KS4-Rates - Free Exam Papers
... Why do most reactions start fast and get slower and slower? A. They run out of energy B. They run out of catalyst. C. The concentration of reactant molecules gets less and less. D. The surface area increases. ...
... Why do most reactions start fast and get slower and slower? A. They run out of energy B. They run out of catalyst. C. The concentration of reactant molecules gets less and less. D. The surface area increases. ...
ConcepTest On Simple Redox Reactions
... Comment to Instructor: Correct answer is 3. HCl. Since the oxidation number of H is decreasing from +1 to 0, it is undergoing reduction. Zn is being oxidized, and HCl is the “agent” that is causing the Zn to be oxidized. #4 indicates that the student is thinking that the Zn+2in ZnCl2 is undergoing r ...
... Comment to Instructor: Correct answer is 3. HCl. Since the oxidation number of H is decreasing from +1 to 0, it is undergoing reduction. Zn is being oxidized, and HCl is the “agent” that is causing the Zn to be oxidized. #4 indicates that the student is thinking that the Zn+2in ZnCl2 is undergoing r ...
File
... Further oxidation of Y to Z occurs in the atmosphere. In this further oxidation, 1 mol of Y reacts with 0.5 mol of gaseous oxygen molecules. X could be either nitrogen or sulfur. Which statements about X, Y and Z can be correct? ...
... Further oxidation of Y to Z occurs in the atmosphere. In this further oxidation, 1 mol of Y reacts with 0.5 mol of gaseous oxygen molecules. X could be either nitrogen or sulfur. Which statements about X, Y and Z can be correct? ...
star test review
... (c) potential energy of the reactants (d) potential energy of the products 8) Which type of bond is formed when an atom of potassium transfers an electron to a bromine atom? 4) Given the reaction at equilibrium: X + Y 2Z + heat The concentration of the product could be increased by (a) adding a ca ...
... (c) potential energy of the reactants (d) potential energy of the products 8) Which type of bond is formed when an atom of potassium transfers an electron to a bromine atom? 4) Given the reaction at equilibrium: X + Y 2Z + heat The concentration of the product could be increased by (a) adding a ca ...
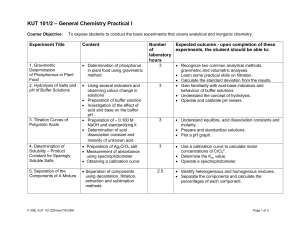
KUT 101/2 – General Chemistry Practical I
... • Recognise coordination compounds, wherein the metal is a Lewis acid and the atoms or molecules joined to the metal are Lewis base or ligands. • Calculate the percentage yield. ...
... • Recognise coordination compounds, wherein the metal is a Lewis acid and the atoms or molecules joined to the metal are Lewis base or ligands. • Calculate the percentage yield. ...
Unit 6 Naming Binary Compounds
... in multiple compounds until the very end; they might take care of themselves. ...
... in multiple compounds until the very end; they might take care of themselves. ...
From (2)
... cooper oxide dissolves slower than metal. This mechanism is incorrect then another mechanism must be found Reactions always take place in steps. The slowest step determines the kinetics of whole process, which Is called rate-determining step to understand the mechanism reaction ...
... cooper oxide dissolves slower than metal. This mechanism is incorrect then another mechanism must be found Reactions always take place in steps. The slowest step determines the kinetics of whole process, which Is called rate-determining step to understand the mechanism reaction ...
C6_rev - boswellsrcd
... (eg could get too hot if exothermic; gas could be produced to quickly and pressure build up) If it is too slow, then product would be made too slowly, and yield low, so profit too low. (economic factors) ...
... (eg could get too hot if exothermic; gas could be produced to quickly and pressure build up) If it is too slow, then product would be made too slowly, and yield low, so profit too low. (economic factors) ...
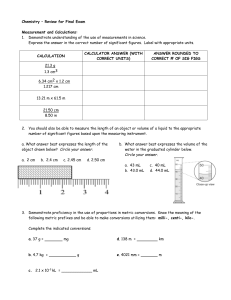
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2006-2007
... a) What is the specific heat of a metal that releases 2500 J of energy. The metal has a mass of 25 g and had a temperature change of 5C. b) How much heat is released when iron is dropped in a beaker of water. The mass of the metal was 43 g and the initial temperature of the metal was 78 C. The water ...
... a) What is the specific heat of a metal that releases 2500 J of energy. The metal has a mass of 25 g and had a temperature change of 5C. b) How much heat is released when iron is dropped in a beaker of water. The mass of the metal was 43 g and the initial temperature of the metal was 78 C. The water ...
SAMPLE EXAM #2
... 15. According to the kinetic molecular theory for gases, particles of a gas a. are very large particles. b. are very far apart. c. lose their valence electrons. d. move slowly. e. decrease kinetic energy as temperature increases. 16. Which relationship is INCORRECT? a. as the temperature of a gas in ...
... 15. According to the kinetic molecular theory for gases, particles of a gas a. are very large particles. b. are very far apart. c. lose their valence electrons. d. move slowly. e. decrease kinetic energy as temperature increases. 16. Which relationship is INCORRECT? a. as the temperature of a gas in ...
2009
... 1 Check that the answer sheet provided is for Chemistry Higher (Section A). 2 For this section of the examination you must use an HB pencil and, where necessary, an eraser. 3 Check that the answer sheet you have been given has your name, date of birth, SCN (Scottish Candidate Number) and Centre Name ...
... 1 Check that the answer sheet provided is for Chemistry Higher (Section A). 2 For this section of the examination you must use an HB pencil and, where necessary, an eraser. 3 Check that the answer sheet you have been given has your name, date of birth, SCN (Scottish Candidate Number) and Centre Name ...
Are You suprised ?
... A) Adding Cl2 will increase heat. B) The equilibrium will move to the left when we remove Cl2. C) Increasing the pressure has no effect on this system. D) Adding catalyst will cool the system. ...
... A) Adding Cl2 will increase heat. B) The equilibrium will move to the left when we remove Cl2. C) Increasing the pressure has no effect on this system. D) Adding catalyst will cool the system. ...
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE
... 40. describe the process of osmosis and its effect on pressure and concentration. 41. differentiate between organic and inorganic compounds. 42. name alkenes and alkynes and draw their structures. 43. identify and name isomers. 44. name and describe cyclic compounds.. 45. recognize compounds contain ...
... 40. describe the process of osmosis and its effect on pressure and concentration. 41. differentiate between organic and inorganic compounds. 42. name alkenes and alkynes and draw their structures. 43. identify and name isomers. 44. name and describe cyclic compounds.. 45. recognize compounds contain ...
File
... D. Venting some CO2 gas from the flask 111. In a sealed bottle that is half full of water, equilibrium will be attained when water molecules A. Cease to evaporate B. Begin to condense C. Are equal in number for both the liquid and the gas phase D. Evaporate and condense at equal rates 112. At equili ...
... D. Venting some CO2 gas from the flask 111. In a sealed bottle that is half full of water, equilibrium will be attained when water molecules A. Cease to evaporate B. Begin to condense C. Are equal in number for both the liquid and the gas phase D. Evaporate and condense at equal rates 112. At equili ...