electrons - Bryant School District
... Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. ...
... Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. ...
Unit 1 Notes (general chem review)
... may NOT indicate shape may or may not show the unbonded pairs of electrons ...
... may NOT indicate shape may or may not show the unbonded pairs of electrons ...
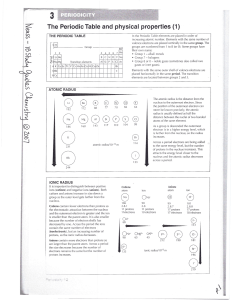
The Periodic Table and physical properties (1)
... The shielding effect is the result of repulsion between the electrons in the inner shell and those" in the outer or valence shell • the nuclear charge (due to the protons) - this is an attractive force that pulls all the electrons closer to the nucleus. With an increase in nuclear charge, the atomic ...
... The shielding effect is the result of repulsion between the electrons in the inner shell and those" in the outer or valence shell • the nuclear charge (due to the protons) - this is an attractive force that pulls all the electrons closer to the nucleus. With an increase in nuclear charge, the atomic ...
quiz questions chapters 1
... De Broglie explained electron movements by relating them to: A) waves only B) particles only C) waves and particles D) none of the above ...
... De Broglie explained electron movements by relating them to: A) waves only B) particles only C) waves and particles D) none of the above ...
4 PERIODIC TABLE AND ATOMIC PROPERTIES W
... constructed a table in which elements were arranged in order of their increasing atomic weights. It was also found that every eighth elements had properties similar to that of the first element. Thus, there was a periodic occurrence of elements with similer properties. One of the most striking appli ...
... constructed a table in which elements were arranged in order of their increasing atomic weights. It was also found that every eighth elements had properties similar to that of the first element. Thus, there was a periodic occurrence of elements with similer properties. One of the most striking appli ...
The Mole - Rothschild Science
... a. Count the atoms on each side of the equation. b. Place coefficients in front to make the sides equal. c. Recheck to make sure it worked ...
... a. Count the atoms on each side of the equation. b. Place coefficients in front to make the sides equal. c. Recheck to make sure it worked ...
5 Early Atomic Theory and Structure Chapter Outline Early Theories
... 3. Atoms of different elements differ in their mass and size. 4. Compounds are formed by combining two or more atoms of different elements. 5. Atoms combine to form compounds in simple whole number ratios. ...
... 3. Atoms of different elements differ in their mass and size. 4. Compounds are formed by combining two or more atoms of different elements. 5. Atoms combine to form compounds in simple whole number ratios. ...
CHAPTER -4 “STRUCTURE OF ATOM” CONCEPT DETAILS Pre
... o The indivisibility of an atom was proved wrong , for, an atom can be further subdivided into protons, neutrons and electrons. o The atoms of same element are similar in all respects , but isotopes of same element have different mass. o Dalton's theory was based on the premise that the atoms of dif ...
... o The indivisibility of an atom was proved wrong , for, an atom can be further subdivided into protons, neutrons and electrons. o The atoms of same element are similar in all respects , but isotopes of same element have different mass. o Dalton's theory was based on the premise that the atoms of dif ...
Quantum Mechanics PPT
... • As protons are added one by one to the nucleus to build up the elements, electrons are similarly added to orbitals • Electrons fill in low energy orbitals before high energy orbitals ...
... • As protons are added one by one to the nucleus to build up the elements, electrons are similarly added to orbitals • Electrons fill in low energy orbitals before high energy orbitals ...
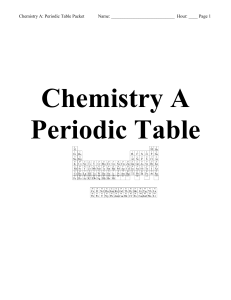
Chemistry A- Periodic Table Packet
... elements that are generally shiny when smooth and clean, solid at room temperature, and good conductors of heat and electricity. Most metals are ductile and malleable, meaning that they can be pounded into thin sheets and drawn into wires. Most group A elements and all group B elements are metals. I ...
... elements that are generally shiny when smooth and clean, solid at room temperature, and good conductors of heat and electricity. Most metals are ductile and malleable, meaning that they can be pounded into thin sheets and drawn into wires. Most group A elements and all group B elements are metals. I ...
4.2 reading
... proton in the nucleus of each and every hydrogen atom. Therefore, hydrogen is assigned the atomic number 1. The atomic number of an element equals the number of protons in an atom of that element. Hydrogen atoms are the only atoms with a single proton. Atoms of different elements have different numb ...
