e - WordPress.com
... Mendeleev noticed that when the elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass, certain similarities in their chemical properties appeared at regular intervals. ...
... Mendeleev noticed that when the elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass, certain similarities in their chemical properties appeared at regular intervals. ...
Final review KEY
... 19. Define the law of multiple proportions. Elements form compounds in simple whole number ratios 20. What do isotopes of the same element have in common and what is different? Isotopes have the same number of protons, electrons and atomic number Isotopes have a different mass number and number of ...
... 19. Define the law of multiple proportions. Elements form compounds in simple whole number ratios 20. What do isotopes of the same element have in common and what is different? Isotopes have the same number of protons, electrons and atomic number Isotopes have a different mass number and number of ...
Unit 3 The History of the ATOM
... 3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine with one another in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. ...
... 3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine with one another in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. ...
Biochemistry
... ______________ of a compound (C6H12O6) It tells us (1) the _____________ in the compound and (2) their __________ (how many atoms there are of each element). ...
... ______________ of a compound (C6H12O6) It tells us (1) the _____________ in the compound and (2) their __________ (how many atoms there are of each element). ...
TRENDS in the PERIODIC TABLE
... It is all about HOW CLOSE IS THE ATOM TO FLUORINE which determines the relative electro-negativity. ...
... It is all about HOW CLOSE IS THE ATOM TO FLUORINE which determines the relative electro-negativity. ...
periodic law
... • The periodic law states that the properties of elements recur in a repeating pattern when arranged according to increasing atomic number. • The arrangement of the periodic table means that the physical properties of the elements follow a regular pattern. ...
... • The periodic law states that the properties of elements recur in a repeating pattern when arranged according to increasing atomic number. • The arrangement of the periodic table means that the physical properties of the elements follow a regular pattern. ...
PeriodicElements
... The properties of the elements exhibit trends. These trends can be predicted using the periodic table and can be explained and understood by analyzing the electron configurations of the elements. Elements tend to gain or lose valence electrons to achieve stable octet formation. Stable octets are see ...
... The properties of the elements exhibit trends. These trends can be predicted using the periodic table and can be explained and understood by analyzing the electron configurations of the elements. Elements tend to gain or lose valence electrons to achieve stable octet formation. Stable octets are see ...
Chapter 5 Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Section 5.1
... Q Atomic number is the same as the in a neutral atom. Q. = the number of protons + neutrons. ...
... Q Atomic number is the same as the in a neutral atom. Q. = the number of protons + neutrons. ...
The Atomic Theory
... – Believed these particles could not be cut into anything smaller pieces – Called these particles atoms, which means not able to be divided ...
... – Believed these particles could not be cut into anything smaller pieces – Called these particles atoms, which means not able to be divided ...
X Unit 11 Test Study Guide (The Periodic Table)
... ***Study old homework questions, notes, warm up problems, and example problems to get a sense of the type of questions you will see!! Sample Review Problems: (answer on a separate piece of paper if needed) 1. Fill in the following information for the element astatine: a. Symbol: At b. Group #: 17 c ...
... ***Study old homework questions, notes, warm up problems, and example problems to get a sense of the type of questions you will see!! Sample Review Problems: (answer on a separate piece of paper if needed) 1. Fill in the following information for the element astatine: a. Symbol: At b. Group #: 17 c ...
Zumdahl`s Chapter 2
... tissue proving protons (p+) in nucleus F.A. Aston (1919) “weighs” atomic ions J. Chadwick (1939) observes neutrons (no charge) by decomposition (to p+, e–, and ). ...
... tissue proving protons (p+) in nucleus F.A. Aston (1919) “weighs” atomic ions J. Chadwick (1939) observes neutrons (no charge) by decomposition (to p+, e–, and ). ...
ATOMS and PERIODIC TABLE - John Q. Adams Middle School
... Atoms that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. The atomic mass given on the periodic table is the average of all the isotopes and is not a whole number. To find the number of neutrons for an element, subtract the number of protons (atomic number) from the atomic mass. ...
... Atoms that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. The atomic mass given on the periodic table is the average of all the isotopes and is not a whole number. To find the number of neutrons for an element, subtract the number of protons (atomic number) from the atomic mass. ...
