Functional Groups
... Dibenzofurans: produced when PCBs are heated in the presence of oxygen. Their structure is that of 2 benzene rings joined by a furan ring (4 carbons and one oxygen joined in a ring structure.) Furans with intermediate amounts of Cl have a toxicity similar of that to TCDD—Dioxin. ...
... Dibenzofurans: produced when PCBs are heated in the presence of oxygen. Their structure is that of 2 benzene rings joined by a furan ring (4 carbons and one oxygen joined in a ring structure.) Furans with intermediate amounts of Cl have a toxicity similar of that to TCDD—Dioxin. ...
Atomic Theory electron charge: -1.6 X 10-19C
... Still, scientists did not have a clear idea of what the atom looked like. The English researcher, Ernest Rutherford, provided clearer focus when he bombarded a thin sheet of gold foil with alpha rays (beams of helium nuclei). If atoms were uniformly dense, as he expected, all of the rays would have ...
... Still, scientists did not have a clear idea of what the atom looked like. The English researcher, Ernest Rutherford, provided clearer focus when he bombarded a thin sheet of gold foil with alpha rays (beams of helium nuclei). If atoms were uniformly dense, as he expected, all of the rays would have ...
Critical Thinking Questions 4
... How many C, H and O atoms are on the left of the arrow and how many C, H and O atoms are on the right of the arrow? ...
... How many C, H and O atoms are on the left of the arrow and how many C, H and O atoms are on the right of the arrow? ...
Quantum Numbers, Orbitals, Electron Configurations, Periodic Trends
... Convert the numbers is questions 1a – 1d into scientific notation. a) c) b) d) Convert the following numbers that are in scientific notation into decimal form. a) 1.2340 × 107 d) 7.0 × 104 b) 3.980 × 102 e) 5.00134 × 10-4 c) 9.23 × 10-5 f) 6.626 × 10-34 A box measures 2.56 in × 4.21 in × 12.00 in. W ...
... Convert the numbers is questions 1a – 1d into scientific notation. a) c) b) d) Convert the following numbers that are in scientific notation into decimal form. a) 1.2340 × 107 d) 7.0 × 104 b) 3.980 × 102 e) 5.00134 × 10-4 c) 9.23 × 10-5 f) 6.626 × 10-34 A box measures 2.56 in × 4.21 in × 12.00 in. W ...
Quantum Numbers, Orbitals, Electron Configurations, Periodic Trends
... Convert the numbers is questions 1a – 1d into scientific notation. a) c) b) d) Convert the following numbers that are in scientific notation into decimal form. a) 1.2340 × 107 d) 7.0 × 104 b) 3.980 × 102 e) 5.00134 × 10-4 c) 9.23 × 10-5 f) 6.626 × 10-34 A box measures 2.56 in × 4.21 in × 12.00 in. W ...
... Convert the numbers is questions 1a – 1d into scientific notation. a) c) b) d) Convert the following numbers that are in scientific notation into decimal form. a) 1.2340 × 107 d) 7.0 × 104 b) 3.980 × 102 e) 5.00134 × 10-4 c) 9.23 × 10-5 f) 6.626 × 10-34 A box measures 2.56 in × 4.21 in × 12.00 in. W ...
10-4 Enthalpy (Section 10.6)
... • System absorbs KE from surroundings as PE in the bonds. Surroundings will feel cold. • ∆H = P – R = positive value (heat absorbed) ...
... • System absorbs KE from surroundings as PE in the bonds. Surroundings will feel cold. • ∆H = P – R = positive value (heat absorbed) ...
File
... All are solids at SATP (Standard Ambient Temperature and Pressure) of 25 oC and 100 kPa. ...
... All are solids at SATP (Standard Ambient Temperature and Pressure) of 25 oC and 100 kPa. ...
N5 Chemistry Summary notes 2017
... Other changes which can be monitored are: colour, pH, concentration and many more As these changes happen over a period of time, the reaction rate is expressed as Rate = Change in something Change in time. Changes in Volume The volume of the gas can be measured using the following experiments. ...
... Other changes which can be monitored are: colour, pH, concentration and many more As these changes happen over a period of time, the reaction rate is expressed as Rate = Change in something Change in time. Changes in Volume The volume of the gas can be measured using the following experiments. ...
Chapter 1 (Matter and Measurement) Objectives
... 2. Biological, chemical, and physical properties of matter result from the ability of atoms to form bonds from electrostatic forces between electrons and protons and between atoms and molecules. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know atoms combine to form molecules by sharing el ...
... 2. Biological, chemical, and physical properties of matter result from the ability of atoms to form bonds from electrostatic forces between electrons and protons and between atoms and molecules. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know atoms combine to form molecules by sharing el ...
NUCLEAR PHYSICS
... In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons of an atom, a molecule, or other physical structure.[1] It concerns the way electrons can be distributed in the orbitals of the given system (atomic or molecular for instance). Like the other elementary p ...
