Organic Chemistry I: Contents
... (Ionic & covalent bonds) -Ionic bond results from transfer of electrons from one atom to another. - Ionic bond is formed when electronegativity difference between two atoms is larger than 1.7 - A covalent bond results from the sharing of a pair of electrons by two atoms. - Carbon forms covalent bond ...
... (Ionic & covalent bonds) -Ionic bond results from transfer of electrons from one atom to another. - Ionic bond is formed when electronegativity difference between two atoms is larger than 1.7 - A covalent bond results from the sharing of a pair of electrons by two atoms. - Carbon forms covalent bond ...
FXM Rev 1 Key - Grande Cache Community High School
... Bohr model This model went beyond the planetary atomic model by placing electrons in definite energy levels. neutron This is a subatomic particle found in the nucleus that is uncharged. pH scale This is a scale that places acids and base substances in a range for 0 to 14. mass number This is the sum ...
... Bohr model This model went beyond the planetary atomic model by placing electrons in definite energy levels. neutron This is a subatomic particle found in the nucleus that is uncharged. pH scale This is a scale that places acids and base substances in a range for 0 to 14. mass number This is the sum ...
Building an Atom
... For this extra credit project you must build a 3D model of the atom Sulfur- 33. You can use whatever type of supplies you can think of, as long as it looks semi-professional. (Sloppy or incorrect models will receive little to no credit, don’t waste your time). Your model of the atom MUST include all ...
... For this extra credit project you must build a 3D model of the atom Sulfur- 33. You can use whatever type of supplies you can think of, as long as it looks semi-professional. (Sloppy or incorrect models will receive little to no credit, don’t waste your time). Your model of the atom MUST include all ...
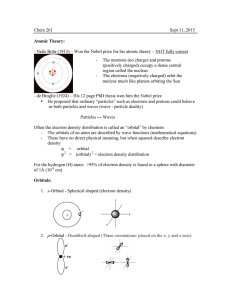
History of atom
... indivisible component of matter was first proposed by early Indian and Greek philosophers. In the 17th and 18th centuries, chemists provided a physical basis for this idea by showing that certain substances could not be further broken down by chemical methods. During the late 19th and early 20th cen ...
... indivisible component of matter was first proposed by early Indian and Greek philosophers. In the 17th and 18th centuries, chemists provided a physical basis for this idea by showing that certain substances could not be further broken down by chemical methods. During the late 19th and early 20th cen ...
Intro Notes - Mrs. Gionta
... • Unequal sharing of electrons causes a partial positive or negative charge for each atom or molecule © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • Unequal sharing of electrons causes a partial positive or negative charge for each atom or molecule © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Nature of Molecules and Water
... • Atom’s affinity for electrons − O and N are more electronegative than C and H • Differences in electronegativity dictate how electrons are distributed in covalent bonds – Nonpolar covalent bonds = equal sharing of electrons – Polar covalent bonds = unequal sharing of electrons • Polar molecules ha ...
... • Atom’s affinity for electrons − O and N are more electronegative than C and H • Differences in electronegativity dictate how electrons are distributed in covalent bonds – Nonpolar covalent bonds = equal sharing of electrons – Polar covalent bonds = unequal sharing of electrons • Polar molecules ha ...
Properties of Matter Power Point
... Valence Electron An electron in the outermost energy level of an atom. ...
... Valence Electron An electron in the outermost energy level of an atom. ...
chemistry i - surrattchemistry
... 32. Diamond, graphite, and silicon dioxide all exhibit which type of intermolecular force? a. metallic b. network covalent c. ionic d. hydrogen e. dipole-dipole 33. Which of the following compounds contains polar bonds, yet the molecule itself is nonpolar? B. ...
... 32. Diamond, graphite, and silicon dioxide all exhibit which type of intermolecular force? a. metallic b. network covalent c. ionic d. hydrogen e. dipole-dipole 33. Which of the following compounds contains polar bonds, yet the molecule itself is nonpolar? B. ...
2. Covalent network
... H, Li, Be, B forms stable molecules when they share two electrons Elements Carbon and beyond stable when they are surrounded by eight molecules. Second row elements (C, N, O, and F) should always obey the octet rule B and Be often have fewer than 8 electrons around them - highly reactive molecules S ...
... H, Li, Be, B forms stable molecules when they share two electrons Elements Carbon and beyond stable when they are surrounded by eight molecules. Second row elements (C, N, O, and F) should always obey the octet rule B and Be often have fewer than 8 electrons around them - highly reactive molecules S ...
