Name: Period
... a. Ionic Solids b. Metallic Solids c. Network Solids 7. How are ionic compounds and molecular compounds different? Ionic Compounds ...
... a. Ionic Solids b. Metallic Solids c. Network Solids 7. How are ionic compounds and molecular compounds different? Ionic Compounds ...
(2) Gph 321- MECHANISM OF ELECTRICAL
... Most earth materials conduct electricity by the motion of ions contained in the water within the pore spaces . ...
... Most earth materials conduct electricity by the motion of ions contained in the water within the pore spaces . ...
Unit 4.4 Bohr`s Model of the Atom Objectives Newton and Light
... majority of the mass of the atom. Electrons orbit the nucleus at fixed distances (energy levels). These orbits are assign integer values (n = 1, 2, 3, etc). These numbers are called the principle quantum number. Electrons can jump from an occupied energy level to an empty level by absorbing or emitt ...
... majority of the mass of the atom. Electrons orbit the nucleus at fixed distances (energy levels). These orbits are assign integer values (n = 1, 2, 3, etc). These numbers are called the principle quantum number. Electrons can jump from an occupied energy level to an empty level by absorbing or emitt ...
Atom (A) or Ion
... 18. This substance is carbon. 19. This substance is an ion. 20. This substance is an isotope of carbon-12 (12C) 21. The Atomic Theory was first stated in the late 1700s. Which of the following is NOT part of this Atomic Theory? A) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. ...
... 18. This substance is carbon. 19. This substance is an ion. 20. This substance is an isotope of carbon-12 (12C) 21. The Atomic Theory was first stated in the late 1700s. Which of the following is NOT part of this Atomic Theory? A) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. ...
Atom (A) or Ion (I)
... 18. This substance is carbon. 19. This substance is an ion. 20. This substance is an isotope of carbon-12 (12C) 21. The Atomic Theory was first stated in the late 1700s. Which of the following is NOT part of this Atomic Theory? A) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. ...
... 18. This substance is carbon. 19. This substance is an ion. 20. This substance is an isotope of carbon-12 (12C) 21. The Atomic Theory was first stated in the late 1700s. Which of the following is NOT part of this Atomic Theory? A) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. ...
Atom (A) or Ion (I)
... 18. This substance is carbon. 19. This substance is an ion. 20. This substance is an isotope of carbon-12 (12C) 21. The Atomic Theory was first stated in the late 1700s. Which of the following is NOT part of this Atomic Theory? A) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. ...
... 18. This substance is carbon. 19. This substance is an ion. 20. This substance is an isotope of carbon-12 (12C) 21. The Atomic Theory was first stated in the late 1700s. Which of the following is NOT part of this Atomic Theory? A) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. ...
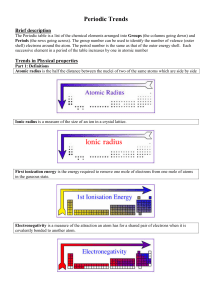
Periodic Trends
... Moving down a group, electronegativity decreases. Why? As you move down a group, the atoms get larger and larger, so the nucleus is farther away from the bonding electrons. Which element is the most electronegative? Fluorine ...
... Moving down a group, electronegativity decreases. Why? As you move down a group, the atoms get larger and larger, so the nucleus is farther away from the bonding electrons. Which element is the most electronegative? Fluorine ...
Part 2
... The mean molecular weight for a partially ionized gas µ = µ0/(E + 1), where µ0 is the molecular weight of the unionized gas, and E the number of free electrons per all atoms. With µ again the ideal gas equation can be used. ...
... The mean molecular weight for a partially ionized gas µ = µ0/(E + 1), where µ0 is the molecular weight of the unionized gas, and E the number of free electrons per all atoms. With µ again the ideal gas equation can be used. ...
Atomic Structure: SOL Review #1 Name: Historical Developments 1
... solid sphere model; Atomic Theory: all elements made of atoms, atoms of an element are identical cathode ray tube; discovered electron; plum pudding model oil drop; discovered mass and charge of electron gold foil; discovered nucleus; the atom is mostly empty space planetary model; (ex) flame test l ...
... solid sphere model; Atomic Theory: all elements made of atoms, atoms of an element are identical cathode ray tube; discovered electron; plum pudding model oil drop; discovered mass and charge of electron gold foil; discovered nucleus; the atom is mostly empty space planetary model; (ex) flame test l ...
