Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... Username – btesta Password - science Vocabulary: coefficient, combination, compound, decomposition, double replacement, element, molecule, product, reactant, single replacement, subscript ...
... Username – btesta Password - science Vocabulary: coefficient, combination, compound, decomposition, double replacement, element, molecule, product, reactant, single replacement, subscript ...
Chemistry
... (a) explain, in terms of rates of the forward and reverse reactions, what is meant by a reversible reaction and dynamic equilibrium (b) state Le Chatelier’s Principle and apply it to deduce qualitatively (from appropriate information) the effects of changes in concentration, pressure or temperature, ...
... (a) explain, in terms of rates of the forward and reverse reactions, what is meant by a reversible reaction and dynamic equilibrium (b) state Le Chatelier’s Principle and apply it to deduce qualitatively (from appropriate information) the effects of changes in concentration, pressure or temperature, ...
CHEM%1212K% Final%Exam% Summer%2011% K
... C)%Water%can%be%a%BronstedJLowry%acid%AND%a%Lewis%base,%depending%on% ...
... C)%Water%can%be%a%BronstedJLowry%acid%AND%a%Lewis%base,%depending%on% ...
Chemistry 2nd Semester Final Review
... CO2(g) + CaO(s). How many grams of calcium carbonate will I need to form 3.45 liters of carbon dioxide? 8. How many liters of water can be made from 55 grams of oxygen gas and an excess of hydrogen at a pressure of 12.4 atm and a temperature of 85C? 9. How many liters of water can be made from 34 g ...
... CO2(g) + CaO(s). How many grams of calcium carbonate will I need to form 3.45 liters of carbon dioxide? 8. How many liters of water can be made from 55 grams of oxygen gas and an excess of hydrogen at a pressure of 12.4 atm and a temperature of 85C? 9. How many liters of water can be made from 34 g ...
Chapter 3 Chemical Reactions
... achieved, the amount of each reactant and product remains constant. ...
... achieved, the amount of each reactant and product remains constant. ...
CHM 122 Chapter 8 -Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy
... Heat: The amount of thermal energy transferred from one object to another as the result of a temperature difference between the two Thermal Energy: The kinetic energy of molecular motion and is measured by finding the temperature of an object We will symbolize heat energy transferred by the letter q ...
... Heat: The amount of thermal energy transferred from one object to another as the result of a temperature difference between the two Thermal Energy: The kinetic energy of molecular motion and is measured by finding the temperature of an object We will symbolize heat energy transferred by the letter q ...
Many thermal and chemical reactions occur during the roasting
... F, carmelization begins. It is at this point that water and carbon dioxide fracture and outgassing begins causing the first mechanical crack. These are the chemical reactions, occurring at approximately 356 degrees F, that are exothermic. Once carmelization begins, it is very important that the coff ...
... F, carmelization begins. It is at this point that water and carbon dioxide fracture and outgassing begins causing the first mechanical crack. These are the chemical reactions, occurring at approximately 356 degrees F, that are exothermic. Once carmelization begins, it is very important that the coff ...
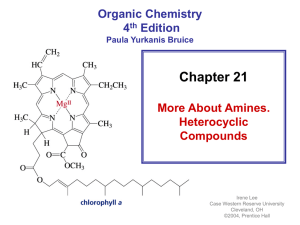
Lecture Resource ()
... • Some amines are heterocyclic compounds (or heterocycles) • Most drugs, vitamins, and many other natural products are heterocycles • A natural product is a compound synthesized by a plant or an animal ...
... • Some amines are heterocyclic compounds (or heterocycles) • Most drugs, vitamins, and many other natural products are heterocycles • A natural product is a compound synthesized by a plant or an animal ...
Document
... It is difficult to measure directly. However, two other reactions are known: C(graphite) + O2(g) CO2(g); DH = -393.5 kJ 2CO2(g) 2CO(g) + O2(g); DH = – 566.0 kJ In order for these to add to give the reaction we want, we must multiply the first reaction by 2. Note that we also multiply DH by 2. ...
