement (sodium) had properties similar to the first (lithium), and the fifteenth element (potassium) had properties similar to the eighth. Therefore the first, eighth, and fifteenth elements made up a chemical family. The pattern Mendeleev discovere ...
... or periodic, intervals. The eighth element in his arrangement (sodium) had properties similar to the first (lithium), and the fifteenth element (potassium) had properties similar to the eighth. Therefore the first, eighth, and fifteenth elements made up a chemical family. The pattern Mendeleev discovere ...
File
... or periodic, intervals. The eighth element in his arrangement (sodium) had properties similar to the first (lithium), and the fifteenth element (potassium) had properties similar to the eighth. Therefore the first, eighth, and fifteenth elements made up a chemical family. The pattern Mendeleev discovere ...
... or periodic, intervals. The eighth element in his arrangement (sodium) had properties similar to the first (lithium), and the fifteenth element (potassium) had properties similar to the eighth. Therefore the first, eighth, and fifteenth elements made up a chemical family. The pattern Mendeleev discovere ...
Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory
... formation. The number of hybrid orbitals formed by this mixing is equal to the number of atomic orbitals involved. These hybrid orbitals are more directed from the central atom to the terminal atoms, have better overlap, and produce stronger bonds. The central atom’s electron-pair geometry determine ...
... formation. The number of hybrid orbitals formed by this mixing is equal to the number of atomic orbitals involved. These hybrid orbitals are more directed from the central atom to the terminal atoms, have better overlap, and produce stronger bonds. The central atom’s electron-pair geometry determine ...
electrons - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... • Reactivity: (look at electrons) – Electrons occupy most of the volume, but almost none of the mass – Higher energy electrons (furthest from nucleus) are MOST reactive – Number of Electrons farthest from nucleus determine most of the reactivity ...
... • Reactivity: (look at electrons) – Electrons occupy most of the volume, but almost none of the mass – Higher energy electrons (furthest from nucleus) are MOST reactive – Number of Electrons farthest from nucleus determine most of the reactivity ...
Bonding Notes
... points or boiling points. (Remember in vapor pressures the liquid with the highest intermolecular forces of attraction had the highest boiling point!) Thus ionic solids have high melting points! -Also ionic compounds in the solids state are in the fixed geometric patterns or crystal lattice. In the ...
... points or boiling points. (Remember in vapor pressures the liquid with the highest intermolecular forces of attraction had the highest boiling point!) Thus ionic solids have high melting points! -Also ionic compounds in the solids state are in the fixed geometric patterns or crystal lattice. In the ...
Chapter3
... Chapter 3. Elements, Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table The Periodic Law and the Periodic Table In the early 1800's many elements had been discovered and found to have different properties. In 1817 Döbreiner's triads –with regularly varying properties: (Mg, Ca, Ba) (F, Cl, Br) and (S Se Te).1865: N ...
... Chapter 3. Elements, Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table The Periodic Law and the Periodic Table In the early 1800's many elements had been discovered and found to have different properties. In 1817 Döbreiner's triads –with regularly varying properties: (Mg, Ca, Ba) (F, Cl, Br) and (S Se Te).1865: N ...
Unit 3: Bonding and Nomenclature Content Outline: Chemical
... b. This is the amount of energy released when one mole of an ionic crystalline compound is formed from gaseous ions. B. The electrical charges are balanced, so as to be neutral. C. Ionic compounds are hard but brittle (crumbly). D. In the solid state, they cannot conduct electricity (as the atoms ca ...
... b. This is the amount of energy released when one mole of an ionic crystalline compound is formed from gaseous ions. B. The electrical charges are balanced, so as to be neutral. C. Ionic compounds are hard but brittle (crumbly). D. In the solid state, they cannot conduct electricity (as the atoms ca ...
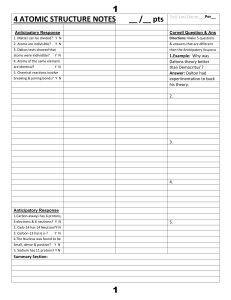
4 ATOMIC STRUCTURE NOTES __ /__ pts 1 1
... 4. Which particle controls what element an atom is (hint: See which particle when added changes the element name in the info box)?_________ 5. What do you get when you change the number of neutrons in the nucleus? 6. What 2 particles control the mass of an atom(hint: Look at which particle doesn’t c ...
... 4. Which particle controls what element an atom is (hint: See which particle when added changes the element name in the info box)?_________ 5. What do you get when you change the number of neutrons in the nucleus? 6. What 2 particles control the mass of an atom(hint: Look at which particle doesn’t c ...
Reading 2.1 A Return to Isotopes
... This whole discussion of isotopes brings us back to Dalton’s atomic theory. According to Dalton, atoms of a given element are identical. But if atoms of a given element can have different numbers of neutrons, then they can have different masses as well. How did Dalton miss this? It turns out that el ...
... This whole discussion of isotopes brings us back to Dalton’s atomic theory. According to Dalton, atoms of a given element are identical. But if atoms of a given element can have different numbers of neutrons, then they can have different masses as well. How did Dalton miss this? It turns out that el ...
Chem312 Au03 Problem Set 4
... When you put the electrons in, you should follow Hund’s rule, that a state is lower in energy when the electrons are in different orbitals with their spins pointing in the same direction (e.g., all spin up, ↑↑). It is higher energy if the electrons pair in one orbital or even if they have opposite s ...
... When you put the electrons in, you should follow Hund’s rule, that a state is lower in energy when the electrons are in different orbitals with their spins pointing in the same direction (e.g., all spin up, ↑↑). It is higher energy if the electrons pair in one orbital or even if they have opposite s ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table
... A. The History of the Periodic Table *1. In 1828, Dobereiner made one of the earliest attempts to “list” the ELEMENTS; proposed the Law of Triads stated there were groups of “3” ELEMENTS where the middle ELEMENT’S atomic MASS was the average of the other “2” ELEMENTS *a. (e.g.) calcium [Ca] = 40.0 ...
... A. The History of the Periodic Table *1. In 1828, Dobereiner made one of the earliest attempts to “list” the ELEMENTS; proposed the Law of Triads stated there were groups of “3” ELEMENTS where the middle ELEMENT’S atomic MASS was the average of the other “2” ELEMENTS *a. (e.g.) calcium [Ca] = 40.0 ...
Structure of the Atom
... A revolution in physics occurred in the early 1900’s when experiments showed that matter, just like light energy, could have a dual nature…it can act as a particle or a wave. 1. The Wave Mechanical Model 1.__________________________________________________________________ 2._________________________ ...
... A revolution in physics occurred in the early 1900’s when experiments showed that matter, just like light energy, could have a dual nature…it can act as a particle or a wave. 1. The Wave Mechanical Model 1.__________________________________________________________________ 2._________________________ ...