Acid Base Equilibrium Diploma Questions
... ____ 37. Acid rain is linked to the leaching of heavy metals and their ions in lakes and rivers. Biomagnification of these metals and ions increases levels of diseases in fish and wildlife. Based on this information, a decision to reduce sulfur dioxide emissions would be a. b. c. d. ...
... ____ 37. Acid rain is linked to the leaching of heavy metals and their ions in lakes and rivers. Biomagnification of these metals and ions increases levels of diseases in fish and wildlife. Based on this information, a decision to reduce sulfur dioxide emissions would be a. b. c. d. ...
PART 3-ICHO 11-15
... E) 2,2,4-trimethylpentane. 6. With which of the following compounds will an aqueous solution of a higher oxide of element No 33 react? A) CO2, B) K2SO4, C) HCl, D) NaOH, E) magnesium. 7. What must be the minimum concentration (% by mass) of 1 kg of a potassium hydroxide solution for a complete neutr ...
... E) 2,2,4-trimethylpentane. 6. With which of the following compounds will an aqueous solution of a higher oxide of element No 33 react? A) CO2, B) K2SO4, C) HCl, D) NaOH, E) magnesium. 7. What must be the minimum concentration (% by mass) of 1 kg of a potassium hydroxide solution for a complete neutr ...
chapter 5 gases
... same whether the reaction takes place in one step or in a series of steps. The law enables us to determine the standard enthalpy of formation of a compound from its elements by an indirect route when direct combination of the elements is not feasible. Using Hess’s law, the standard enthalpy change f ...
... same whether the reaction takes place in one step or in a series of steps. The law enables us to determine the standard enthalpy of formation of a compound from its elements by an indirect route when direct combination of the elements is not feasible. Using Hess’s law, the standard enthalpy change f ...
Chapter 4 "Reactions in Aqueous Solution"
... the solvent3. An aqueous solution4 is a solution in which the solvent is water, whereas in a nonaqueous solution, the solvent is a substance other than water. Familiar examples of nonaqueous solvents are ethyl acetate, used in nail polish removers, and turpentine, used to clean paint brushes. In thi ...
... the solvent3. An aqueous solution4 is a solution in which the solvent is water, whereas in a nonaqueous solution, the solvent is a substance other than water. Familiar examples of nonaqueous solvents are ethyl acetate, used in nail polish removers, and turpentine, used to clean paint brushes. In thi ...
Chapter 9 Review, pages 628–633
... from the carbon atom. Thus the oxidation number of N in HCN(g) is –3. (d) The oxidation number of hydrogen in its compounds is +1, and the oxidation number of oxygen in its compounds is –2. Since there are 2 hydrogen atoms in H2C2O4(aq), the total contribution of the hydrogen atoms is +2. Since ther ...
... from the carbon atom. Thus the oxidation number of N in HCN(g) is –3. (d) The oxidation number of hydrogen in its compounds is +1, and the oxidation number of oxygen in its compounds is –2. Since there are 2 hydrogen atoms in H2C2O4(aq), the total contribution of the hydrogen atoms is +2. Since ther ...
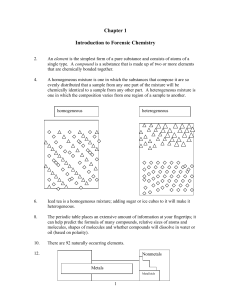
Chapter 1 Introduction to Forensic Chemistry
... Precipitation reactions begin with reagents dissolved in solution and produce a solid as a product. Combustion reactions involve the reaction of a substance with oxygen (often with applied heat); carbon-containing compounds then produce carbon dioxide and hydrogen-containing compounds then produce w ...
... Precipitation reactions begin with reagents dissolved in solution and produce a solid as a product. Combustion reactions involve the reaction of a substance with oxygen (often with applied heat); carbon-containing compounds then produce carbon dioxide and hydrogen-containing compounds then produce w ...
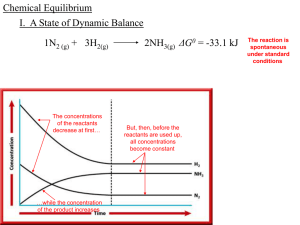
Chemical Equilibrium - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... products are in the same ________ physical _____ state are ____________, homogeneous but reactions with _________ reactants and ________ products in _____ more than ___ one ________ physical ________ _____ state result in _____________ heterogeneous gaseous _________ equilibria ethanol 1C2H5OH (l) K ...
... products are in the same ________ physical _____ state are ____________, homogeneous but reactions with _________ reactants and ________ products in _____ more than ___ one ________ physical ________ _____ state result in _____________ heterogeneous gaseous _________ equilibria ethanol 1C2H5OH (l) K ...
Document
... Analyze We are given a volume and initial molar amounts of the species in a reaction and asked to determine in which direction the reaction must proceed to achieve equilibrium. Plan We can determine the starting concentration of each species in the reaction mixture. We can then substitute the starti ...
... Analyze We are given a volume and initial molar amounts of the species in a reaction and asked to determine in which direction the reaction must proceed to achieve equilibrium. Plan We can determine the starting concentration of each species in the reaction mixture. We can then substitute the starti ...