... It is difficult to measure directly. However, two other reactions are known: C(graphite) + O2(g) CO2(g); DH = -393.5 kJ 2CO2(g) 2CO(g) + O2(g); DH = – 566.0 kJ In order for these to add to give the reaction we want, we must multiply the first reaction by 2. Note that we also multiply DH by 2. ...
Honors Chemistry I
... hydrogen gas. Balanced the following equations for these two processes: a. Fe3O4(s) + H2(g) Fe(s) + H2O(g) b. Fe3O4(s) + CO(g) Fe(s) + CO2(g) 3) Chromium compounds exhibit a wide variety of bright colors. When solid ammonium dichromate—a vivid orange compound—is ignited, a spectacular reaction o ...
... hydrogen gas. Balanced the following equations for these two processes: a. Fe3O4(s) + H2(g) Fe(s) + H2O(g) b. Fe3O4(s) + CO(g) Fe(s) + CO2(g) 3) Chromium compounds exhibit a wide variety of bright colors. When solid ammonium dichromate—a vivid orange compound—is ignited, a spectacular reaction o ...
Chapter 2 - Molecules of Life (Biochemistry) Periodic Table of
... • Electrons not shared equally! • One atom “hogs” the electrons! • This leads to the formation of hydrogen bonds.! ...
... • Electrons not shared equally! • One atom “hogs” the electrons! • This leads to the formation of hydrogen bonds.! ...
AP Chapter Five Outline
... When ionic compounds dissolve in water, they dissociate into ions surrounded by water molecules. An ionic compound that completely dissolves into ions is a strong electrolyte. A. Exchange Reactions: AB + CD AD + CB 1. If both reactants and products are water-soluble compounds, then no overall re ...
... When ionic compounds dissolve in water, they dissociate into ions surrounded by water molecules. An ionic compound that completely dissolves into ions is a strong electrolyte. A. Exchange Reactions: AB + CD AD + CB 1. If both reactants and products are water-soluble compounds, then no overall re ...
MIDDLE COLLEGE HIGH SCHOOL
... The rate of this reaction can be increased by (1) formation of a precipitate using 5.0 grams of powdered zinc instead of a (2) formation of a gas 5.0-gram strip of zinc because the powdered (3) effective collisions between reacting zinc has particles (1) lower kinetic energy (4) addition of a cataly ...
... The rate of this reaction can be increased by (1) formation of a precipitate using 5.0 grams of powdered zinc instead of a (2) formation of a gas 5.0-gram strip of zinc because the powdered (3) effective collisions between reacting zinc has particles (1) lower kinetic energy (4) addition of a cataly ...
Chemistry - Swami Ramanand Teerth Marathwada University
... Quantum yield, experimental determination of quantum yield. High and low quantum yield reactions. Reasons for high and low quantum yield. Jablonski diagram with various Processes occurring in the excited state. Qualitative description of Fluorescence, phosphorescence, non-radiative processes (intern ...
... Quantum yield, experimental determination of quantum yield. High and low quantum yield reactions. Reasons for high and low quantum yield. Jablonski diagram with various Processes occurring in the excited state. Qualitative description of Fluorescence, phosphorescence, non-radiative processes (intern ...
Full answers
... Rearranging gives x = [I2(g)] = 0.0139 M. Answer: 0.0139 M If 0.274 g of H2S were now introduced into the same flask, what would be the concentration of S2(g) at equilibrium? The molar mass of H2S is (2 × 1.008 (H) + 32.06 (S)) = 34.08 g mol-1. Hence, 0.274 g of H2S corresponds to: number of moles = ...
... Rearranging gives x = [I2(g)] = 0.0139 M. Answer: 0.0139 M If 0.274 g of H2S were now introduced into the same flask, what would be the concentration of S2(g) at equilibrium? The molar mass of H2S is (2 × 1.008 (H) + 32.06 (S)) = 34.08 g mol-1. Hence, 0.274 g of H2S corresponds to: number of moles = ...
Student Activity PDF - TI Education
... An integer immediately following a letter or closing parenthesis is converted to subscript. This is the number of atoms or group of atoms in a molecule. ...
... An integer immediately following a letter or closing parenthesis is converted to subscript. This is the number of atoms or group of atoms in a molecule. ...