1. What are micelles? Give two examples of micellar systems. Sol. A
... distribution in the nucleus is a function of its internal structure and if this is spherical (ie analogous to the symmetry of a 1s hydrogen orbital), it is said to have a corresponding spin angular momentum number of I=1/2, of which examples are 1H, 13C, 15N, 19F, 31P etc. Nuclei which have a non-sp ...
... distribution in the nucleus is a function of its internal structure and if this is spherical (ie analogous to the symmetry of a 1s hydrogen orbital), it is said to have a corresponding spin angular momentum number of I=1/2, of which examples are 1H, 13C, 15N, 19F, 31P etc. Nuclei which have a non-sp ...
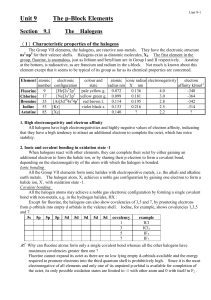
Unit 9 The p-Block Elements
... (a) Describe and explain the trends in melting points and boiling points of the halogen group. Melting points and boiling points increase down the group due to the increase in van der Waals forces. Van der Waals forces increase as the number of electrons of a molecule increases. The greater the numb ...
... (a) Describe and explain the trends in melting points and boiling points of the halogen group. Melting points and boiling points increase down the group due to the increase in van der Waals forces. Van der Waals forces increase as the number of electrons of a molecule increases. The greater the numb ...
FREE Sample Here
... 78) How would the lack of a cofactor for an enzyme affect that enzyme's function? A) The enzyme would cease to function after reaching a maximum rate. B) The enzyme would function more slowly. C) The enzyme's function would not be altered. D) The enzyme would not be able to function. E) The enzyme w ...
... 78) How would the lack of a cofactor for an enzyme affect that enzyme's function? A) The enzyme would cease to function after reaching a maximum rate. B) The enzyme would function more slowly. C) The enzyme's function would not be altered. D) The enzyme would not be able to function. E) The enzyme w ...
CHEM 1211K Test IV MULTIPLE CHOICE. (3 points each) 1) The
... among different I2 molecules in the solid? A) London dispersion forces B) ionic-dipole interactions C) dipole-dipole attractions D) dipole-dipole rejections E) covalent-ionic interactions 22) The heat of fusion of water is 6.01 kJ/mol. The heat capacity of liquid water is 75.2 J/mol(K) the conversio ...
... among different I2 molecules in the solid? A) London dispersion forces B) ionic-dipole interactions C) dipole-dipole attractions D) dipole-dipole rejections E) covalent-ionic interactions 22) The heat of fusion of water is 6.01 kJ/mol. The heat capacity of liquid water is 75.2 J/mol(K) the conversio ...
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
... • The 2p orbitals in C are at right angles to each other, the 1s orbital in H is spherical. • According to Pauling’s theory of orbital hybridization, a new set of orbitals called hybrid orbitals can be created by combining the appropriate # of s, p, d and f orbitals. • This combination results in hy ...
... • The 2p orbitals in C are at right angles to each other, the 1s orbital in H is spherical. • According to Pauling’s theory of orbital hybridization, a new set of orbitals called hybrid orbitals can be created by combining the appropriate # of s, p, d and f orbitals. • This combination results in hy ...
Concept Reviews Answer sheet Section: matter and Energy 1. a
... 3. Coffee at 38°C has more kinetic energy than coffee at 34°C. Although there is less tea than coffee, the temperature of the tea is greater, so the tea has more average kinetic energy than the coffee. 4. The temperature, and therefore the kinetic energy of the particles in 0.5 L of coffee and 0.25 ...
... 3. Coffee at 38°C has more kinetic energy than coffee at 34°C. Although there is less tea than coffee, the temperature of the tea is greater, so the tea has more average kinetic energy than the coffee. 4. The temperature, and therefore the kinetic energy of the particles in 0.5 L of coffee and 0.25 ...
Part a
... (a) The slightly positive ends (+) of the water molecules become aligned with the slightly negative ends (–) of other water molecules. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... (a) The slightly positive ends (+) of the water molecules become aligned with the slightly negative ends (–) of other water molecules. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Chapter 8 (2)
... Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion – minimizes the repulsion of shared and unshared pairs of electrons around the central atom. The shape of a molecule determines many of its physical and ...
... Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion – minimizes the repulsion of shared and unshared pairs of electrons around the central atom. The shape of a molecule determines many of its physical and ...
Writing formulas and naming ionic bonds
... What type of nuclear reaction produces electricity? Fission When a chemical reaction occurs, the mass of the reactants ___ the mass of the products. Equals If the mass of the reactants is 10 g, then the mass of the products is ___ g. ...
... What type of nuclear reaction produces electricity? Fission When a chemical reaction occurs, the mass of the reactants ___ the mass of the products. Equals If the mass of the reactants is 10 g, then the mass of the products is ___ g. ...
