Answers to questions on test #2
... [3] (10) The absolute hardness of a molecule, η, is given by the formula η = (IE − EA)/2 Give the SI units attached to η, and explain what η represents (in other words, what is the main difference between two molecules if one has a big η and the other has a small η). Joule (unit of energy) The hardn ...
... [3] (10) The absolute hardness of a molecule, η, is given by the formula η = (IE − EA)/2 Give the SI units attached to η, and explain what η represents (in other words, what is the main difference between two molecules if one has a big η and the other has a small η). Joule (unit of energy) The hardn ...
pptx
... • How to best parallelize existing GW-BSE algorithms? Will rely on Charm++ to deliver high performance Coding, maintenance, migration to other computers much easier for user • Need to improve GW-BSE algorithms to use the computers ...
... • How to best parallelize existing GW-BSE algorithms? Will rely on Charm++ to deliver high performance Coding, maintenance, migration to other computers much easier for user • Need to improve GW-BSE algorithms to use the computers ...
FREE Sample Here
... A) the number of electrons in the element B) the number of protons in the element C) the number of protons plus neutrons in the element D) the number of protons plus electrons in the element Answer: C Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis Section: 2.2 6) In what way are elements in the same column ...
... A) the number of electrons in the element B) the number of protons in the element C) the number of protons plus neutrons in the element D) the number of protons plus electrons in the element Answer: C Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis Section: 2.2 6) In what way are elements in the same column ...
chem 1411- chapter 7
... get excited to higher energy levels by absorbing energy. This is the excited state of an atom, which is unstable. The electrons then start falling from higher levels to lower levels, releasing energy. This energy when resolved through a spectroscope, we get different lines of specific wavelengths. T ...
... get excited to higher energy levels by absorbing energy. This is the excited state of an atom, which is unstable. The electrons then start falling from higher levels to lower levels, releasing energy. This energy when resolved through a spectroscope, we get different lines of specific wavelengths. T ...
1st mid unit test formative (pre-test)
... The horizontal rows of the periodic table are called periods. The horizontal columns are called families or groups. Metals are on the left and in the center of the table. Non-metals are located on the right-hand side of the table. Metals are separated from non-metals by a staircase of elements calle ...
... The horizontal rows of the periodic table are called periods. The horizontal columns are called families or groups. Metals are on the left and in the center of the table. Non-metals are located on the right-hand side of the table. Metals are separated from non-metals by a staircase of elements calle ...
Section 3.6
... were identical, any magnetic moment caused by the external field should move the atoms in random directions, since it could be oriented in any direction as the atoms enter the field. The two distinct lines indicate that a silver atom must have one of two distinct and opposite magnetic moments. This ...
... were identical, any magnetic moment caused by the external field should move the atoms in random directions, since it could be oriented in any direction as the atoms enter the field. The two distinct lines indicate that a silver atom must have one of two distinct and opposite magnetic moments. This ...
Transparancies for Atomic Structure Section
... We have neglected any interaction of electrons BUT we no longer have a coulomb potential ...
... We have neglected any interaction of electrons BUT we no longer have a coulomb potential ...
1st mid unit test formative (pre-test)
... The horizontal rows of the periodic table are called periods. The horizontal columns are called families or groups. Metals are on the left and in the center of the table. Non-metals are located on the right-hand side of the table. Metals are separated from non-metals by a staircase of elements calle ...
... The horizontal rows of the periodic table are called periods. The horizontal columns are called families or groups. Metals are on the left and in the center of the table. Non-metals are located on the right-hand side of the table. Metals are separated from non-metals by a staircase of elements calle ...
c2 atomic structure f pmh
... A lithium atom can lose one electron to form a lithium ion which can be written (2)+ A fluorine atom can gain one electron to form a fluoride ion. Choose from the list the correct way to write the fluoride ion. ...
... A lithium atom can lose one electron to form a lithium ion which can be written (2)+ A fluorine atom can gain one electron to form a fluoride ion. Choose from the list the correct way to write the fluoride ion. ...
AP Semestar Exam REVIEW
... ____ 42. Place the following atoms in order of increasing size: Al, Cl, Mg, O, and P. a. Cl < O < P < Al < Mg b. Cl < P < Al < Mg < O c. O < Cl < P < Al < Mg d. O < Mg < Al < P < Cl e. none of the above ____ 43. A pair of electrons that is shared between two atoms is a. a covalent bond. b. a lone pa ...
