Ch 5 Electron Structure
... having a frequency of 3.44 x 109 Hz? • Solve the equation relating the speed, frequency, and wavelength of an electromagnetic wave for wavelength (λ). ...
... having a frequency of 3.44 x 109 Hz? • Solve the equation relating the speed, frequency, and wavelength of an electromagnetic wave for wavelength (λ). ...
File
... reversible blue complex. The disappearance of this blue coloured complex is a much more sensitive method of determining the end point. However, if the starch is added to a solution which contains a great deal of iodine, the complex which forms may not be reversible. Therefore, the starch is not adde ...
... reversible blue complex. The disappearance of this blue coloured complex is a much more sensitive method of determining the end point. However, if the starch is added to a solution which contains a great deal of iodine, the complex which forms may not be reversible. Therefore, the starch is not adde ...
CHAPTER 2 ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS
... Dividing both subscripts by 2, the simplest whole number ratio of the atoms in Al2Br6 is AlBr3. Dividing all subscripts by 2, the simplest whole number ratio of the atoms in Na2S2O4 is NaSO2. The molecular formula as written, N2O5, contains the simplest whole number ratio of the atoms present. In th ...
... Dividing both subscripts by 2, the simplest whole number ratio of the atoms in Al2Br6 is AlBr3. Dividing all subscripts by 2, the simplest whole number ratio of the atoms in Na2S2O4 is NaSO2. The molecular formula as written, N2O5, contains the simplest whole number ratio of the atoms present. In th ...
Lesson 3
... In the previous lesson, you have studied that the atoms are the smallest constituents of matter. But what is the structure of an atom? Why are atoms of different elements different? Let us try to find out the answers to some of these questions in this lesson. We will start the study of this lesson b ...
... In the previous lesson, you have studied that the atoms are the smallest constituents of matter. But what is the structure of an atom? Why are atoms of different elements different? Let us try to find out the answers to some of these questions in this lesson. We will start the study of this lesson b ...
atomic number - iGCSE Science Courses
... only one or two stable ones. The other isotopes tend to be radioactive, which means that they decay into other elements and give out radiation. This is where all radioactivity comes from – unstable radioactive isotopes undergoing nuclear decay and spitting out high energy particles. ...
... only one or two stable ones. The other isotopes tend to be radioactive, which means that they decay into other elements and give out radiation. This is where all radioactivity comes from – unstable radioactive isotopes undergoing nuclear decay and spitting out high energy particles. ...
Nuclear physics is the subfield of physics that studies the building
... Enrico Fermi used this particle, which he called a neutrino (little neutron) in his theory of radioactive decay. The neutrino was not observed experimentally unitl 1959. The neutrino is represented by a Greek letter ν. Beta decay is thus the result of the decay of a neutron into a proton, an electro ...
... Enrico Fermi used this particle, which he called a neutrino (little neutron) in his theory of radioactive decay. The neutrino was not observed experimentally unitl 1959. The neutrino is represented by a Greek letter ν. Beta decay is thus the result of the decay of a neutron into a proton, an electro ...
Revision Y12 Chemistry PLC
... flammable and toxic substances (l) measurement of rates of reaction by at least two different methods, for example: i) an initial rate method such as a clock reaction (ii) ...
... flammable and toxic substances (l) measurement of rates of reaction by at least two different methods, for example: i) an initial rate method such as a clock reaction (ii) ...
Chapter 10 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry Bonding Theory and
... “Precise molecular geometry can be determined only by experiment but the shapes of many molecules and polyatomic ions can be predicted fairly well …” (Hill, p. 388) “As the name implies, the valence-shell electron pair repulsion method is based on the idea that pairs of valence electrons in bonded a ...
... “Precise molecular geometry can be determined only by experiment but the shapes of many molecules and polyatomic ions can be predicted fairly well …” (Hill, p. 388) “As the name implies, the valence-shell electron pair repulsion method is based on the idea that pairs of valence electrons in bonded a ...
The Structure of Matter
... point charges should annihilate one another, and therefore, cause the atom to not have even existed [5]. To solve this problem, Jeans proposed that the electron and its positive counterpart are not point charges, but that they have size. Then he proposed that the law of inverse square would not alwa ...
... point charges should annihilate one another, and therefore, cause the atom to not have even existed [5]. To solve this problem, Jeans proposed that the electron and its positive counterpart are not point charges, but that they have size. Then he proposed that the law of inverse square would not alwa ...
Chemistry General v. 2016
... Relate an element’s position on the periodic table to its electron configuration. Compare an element’s relativity to that of other elements. Describe chemical reactions in terms of atomic rearrangement and /or electron configuration. Explain how the periodicity of chemical properties led to the arra ...