Name Period ______ Unit 4 Study Guide A common isotope of iron
... The lowest energy level can hold ________ electrons. A repeating pattern across a row of the periodic table is called…. The noble gases such as helium and xenon do not form chemical bonds with other elements because they: Most metals are ________________ (choose one: ductile, brittle, poor conductor ...
... The lowest energy level can hold ________ electrons. A repeating pattern across a row of the periodic table is called…. The noble gases such as helium and xenon do not form chemical bonds with other elements because they: Most metals are ________________ (choose one: ductile, brittle, poor conductor ...
Chemistry
... The Examination consists of one three-hour paper. The paper will be divided into three sections: Section A will contain between eight and ten compulsory questions of the fill-in type requiring short answers; Section B will consist of between four and sixcompulsory structured questions; Section C wil ...
... The Examination consists of one three-hour paper. The paper will be divided into three sections: Section A will contain between eight and ten compulsory questions of the fill-in type requiring short answers; Section B will consist of between four and sixcompulsory structured questions; Section C wil ...
Structure and Bonding
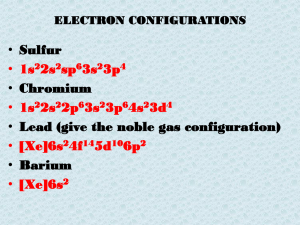
... A group of an atom’s electrons with the same principal quantum number First shell contains one s orbital, denoted 1s, which holds only two electrons Second shell contains four orbitals, one s orbital (2s) and three p orbitals (2p), which hold a total of eight electrons Third shell contains nine orbi ...
... A group of an atom’s electrons with the same principal quantum number First shell contains one s orbital, denoted 1s, which holds only two electrons Second shell contains four orbitals, one s orbital (2s) and three p orbitals (2p), which hold a total of eight electrons Third shell contains nine orbi ...
With Atoms
... – An attractive force that arises between two atoms when their electrons interact ...
... – An attractive force that arises between two atoms when their electrons interact ...
Chem Basics
... Model 2: Although an atom is defined by it’s protons, it’s the electrons that determine how it will behave. In a neutral atom (no charge), the number of protons and electrons is equal. The electrons move within ‘shells’ or ‘orbits’ about the nucleus; those in the outermost shell are called valence e ...
... Model 2: Although an atom is defined by it’s protons, it’s the electrons that determine how it will behave. In a neutral atom (no charge), the number of protons and electrons is equal. The electrons move within ‘shells’ or ‘orbits’ about the nucleus; those in the outermost shell are called valence e ...
4. bonding - New Hartford Central Schools
... Elements with more than one positive oxidation number (Transition Metals) (This is called the Stock System) When the oxidation number varies we us a Roman numeral in parentheses to indicate the charge. Roman number is used for the positive element only!!! ...
... Elements with more than one positive oxidation number (Transition Metals) (This is called the Stock System) When the oxidation number varies we us a Roman numeral in parentheses to indicate the charge. Roman number is used for the positive element only!!! ...
Quiz Show Review of Simple Bonding Theory
... 2 sigma, 2 pi 3 sigma, 1 pi 2 sigma, 1 pi The CH bond is a sigma bond, one of the bonds from the CN triple bond is a sigma bond and the other two are pi bonds ...
... 2 sigma, 2 pi 3 sigma, 1 pi 2 sigma, 1 pi The CH bond is a sigma bond, one of the bonds from the CN triple bond is a sigma bond and the other two are pi bonds ...
CHEMISTRY IM 06 SYLLABUS 1
... The Examination consists of one three-hour paper. The paper will be divided into three sections: Section A will contain between eight and ten compulsory questions of the fill-in type requiring short answers; Section B will consist of between four and sixcompulsory structured questions; Section C wil ...
... The Examination consists of one three-hour paper. The paper will be divided into three sections: Section A will contain between eight and ten compulsory questions of the fill-in type requiring short answers; Section B will consist of between four and sixcompulsory structured questions; Section C wil ...
Test #5 Review
... Why do elements in the same family behave the same? They all have the same number of valence electrons. ...
... Why do elements in the same family behave the same? They all have the same number of valence electrons. ...
II.I Corhon compounds lI.2 Hydrocorhons
... tetrahedron. The tetrahedral angle of 109.5degreesbetween u.tyftto hybrid orbitals minimizes unfavorable interactions among the orbitals. Now the four sp3orbitals of carbon, each of which has one electron, can overlap with the 1sorbitals of four hydrogen atoms, each with one electron. The product is ...
... tetrahedron. The tetrahedral angle of 109.5degreesbetween u.tyftto hybrid orbitals minimizes unfavorable interactions among the orbitals. Now the four sp3orbitals of carbon, each of which has one electron, can overlap with the 1sorbitals of four hydrogen atoms, each with one electron. The product is ...