... ____ 42. Place the following atoms in order of increasing size: Al, Cl, Mg, O, and P. a. Cl < O < P < Al < Mg b. Cl < P < Al < Mg < O c. O < Cl < P < Al < Mg d. O < Mg < Al < P < Cl e. none of the above ____ 43. A pair of electrons that is shared between two atoms is a. a covalent bond. b. a lone pa ...
CHEMISTRY The Central Science 9th Edition
... between the electrodes about 3000 v and a low pressure of inert gas about 10ˉ⁵ Torr,he noticed that a beam of gluing rays comes from the cathode to the anode , he called it the cathodic rays. Thompson found that the cathodic rays are composed of tiny small particles with a mass and negative charge, ...
... between the electrodes about 3000 v and a low pressure of inert gas about 10ˉ⁵ Torr,he noticed that a beam of gluing rays comes from the cathode to the anode , he called it the cathodic rays. Thompson found that the cathodic rays are composed of tiny small particles with a mass and negative charge, ...
Practice Multiple Choice Questions for the Chemistry Final Exam
... 93. What is the boiling point of water at standard pressure? a) 100 C b) 112 C c) 212 C d) 200 C 94. Which of the following is a pure substance? a) water b) milk c) soil d) concrete 95. Sugar in water is an example of which solute-solvent combination? a) gas-liquid b) liquid-liquid c) solid-liquid ...
... 93. What is the boiling point of water at standard pressure? a) 100 C b) 112 C c) 212 C d) 200 C 94. Which of the following is a pure substance? a) water b) milk c) soil d) concrete 95. Sugar in water is an example of which solute-solvent combination? a) gas-liquid b) liquid-liquid c) solid-liquid ...
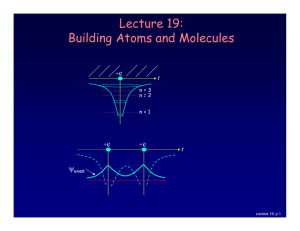
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules
... • Electrons do not pile up in the lowest energy state. It’s more like filling a bucket with water. • They are distributed among the energy levels according to the Exclusion Principle. • Particles that obey this principle are called “fermions”. Protons and neutrons are also fermions, but photons are ...
... • Electrons do not pile up in the lowest energy state. It’s more like filling a bucket with water. • They are distributed among the energy levels according to the Exclusion Principle. • Particles that obey this principle are called “fermions”. Protons and neutrons are also fermions, but photons are ...
Chapter 2
... • The atom is mostly empty space. • These electrons are held in the atom by their attraction for a positively charged electric field within the atom. – There had to be a source of positive charge because the atom is neutral. – Thomson assumed there were no positively charged pieces because none show ...
... • The atom is mostly empty space. • These electrons are held in the atom by their attraction for a positively charged electric field within the atom. – There had to be a source of positive charge because the atom is neutral. – Thomson assumed there were no positively charged pieces because none show ...
Quantum Mechanics Problem Set
... charge at the center and a diffuse negative charge surrounding it. The empirical evidence provided this idea because a majority of the alpha particles passed through the gold foil with only a small percentage being randomly deflected. Bohr’s theory then specified the nature of the diffuse negative c ...
... charge at the center and a diffuse negative charge surrounding it. The empirical evidence provided this idea because a majority of the alpha particles passed through the gold foil with only a small percentage being randomly deflected. Bohr’s theory then specified the nature of the diffuse negative c ...
CHAPTER 4: Structure of the Atom
... electron left. Only modification in all equations Ze instead of e, where Z is the number of positive charges in the nucleus Could neither account for the intensities nor the fine structure of the spectral lines (they are actually doublets) for hydrogen when atoms were put into magnetic fields (Nobel ...
... electron left. Only modification in all equations Ze instead of e, where Z is the number of positive charges in the nucleus Could neither account for the intensities nor the fine structure of the spectral lines (they are actually doublets) for hydrogen when atoms were put into magnetic fields (Nobel ...
