Chapter 15 Chemical Equilibrium
... 2. For those species for which both the initial and equilibrium concentrations are known, calculate the change in concentration that occurs as the system reaches equilibrium. 3. Use the stoichiometry of the reaction (that is, use the coefficients in the balanced chemical equation) to calculate the c ...
... 2. For those species for which both the initial and equilibrium concentrations are known, calculate the change in concentration that occurs as the system reaches equilibrium. 3. Use the stoichiometry of the reaction (that is, use the coefficients in the balanced chemical equation) to calculate the c ...
General and Inorganic Chemistry – Laboratory Techniques
... mixture is a material that can be separated by physical means into two or more substances. A substance is a kind of matter that cannot be separated into other kinds of matter by any physical process. Substances can be classified into two classes. These are elements (e.g., hydrogen and oxygen) and co ...
... mixture is a material that can be separated by physical means into two or more substances. A substance is a kind of matter that cannot be separated into other kinds of matter by any physical process. Substances can be classified into two classes. These are elements (e.g., hydrogen and oxygen) and co ...
Chapter 12
... What if we had 3 moles of oxygen, how much hydrogen would we need to react and how much water would we ...
... What if we had 3 moles of oxygen, how much hydrogen would we need to react and how much water would we ...
2nd Semester Practice Chemistry Final 2009
... d. All of these burn at the same rate. 74. A sample of a substance burns more rapidly in pure oxygen than in air. Which factor is most responsible for this high rate of reaction? a. the pressure of the reactants c. concentration of the reactants b. temperature d. surface area exposed to air 75. Cata ...
... d. All of these burn at the same rate. 74. A sample of a substance burns more rapidly in pure oxygen than in air. Which factor is most responsible for this high rate of reaction? a. the pressure of the reactants c. concentration of the reactants b. temperature d. surface area exposed to air 75. Cata ...
CHAPTER 12 | The Chemistry of Solids
... The orbital energy diagram for these metals will be similar to that of zinc in Figure 12.3. 12.27. Collect and Organize We are asked why it might be important to exclude phosphorus contaminants in the manufacture of silicon chips. Analyze The difference between silicon and phosphorus is that phospho ...
... The orbital energy diagram for these metals will be similar to that of zinc in Figure 12.3. 12.27. Collect and Organize We are asked why it might be important to exclude phosphorus contaminants in the manufacture of silicon chips. Analyze The difference between silicon and phosphorus is that phospho ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... 2 molecules of C8H18 react with 25 molecules of O2 to form 16 molecules of CO2 and 18 molecules of H2O 2 moles of C8H18 react with 25 moles of O2 to form 16 moles of CO2 and 18 moles of H2O 2 mol C8H18 : 25 mol O2 : 16 mol CO2 : 18 mol H2O ...
... 2 molecules of C8H18 react with 25 molecules of O2 to form 16 molecules of CO2 and 18 molecules of H2O 2 moles of C8H18 react with 25 moles of O2 to form 16 moles of CO2 and 18 moles of H2O 2 mol C8H18 : 25 mol O2 : 16 mol CO2 : 18 mol H2O ...
Solutions Manual
... Cellulose is made from repeating units of β-glucose with inversion of every second unit. This produces long, straight chains of cellulose which are linked to each other by hydrogen bonding. In plants, cellulose acts as a structural material. Starch (both amylase and amylopectin) is made from long-ch ...
... Cellulose is made from repeating units of β-glucose with inversion of every second unit. This produces long, straight chains of cellulose which are linked to each other by hydrogen bonding. In plants, cellulose acts as a structural material. Starch (both amylase and amylopectin) is made from long-ch ...
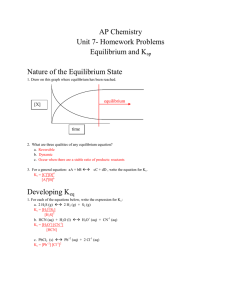
AP Chemistry Unit 7- Homework Problems Equilibrium and Ksp
... n = PV/RT = (1.2 atm)(2.5 L)/[(0.0821)(500 K)] n = 0.0731 moles NH3 so there must have been the same moles of NH4HS that broke up (0.0731 mol)(51.1 g/mol) = 3.735 g broke up so: 100 g – 3.735 g = 96.265 g remain ...
... n = PV/RT = (1.2 atm)(2.5 L)/[(0.0821)(500 K)] n = 0.0731 moles NH3 so there must have been the same moles of NH4HS that broke up (0.0731 mol)(51.1 g/mol) = 3.735 g broke up so: 100 g – 3.735 g = 96.265 g remain ...
Reactive absorption of carbon dioxide into promoted potassium
... 31.8 kJ mol-1. Experimental results have been incorporated into an existing Aspen PlusTM model using the E-NRTL thermodynamic package. The resulting model replicates pilot plant data and simulates industrial capture processes employing K2CO3 and MEA as the capture agent. In addition, the absorption ...
... 31.8 kJ mol-1. Experimental results have been incorporated into an existing Aspen PlusTM model using the E-NRTL thermodynamic package. The resulting model replicates pilot plant data and simulates industrial capture processes employing K2CO3 and MEA as the capture agent. In addition, the absorption ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.