... Relate an element’s position on the periodic table to its electron configuration. Compare an element’s relativity to that of other elements. Describe chemical reactions in terms of atomic rearrangement and /or electron configuration. Explain how the periodicity of chemical properties led to the arra ...
t2 – modern atomic theory continued
... A) The models developed by both Nagaoka and Thomson explained the existing evidence equally well, thus both models were equally valid. Ernest Rutherford’s studies of radioactive decay in the early 1900’s led him to favour one over the other. His research led him to modify it creating his own model. ...
... A) The models developed by both Nagaoka and Thomson explained the existing evidence equally well, thus both models were equally valid. Ernest Rutherford’s studies of radioactive decay in the early 1900’s led him to favour one over the other. His research led him to modify it creating his own model. ...
A Journey Through Time The Atom Introduction: If you were asked to
... Use any of the following Web sites to get information about listed scientists and their discoveries that were not in your text. You may search other Web sites on your own or use library resources. Include the following on your slideshow timeline: ...
... Use any of the following Web sites to get information about listed scientists and their discoveries that were not in your text. You may search other Web sites on your own or use library resources. Include the following on your slideshow timeline: ...
chem100chapter5 - Imperial Valley College Faculty Websites
... 2000 years after Aristotle, John Dalton, an English schoolmaster, proposed his model of the atom–which was based on experimentation. ...
... 2000 years after Aristotle, John Dalton, an English schoolmaster, proposed his model of the atom–which was based on experimentation. ...
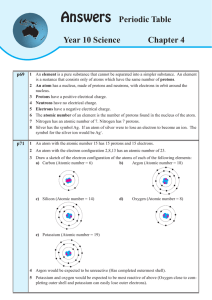
Answers - Dr Terry Dwyer National Curriculum mathematics and
... The halogens are non-metals. Fluorine (F) and chlorine (Cl) are gases at room temperature (25°C), while bromine (Br) is a liquid, and iodine (I) is a solid. The halogens have low melting and boiling points. 3 Why are the halogens the most reactive of the non-metal groups? The halogens have seve ...
... The halogens are non-metals. Fluorine (F) and chlorine (Cl) are gases at room temperature (25°C), while bromine (Br) is a liquid, and iodine (I) is a solid. The halogens have low melting and boiling points. 3 Why are the halogens the most reactive of the non-metal groups? The halogens have seve ...
Document
... The mass of one mole is called “molar mass” E.g. 1 mol Li = 6.94 g Li This is expressed as 6.94 g/mol What are the following molar masses? S 32.06 g/mol SO2 64.06 g/mol Cu3(BO3)2 308.27 g/mol ...
... The mass of one mole is called “molar mass” E.g. 1 mol Li = 6.94 g Li This is expressed as 6.94 g/mol What are the following molar masses? S 32.06 g/mol SO2 64.06 g/mol Cu3(BO3)2 308.27 g/mol ...
Chapte 11 Study Questions
... ____ 52. Which of the following statements describes isotopes? a. Isotopes are atoms of the same element. b. Isotopes have the same number of protons but have different numbers of neutrons. c. Isotopes have the same atomic number but have different mass numbers. d. all of the above ____ 53. Isotopes ...
... ____ 52. Which of the following statements describes isotopes? a. Isotopes are atoms of the same element. b. Isotopes have the same number of protons but have different numbers of neutrons. c. Isotopes have the same atomic number but have different mass numbers. d. all of the above ____ 53. Isotopes ...
atom
... 3- Atoms of different elements can combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. 4 – Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined or rearranged. However, atoms of one element are not changed into atoms of another element by a chemical reaction. NC Competency Goal 2 ...
... 3- Atoms of different elements can combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. 4 – Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined or rearranged. However, atoms of one element are not changed into atoms of another element by a chemical reaction. NC Competency Goal 2 ...
Atomic mass
... • Define isotope and nuclide • Use atomic number, mass number, and charge to determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an isotope or ion • Identify carbon-12 as the standard atom for measuring relative atomic mass • Determine the process to calculate atomic mass of an element ...
... • Define isotope and nuclide • Use atomic number, mass number, and charge to determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an isotope or ion • Identify carbon-12 as the standard atom for measuring relative atomic mass • Determine the process to calculate atomic mass of an element ...
Atomic Theory PowerPoint Notes
... 1. Atoms of the same element may have different numbers of ____________, and they may gain or lose ____________, but they ALWAYS have the same number of _____________. ...
... 1. Atoms of the same element may have different numbers of ____________, and they may gain or lose ____________, but they ALWAYS have the same number of _____________. ...
Hands-On Chemistry Unit
... 7. Activities and Worksheets .................................................................................................................... 8 7.1. Introduction to Chemistry .............................................................................................................. 8 7.2. Exa ...
... 7. Activities and Worksheets .................................................................................................................... 8 7.1. Introduction to Chemistry .............................................................................................................. 8 7.2. Exa ...