Name: Period: ______ Date: Atom Models Elements are made up of
... 1. You will be drawing the electrons, protons, and neutrons of a given element on the periodic table Number of protons: 2. By looking at the atomic number, figure out how many protons it has 3. Draw those number of protons inside the nucleus Number of neutrons: 4. Then, subtract the number of proton ...
... 1. You will be drawing the electrons, protons, and neutrons of a given element on the periodic table Number of protons: 2. By looking at the atomic number, figure out how many protons it has 3. Draw those number of protons inside the nucleus Number of neutrons: 4. Then, subtract the number of proton ...
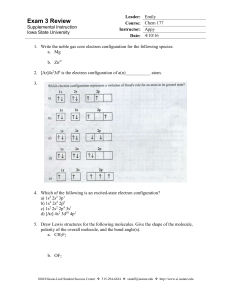
Exam 3 Review - Iowa State University
... 8. Which of the following has the smallest ionization energy. a. Mg b. Se c. Ba d. Po 9. Which has the largest 2nd Ionization energy between K and Ca? a. K b. Ca c. Both K and Ca have the same second Ionization energy d. It’s impossible to tell 10. In terms of electronegativity, determine whether th ...
... 8. Which of the following has the smallest ionization energy. a. Mg b. Se c. Ba d. Po 9. Which has the largest 2nd Ionization energy between K and Ca? a. K b. Ca c. Both K and Ca have the same second Ionization energy d. It’s impossible to tell 10. In terms of electronegativity, determine whether th ...
Nature of Matter
... • If we change the atomic number, we change the element we are talking about… ...
... • If we change the atomic number, we change the element we are talking about… ...
Self-Quiz - mrsgooyers
... metals, non-metals; Metalloids are located in the periodic table between the metals and non-metals. Metalloids, such as silicon, possess some properties of metals and some properties of non-metals. ...
... metals, non-metals; Metalloids are located in the periodic table between the metals and non-metals. Metalloids, such as silicon, possess some properties of metals and some properties of non-metals. ...
Chemistry Fall Semester Review Sheet
... 19. Define the law of multiple proportions. Elements form compounds in simple whole number ratios 20. What do isotopes of the same element have in common and what is different? Isotopes have the same number of protons, electrons and atomic number Isotopes have a different mass number and number of ...
... 19. Define the law of multiple proportions. Elements form compounds in simple whole number ratios 20. What do isotopes of the same element have in common and what is different? Isotopes have the same number of protons, electrons and atomic number Isotopes have a different mass number and number of ...
Units 3 and 4 Revision
... Standard Grade Revision Units 3 and 4 Q1. The box below shows the names of some elements. ...
... Standard Grade Revision Units 3 and 4 Q1. The box below shows the names of some elements. ...
Structure of the Atom - Effingham County Schools
... positive charge to balance the negative electrons. They also showed that atoms must contain other particles that account for most of their mass. ...
... positive charge to balance the negative electrons. They also showed that atoms must contain other particles that account for most of their mass. ...
6.1 Atoms and Elements
... 3. Atoms consist of protons and neutrons in the central core surrounded by electrons. Parts of the Atom Proton: a positively charged particle in an atom. Neutron: a particle in an atom that has no electrical charge. Electron: is a negatively charged particle found in an orbit outside the nucleus of ...
... 3. Atoms consist of protons and neutrons in the central core surrounded by electrons. Parts of the Atom Proton: a positively charged particle in an atom. Neutron: a particle in an atom that has no electrical charge. Electron: is a negatively charged particle found in an orbit outside the nucleus of ...
periodic-data-and-trends-assign-2016
... 1. Based on your graphs, what is the trend in atomic radius across a period? Down a family? Observing the Atomic Number Vs. Atomic Radius graph the Alkali metals have a noticeably greater atomic radius then the other elements. Also, the noble gases have a substantially smaller atomic radius then all ...
... 1. Based on your graphs, what is the trend in atomic radius across a period? Down a family? Observing the Atomic Number Vs. Atomic Radius graph the Alkali metals have a noticeably greater atomic radius then the other elements. Also, the noble gases have a substantially smaller atomic radius then all ...