Chapter 4 - AP Chemistry with dr hart
... • It is helpful to pay attention to exactly what species are present in a reaction mixture (i.e., solid, liquid, gas, aqueous solution). • If we are to understand reactivity, we must be aware of just what is changing during the course of a reaction. Aqueous Reactions © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... • It is helpful to pay attention to exactly what species are present in a reaction mixture (i.e., solid, liquid, gas, aqueous solution). • If we are to understand reactivity, we must be aware of just what is changing during the course of a reaction. Aqueous Reactions © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
AP Chemistry - Siva Kodali
... 2,000 students per year. She is the author of ACT For Dummies, Pre-Calculus For Dummies, AP Biology For Dummies, Chemistry Workbook For Dummies, GRE For Dummies, Pre-Calculus Workbook for Dummies, and other books on self-esteem, writing, and motivational topics. Michelle has overseen dozens of progr ...
... 2,000 students per year. She is the author of ACT For Dummies, Pre-Calculus For Dummies, AP Biology For Dummies, Chemistry Workbook For Dummies, GRE For Dummies, Pre-Calculus Workbook for Dummies, and other books on self-esteem, writing, and motivational topics. Michelle has overseen dozens of progr ...
No Slide Title
... you get one carbon dioxide molecule for every carbon atom in the original and one water molecule for every two hydrogen atoms When you have done this, go back and balance the oxygen. ...
... you get one carbon dioxide molecule for every carbon atom in the original and one water molecule for every two hydrogen atoms When you have done this, go back and balance the oxygen. ...
Chemistry (Revised)
... FeS(s) + 2HCl(aq) → FeCl2(aq) + H2S(g) (i) Hydrogen sulfide gas is very soluble in water. Draw a diagram to show an assembled apparatus that could be used to measure the volume of H2S gas produced when a sample of ...
... FeS(s) + 2HCl(aq) → FeCl2(aq) + H2S(g) (i) Hydrogen sulfide gas is very soluble in water. Draw a diagram to show an assembled apparatus that could be used to measure the volume of H2S gas produced when a sample of ...
content - Thesis Scientist
... them until 1.45 g of silver were deposited at the cathode of cell B. How long did the current flow? What mass of copper and what mass of zinc were deposited in the concerned cells? (Atomic masses of Ag = 108, Zn = 65.4, Cu = 63.5) 29. Assign reasons for the following: (i) The enthalpies of atomisati ...
... them until 1.45 g of silver were deposited at the cathode of cell B. How long did the current flow? What mass of copper and what mass of zinc were deposited in the concerned cells? (Atomic masses of Ag = 108, Zn = 65.4, Cu = 63.5) 29. Assign reasons for the following: (i) The enthalpies of atomisati ...
Changing Matter
... • Atoms that bond form molecules – May be the same type (nonmetals) of atom or, – Different types (metal + nonmetal) of atoms ...
... • Atoms that bond form molecules – May be the same type (nonmetals) of atom or, – Different types (metal + nonmetal) of atoms ...
Specification and sample assessment material - Edexcel
... This specification is Issue 5. We will inform centres of any changes to this issue. The latest issue can be found on our website: qualifications.pearson.com ...
... This specification is Issue 5. We will inform centres of any changes to this issue. The latest issue can be found on our website: qualifications.pearson.com ...
2013 - SQA
... FeS(s) + 2HCl(aq) → FeCl2(aq) + H2S(g) (i) Hydrogen sulfide gas is very soluble in water. Draw a diagram to show an assembled apparatus that could be used to measure the volume of H2S gas produced when a sample of ...
... FeS(s) + 2HCl(aq) → FeCl2(aq) + H2S(g) (i) Hydrogen sulfide gas is very soluble in water. Draw a diagram to show an assembled apparatus that could be used to measure the volume of H2S gas produced when a sample of ...
M - coercingmolecules
... MH2O = 18.0 g/mol (one mole of H2O molecule weighs 18.0 g) MNO3- = 62.0 g/mol (one mole of NO3- ion weighs 62.0 g) Brown, T., E. LeMay, and B. Bursten. 2000. Chemistry: The Central Science. 8th ed. Phils: Pearson Education Asia Pte. Ltd. ...
... MH2O = 18.0 g/mol (one mole of H2O molecule weighs 18.0 g) MNO3- = 62.0 g/mol (one mole of NO3- ion weighs 62.0 g) Brown, T., E. LeMay, and B. Bursten. 2000. Chemistry: The Central Science. 8th ed. Phils: Pearson Education Asia Pte. Ltd. ...
Instructor`s Guide to General Chemistry: Guided
... (b) Steps 2 and 3 make clear what information is given and what needs to be found. Molecules/ions react and molecules/ions are produced, so the units to keep track of reactants turning into products must be moles, which specify the number of molecules and/or ions. (c) The stoichiometric coefficients ...
... (b) Steps 2 and 3 make clear what information is given and what needs to be found. Molecules/ions react and molecules/ions are produced, so the units to keep track of reactants turning into products must be moles, which specify the number of molecules and/or ions. (c) The stoichiometric coefficients ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.