CHEM121 Lecture Ch5 student
... molecule C3H8 produces _______ molecules CO2 molecule C3H8 produces _______ molcules H2O molecules O2 produces _______ molecules CO2 molecules C3H8 produces _______ molecules CO2 ...
... molecule C3H8 produces _______ molecules CO2 molecule C3H8 produces _______ molcules H2O molecules O2 produces _______ molecules CO2 molecules C3H8 produces _______ molecules CO2 ...
GCSE_C2_Revision_+_Exam_Questions
... that lose electrons become positively charged ions. Atoms that gain electrons become negatively charged ions. Ions have the electronic structure of a noble gas (Group 0). The elements in Group 1 of the periodic table, the alkali metals, have similar chemical properties. They all react with non-metal ...
... that lose electrons become positively charged ions. Atoms that gain electrons become negatively charged ions. Ions have the electronic structure of a noble gas (Group 0). The elements in Group 1 of the periodic table, the alkali metals, have similar chemical properties. They all react with non-metal ...
Bourdel-3 (doc, 273 KiB)
... Atomic gases have proven to be a useful ressource for precision measurements of the atom properties or of the external forces acting on them. For example, atom interferometers permit the measurement of the local gravity constant g with a relative accuracy of the order of 10 -8 at 1s 1. A long observ ...
... Atomic gases have proven to be a useful ressource for precision measurements of the atom properties or of the external forces acting on them. For example, atom interferometers permit the measurement of the local gravity constant g with a relative accuracy of the order of 10 -8 at 1s 1. A long observ ...
Document
... simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle a. Electrons are located by their interactions with photons b. Electrons and photons have similar energies c. Interaction between a photon and an electron knocks the electron off of its course ...
... simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle a. Electrons are located by their interactions with photons b. Electrons and photons have similar energies c. Interaction between a photon and an electron knocks the electron off of its course ...
Nature template - PC Word 97
... Atomic gases have proven to be a useful ressource for precision measurements of the atom properties or of the external forces acting on them. For example, atom interferometers permit the measurement of the local gravity constant g with a relative accuracy of the order of 10 -8 at 1s 1. A long observ ...
... Atomic gases have proven to be a useful ressource for precision measurements of the atom properties or of the external forces acting on them. For example, atom interferometers permit the measurement of the local gravity constant g with a relative accuracy of the order of 10 -8 at 1s 1. A long observ ...
ap chemistry – 2013-2014
... AP CHEMISTRY – 2013-2014 Course Description: This AP Chemistry course is designed to be the equivalent of the general chemistry course usually taken during the first year of college. This course is structured around six big ideas that include: Structure of matter, properties of matter-characteristic ...
... AP CHEMISTRY – 2013-2014 Course Description: This AP Chemistry course is designed to be the equivalent of the general chemistry course usually taken during the first year of college. This course is structured around six big ideas that include: Structure of matter, properties of matter-characteristic ...
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electrostatic force of attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are ""strong bonds"" such as covalent or ionic bonds and ""weak bonds"" such as Dipole-dipole interaction, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding.Since opposite charges attract via a simple electromagnetic force, the negatively charged electrons that are orbiting the nucleus and the positively charged protons in the nucleus attract each other. An electron positioned between two nuclei will be attracted to both of them, and the nuclei will be attracted toward electrons in this position. This attraction constitutes the chemical bond. Due to the matter wave nature of electrons and their smaller mass, they must occupy a much larger amount of volume compared with the nuclei, and this volume occupied by the electrons keeps the atomic nuclei relatively far apart, as compared with the size of the nuclei themselves. This phenomenon limits the distance between nuclei and atoms in a bond.In general, strong chemical bonding is associated with the sharing or transfer of electrons between the participating atoms. The atoms in molecules, crystals, metals and diatomic gases—indeed most of the physical environment around us—are held together by chemical bonds, which dictate the structure and the bulk properties of matter.All bonds can be explained by quantum theory, but, in practice, simplification rules allow chemists to predict the strength, directionality, and polarity of bonds. The octet rule and VSEPR theory are two examples. More sophisticated theories are valence bond theory which includes orbital hybridization and resonance, and the linear combination of atomic orbitals molecular orbital method which includes ligand field theory. Electrostatics are used to describe bond polarities and the effects they have on chemical substances.