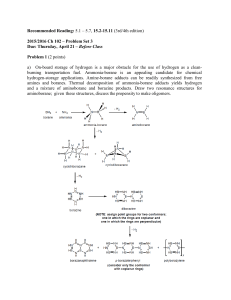
2015/2016 Ch 102 – Problem Set 3 Due: Thursday
... which one is the best), use VSEPR theory to predict the molecular geometry (label expected values of bond angles based on this analysis, i.e. 180 º, ≤ 120 º, etc.), and provide the point group of the resulting molecule (draw it in a reasonable conformation and assume delocalization where appropriate ...
... which one is the best), use VSEPR theory to predict the molecular geometry (label expected values of bond angles based on this analysis, i.e. 180 º, ≤ 120 º, etc.), and provide the point group of the resulting molecule (draw it in a reasonable conformation and assume delocalization where appropriate ...
Chemistry Notes
... hydrogen, helium, lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, neon, sodium, magnesium, aluminum, silicon, phosphorous, sulfur, chlorine, argon, potassium, calcium, iron, copper, zinc, bromine, silver, iodine, gold, lead, mercury, radon. Day 3 99% of the atoms mass in the nucleus T ...
... hydrogen, helium, lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, neon, sodium, magnesium, aluminum, silicon, phosphorous, sulfur, chlorine, argon, potassium, calcium, iron, copper, zinc, bromine, silver, iodine, gold, lead, mercury, radon. Day 3 99% of the atoms mass in the nucleus T ...
Molecular Geometry Why?
... is based on the premise that electrons around a central atom repel each other. Electron domains are areas of high electron density such as bonds (single, double or triple) and lone-pairs of electrons. In simple terms VSEPR means that all electron bonding domains and electron nonbonding domains aroun ...
... is based on the premise that electrons around a central atom repel each other. Electron domains are areas of high electron density such as bonds (single, double or triple) and lone-pairs of electrons. In simple terms VSEPR means that all electron bonding domains and electron nonbonding domains aroun ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... Polyatomic Ions Polyatomic Ions – many atoms with a charge See test packet for a list of common PAI’s Covalently bonded (nonmetals) ...
... Polyatomic Ions Polyatomic Ions – many atoms with a charge See test packet for a list of common PAI’s Covalently bonded (nonmetals) ...
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
... atomic orbitals does not account for a number of fundamental observations of chemistry. To reconcile these and other differences, we turn to molecular orbital theory (MO theory). In MO theory, covalent bonding is described in terms of molecular orbitals, i.e., the combination of atomic orbitals that ...
... atomic orbitals does not account for a number of fundamental observations of chemistry. To reconcile these and other differences, we turn to molecular orbital theory (MO theory). In MO theory, covalent bonding is described in terms of molecular orbitals, i.e., the combination of atomic orbitals that ...
Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory
... Considered a satisfactory method of explaining the electron pair, or covalent bond from a quantum mechanics point of view. According to this theory, a bond forms between two atoms when the following conditions are met. Two atomic orbitals "overlap" ...
... Considered a satisfactory method of explaining the electron pair, or covalent bond from a quantum mechanics point of view. According to this theory, a bond forms between two atoms when the following conditions are met. Two atomic orbitals "overlap" ...
Introduction to Atoms & Bonding
... • Represent the Electron Orbits First Orbit = holds up to 2 electrons Second Orbit = holds up to 8 electrons Third Orbit = holds up to 8 electrons Fourth Orbit = at least 8 electrons ...
... • Represent the Electron Orbits First Orbit = holds up to 2 electrons Second Orbit = holds up to 8 electrons Third Orbit = holds up to 8 electrons Fourth Orbit = at least 8 electrons ...
Chemistry I Honors – Semester Exam Review – Fall 2000
... Matter – Ch. 1 6. Classify the following substances as solid, liquid, gas, or plasma based on their properties. a. flexible volume, high KE, particles can disperse freely. b. flexible volume, very high KE, particles are charged. c. fixed volume, very low KE, orderly particles. d. fixed volume, low K ...
... Matter – Ch. 1 6. Classify the following substances as solid, liquid, gas, or plasma based on their properties. a. flexible volume, high KE, particles can disperse freely. b. flexible volume, very high KE, particles are charged. c. fixed volume, very low KE, orderly particles. d. fixed volume, low K ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
... 11) Ionic bonds are formed when A) atoms share electrons. B) two or more atoms lose electrons at the same time. C) electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another. D) hydrogen forms bonds with negatively charged atoms in the same or different molecule. E) a pair of electrons is shared ...
... 11) Ionic bonds are formed when A) atoms share electrons. B) two or more atoms lose electrons at the same time. C) electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another. D) hydrogen forms bonds with negatively charged atoms in the same or different molecule. E) a pair of electrons is shared ...