... proton in the nucleus of each and every hydrogen atom. Therefore, hydrogen is assigned the atomic number 1. The atomic number of an element equals the number of protons in an atom of that element. Hydrogen atoms are the only atoms with a single proton. Atoms of different elements have different numb ...
INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY - Chapter 1
... an experiment must be reproducible. It is often difficult when performing a chemical reaction or test to make sure that all of the variables are exactly the same as for a previous run. In addition, chemical reactions can give off terrible smelling, sometimes toxic gases and on rare occasions give of ...
... an experiment must be reproducible. It is often difficult when performing a chemical reaction or test to make sure that all of the variables are exactly the same as for a previous run. In addition, chemical reactions can give off terrible smelling, sometimes toxic gases and on rare occasions give of ...
Elements, Compounds and Mixtures
... • 2 or more atoms bonded together • Represents the smallest particle in a chemical compound that can take place in a chemical reaction. • Has the same chemical properties of that element or compound. • Some molecules consist of two atoms of the same element. • Ex. O2 • Other molecules consists of tw ...
... • 2 or more atoms bonded together • Represents the smallest particle in a chemical compound that can take place in a chemical reaction. • Has the same chemical properties of that element or compound. • Some molecules consist of two atoms of the same element. • Ex. O2 • Other molecules consists of tw ...
document
... chemically combine in simple wholenumber ratios to form compounds. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. Atoms of one element, however, are never changed into atoms of another element as a result of a chemical reaction. ...
... chemically combine in simple wholenumber ratios to form compounds. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. Atoms of one element, however, are never changed into atoms of another element as a result of a chemical reaction. ...
CHEMISTRY Periodic Table of the Elements
... b) smallest atomic radius c) smallest electronegativity of the alkali metals d) largest first ionization energy of period 3 e) smallest first ionization energy of the noble gases f) largest atomic radius of period 5 g) greatest electronegativity of the halogens ...
... b) smallest atomic radius c) smallest electronegativity of the alkali metals d) largest first ionization energy of period 3 e) smallest first ionization energy of the noble gases f) largest atomic radius of period 5 g) greatest electronegativity of the halogens ...
Chemistry Mid-Term Review: 2015-2016
... 11. Which noble gas does not have eight electrons in its highest occupied energy level? 12. Explain the difference between the first and second ionization energy of an element. 13. For groups 1A – 7A, how many electrons fill the outermost sublevel? 14. How are the electron configurations for the ato ...
... 11. Which noble gas does not have eight electrons in its highest occupied energy level? 12. Explain the difference between the first and second ionization energy of an element. 13. For groups 1A – 7A, how many electrons fill the outermost sublevel? 14. How are the electron configurations for the ato ...
Mass/Mole Conversions
... • __________: atoms of the same element that have _______________ due to different numbers of __________. • _____________: the total number of _______ and _________ that make up the nucleus of an isotope ~ Isotopes are written with the _____________ written after the element name or symbol with a __ ...
... • __________: atoms of the same element that have _______________ due to different numbers of __________. • _____________: the total number of _______ and _________ that make up the nucleus of an isotope ~ Isotopes are written with the _____________ written after the element name or symbol with a __ ...
CHAPTER 2: ATOMS, MOLECULES AND IONS ULES AND IONS
... Mass of reactant is equal to mass of product. Law of Definite Proportion: A given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by mass. Law of Multiple Proportions: When chemical elements combine to form a compound, they do so in a ratio of small whole numbers. ...
... Mass of reactant is equal to mass of product. Law of Definite Proportion: A given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by mass. Law of Multiple Proportions: When chemical elements combine to form a compound, they do so in a ratio of small whole numbers. ...
An Overview of Chemistry Lecture 3 Lecture 3
... Matter can be classified into three types, based on their atomic makeup: Elements • Matter composed of only one type of atom. Compounds • Matter composed two or more different elements that are chemically bound together and do not vary in composition Mixtures • Matter composed two or more different ...
... Matter can be classified into three types, based on their atomic makeup: Elements • Matter composed of only one type of atom. Compounds • Matter composed two or more different elements that are chemically bound together and do not vary in composition Mixtures • Matter composed two or more different ...
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table Essential Question: How are
... is called a group, or family. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. ...
... is called a group, or family. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. ...
Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements
... Lavoisier proposed from his experimental evidence the following law: ...
... Lavoisier proposed from his experimental evidence the following law: ...