Atomic Theory - WaylandHighSchoolChemistry
... Schrödinger and Heisenberg, and many, many more. Used their brains to venture in the realm of inner space and found the world of the atom was a weird and wondrous place. ...
... Schrödinger and Heisenberg, and many, many more. Used their brains to venture in the realm of inner space and found the world of the atom was a weird and wondrous place. ...
Chemical Bonding
... A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms. Atoms are held together by the interaction of their outer shells (valence electrons) Atoms can join together to form larger substances . ...
... A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms. Atoms are held together by the interaction of their outer shells (valence electrons) Atoms can join together to form larger substances . ...
Chemical Bonding
... A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms. Atoms are held together by the interaction of their outer shells (valence electrons) Atoms can join together to form larger substances . ...
... A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms. Atoms are held together by the interaction of their outer shells (valence electrons) Atoms can join together to form larger substances . ...
I believe the chemical bond is not so simple as people seem to think
... Hea2 .butterfly, Its existence was for a long delicate molecule formed by two helium atoms requires a light touch. time disputed because of its extremely small binding enThe helium dimer is the largest two-atom molecule and has the ...
... Hea2 .butterfly, Its existence was for a long delicate molecule formed by two helium atoms requires a light touch. time disputed because of its extremely small binding enThe helium dimer is the largest two-atom molecule and has the ...
Document
... (A) increases, increases (B) decreases, decreases (C) increases, decreases (D) decreases, increases (E) More information is needed to answer this question 43. Which of the following is an acid-base neutralization reaction? (A) 2Al(s) + 3H2SO4(aq) Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 3H2(g) (B) SO2(g) + H2O(l) H2SO3( ...
... (A) increases, increases (B) decreases, decreases (C) increases, decreases (D) decreases, increases (E) More information is needed to answer this question 43. Which of the following is an acid-base neutralization reaction? (A) 2Al(s) + 3H2SO4(aq) Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 3H2(g) (B) SO2(g) + H2O(l) H2SO3( ...
AP Unit 1 Test Review
... (D) Iodine liberates free bromine from a solution of bromide ion. (E) Fluorine is the most electronegative of the halogens. 8. Question 8-11 refer to atoms for which the occupied atomic orbitals shown below. 8. Represents an atom that is chemically unreactive 9. Represents an atom in an excited stat ...
... (D) Iodine liberates free bromine from a solution of bromide ion. (E) Fluorine is the most electronegative of the halogens. 8. Question 8-11 refer to atoms for which the occupied atomic orbitals shown below. 8. Represents an atom that is chemically unreactive 9. Represents an atom in an excited stat ...
Metastable inner-shell molecular state

Metastable Innershell Molecular State (MIMS) is a class of ultra-high-energy short-lived molecules have the binding energy up to 1,000 times larger and bond length up to 100 times smaller than typical molecules. MIMS is formed by inner-shell electrons that are normally resistant to molecular formation. However, in stellar conditions, the inner-shell electrons become reactive to form molecular structures (MIMS) from combinations of all elements in the periodic table. MIMS upon dissociation can emit x-ray photons with energies up to 100 keV at extremely high conversion efficiencies from compression energy to photon energy. MIMS is predicted to exist and dominate radiation processes in extreme astrophysical environments, such as large planet cores, star interiors, and black hole and neutron star surroundings. There, MIMS is predicted to enable highly energy-efficient transformation of the stellar compression energy into the radiation energy.The right schematic illustration shows the proposed four stages of the K-shell MIMS (K-MIMS) formation and x-ray generation process. Stage I: Individual atoms are subjected to the stellar compression and ready for absorbing the compression energy. Stage II: The outer electron shells fuse together under increasing ""stellar"" pressure. Stage III: At the peak pressure, via pressure ionization K-shell orbits form the K-MIMS, which is vibrationally hot and encapsulated by a Rydberg-like pseudo-L-Shell structure. Stage IV: The K-MIMS cools down by ionizing (""boiling-off"") a number of pseudo-L-shell electrons and subsequent optical decay by emitting an x-ray photon. The dissociated atoms return their original atoms states and are ready for absorbing the compression energy.MIMS also can be readily produced in laboratory and industrial environments, such as hypervelocity particle impact, laser fusion and z-machine. MIMS can be exploited for highly energy-efficient production of high intensity x-ray beams for a wide range of innovative applications, such as photolithography, x-ray lasers, and inertial fusion.