... In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons of an atom, a molecule, or other physical structure.[1] It concerns the way electrons can be distributed in the orbitals of the given system (atomic or molecular for instance). Like the other elementary p ...
Empirical Formula
... • Oxygen gas (_____) is not explosive but must be present for combustion (fire) to occur • When these two gases come together to react, they form water – A molecule now with completely different properties!!! ...
... • Oxygen gas (_____) is not explosive but must be present for combustion (fire) to occur • When these two gases come together to react, they form water – A molecule now with completely different properties!!! ...
File
... 6. The effective nuclear charge experienced by the outermost electron of Na is different than the effective nuclear charge experienced by the outermost electron of Ne. This difference best accounts for which of the following? A. Na has a greater density at standard conditions than Ne. B. Na has a lo ...
... 6. The effective nuclear charge experienced by the outermost electron of Na is different than the effective nuclear charge experienced by the outermost electron of Ne. This difference best accounts for which of the following? A. Na has a greater density at standard conditions than Ne. B. Na has a lo ...
Scientific Principles: Chemical Properties
... in the nucleus – electrons- small, negatively charged particles located in atomic orbitals ...
... in the nucleus – electrons- small, negatively charged particles located in atomic orbitals ...
Chem20u2(5.2) - Mr. Searcy Chemistry 20
... 3. Compare the Bohr and quantum mechanical models of the atom. 4. Explain the impact of de Broglie’s wave-particle duality and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle on the modern view of electrons in atoms. 5. Identify the relationships among a hydrogen atom’s energy levels, sublevels, and atomic orb ...
... 3. Compare the Bohr and quantum mechanical models of the atom. 4. Explain the impact of de Broglie’s wave-particle duality and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle on the modern view of electrons in atoms. 5. Identify the relationships among a hydrogen atom’s energy levels, sublevels, and atomic orb ...
File - Mr Weng`s IB Chemistry
... • Elastomers are flexible and can be deformed under force but will return to nearly their original shape once the stress is released. • High density polyethene (HDPE) has no branching allowing chains to be packed together. • Low density polyethene (LDPE) has some branching and is more flexible. • Pl ...
... • Elastomers are flexible and can be deformed under force but will return to nearly their original shape once the stress is released. • High density polyethene (HDPE) has no branching allowing chains to be packed together. • Low density polyethene (LDPE) has some branching and is more flexible. • Pl ...
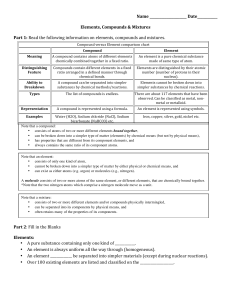
Compound vs Element chart
... • can be broken down into a simpler type of matter (elements) by chemical means (but not by physical means), • has properties that are different from its component elements, and • always contains the same ratio of its component atoms. Note that an element: • consists of only one kind of atom, • cann ...
... • can be broken down into a simpler type of matter (elements) by chemical means (but not by physical means), • has properties that are different from its component elements, and • always contains the same ratio of its component atoms. Note that an element: • consists of only one kind of atom, • cann ...
Final Exam Review Day 1
... Many electrons are shared. They are ______________. Classify the following chemical bonds as ionic, covalent or metallic: _____ CuO _____AlBr3 _____ H2O _____ PCl5 _____ MgSO4 ...
... Many electrons are shared. They are ______________. Classify the following chemical bonds as ionic, covalent or metallic: _____ CuO _____AlBr3 _____ H2O _____ PCl5 _____ MgSO4 ...
Quantum Mechanical Model
... A function of the coordinates (x, y, and z) of the electron’s position in 3-D space ...
... A function of the coordinates (x, y, and z) of the electron’s position in 3-D space ...
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electrostatic force of attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are ""strong bonds"" such as covalent or ionic bonds and ""weak bonds"" such as Dipole-dipole interaction, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding.Since opposite charges attract via a simple electromagnetic force, the negatively charged electrons that are orbiting the nucleus and the positively charged protons in the nucleus attract each other. An electron positioned between two nuclei will be attracted to both of them, and the nuclei will be attracted toward electrons in this position. This attraction constitutes the chemical bond. Due to the matter wave nature of electrons and their smaller mass, they must occupy a much larger amount of volume compared with the nuclei, and this volume occupied by the electrons keeps the atomic nuclei relatively far apart, as compared with the size of the nuclei themselves. This phenomenon limits the distance between nuclei and atoms in a bond.In general, strong chemical bonding is associated with the sharing or transfer of electrons between the participating atoms. The atoms in molecules, crystals, metals and diatomic gases—indeed most of the physical environment around us—are held together by chemical bonds, which dictate the structure and the bulk properties of matter.All bonds can be explained by quantum theory, but, in practice, simplification rules allow chemists to predict the strength, directionality, and polarity of bonds. The octet rule and VSEPR theory are two examples. More sophisticated theories are valence bond theory which includes orbital hybridization and resonance, and the linear combination of atomic orbitals molecular orbital method which includes ligand field theory. Electrostatics are used to describe bond polarities and the effects they have on chemical substances.