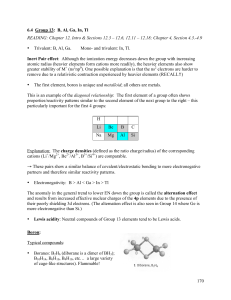
6.5 Main Group
... used to add it to their wine. Some historians claim that this habit contributed to the collapse of their empire – they were all a little dumber than they should have been … ...
... used to add it to their wine. Some historians claim that this habit contributed to the collapse of their empire – they were all a little dumber than they should have been … ...
CHEMISTRY IM 06 SYLLABUS
... Chemistry of some common functional groups: alcohols; ethers; aldehydes and ketones; carboxylic acids; amines. The treatment should be an outline survey and should include the following topics (mechanisms will not be tested): (a) alcohols: oxidation, dehydration to alkenes and ethers, esterification ...
... Chemistry of some common functional groups: alcohols; ethers; aldehydes and ketones; carboxylic acids; amines. The treatment should be an outline survey and should include the following topics (mechanisms will not be tested): (a) alcohols: oxidation, dehydration to alkenes and ethers, esterification ...
CHEMISTRY IM 06 SYLLABUS
... Chemistry of some common functional groups: alcohols; ethers; aldehydes and ketones; carboxylic acids; amines. The treatment should be an outline survey and should include the following topics (mechanisms will not be tested): (a) alcohols: oxidation, dehydration to alkenes and ethers, esterification ...
... Chemistry of some common functional groups: alcohols; ethers; aldehydes and ketones; carboxylic acids; amines. The treatment should be an outline survey and should include the following topics (mechanisms will not be tested): (a) alcohols: oxidation, dehydration to alkenes and ethers, esterification ...
solutions
... 5. Consider the MO's in O2 and N2 from which an electron is removed when these molecules are ionized. Then compare the energy of these MO's to that of the AO's on O and N, from which the electron is removed when these atoms are ionized. For O2 , with 12 valence electrons, using the appropriate sche ...
... 5. Consider the MO's in O2 and N2 from which an electron is removed when these molecules are ionized. Then compare the energy of these MO's to that of the AO's on O and N, from which the electron is removed when these atoms are ionized. For O2 , with 12 valence electrons, using the appropriate sche ...
HW 2 Key
... graph paper. You must label each set in the upper left hand corner with your name, the date and the chapter. Problems must be identified by number and all work must be shown with answers boxed. Be sure your handwriting is legible. An example is posted in the ‘course basics’ section of our Moodle pag ...
... graph paper. You must label each set in the upper left hand corner with your name, the date and the chapter. Problems must be identified by number and all work must be shown with answers boxed. Be sure your handwriting is legible. An example is posted in the ‘course basics’ section of our Moodle pag ...
form revision a
... Check your key area statements. If not green you need to do more work! Knowledge of the structure of the periodic table, groups and periods. All matter is made of atoms. When a substance contains only one kind of atom it is known as an element. Atoms contain protons, neutrons and electrons each with ...
... Check your key area statements. If not green you need to do more work! Knowledge of the structure of the periodic table, groups and periods. All matter is made of atoms. When a substance contains only one kind of atom it is known as an element. Atoms contain protons, neutrons and electrons each with ...
Name - Net Start Class
... c. Ex. 2 Mass d. Ex. 3 Volume 2. Define ‘intensive properties and give 3 examples. a. Definition - a property that does not depend on how much matter is being considered. b. Ex. 1 Density c. Ex. 2 Temperature d. Ex. 3 Freezing Point 3. Define ‘valance electron’ and tell how many valance electrons ea ...
... c. Ex. 2 Mass d. Ex. 3 Volume 2. Define ‘intensive properties and give 3 examples. a. Definition - a property that does not depend on how much matter is being considered. b. Ex. 1 Density c. Ex. 2 Temperature d. Ex. 3 Freezing Point 3. Define ‘valance electron’ and tell how many valance electrons ea ...
Document
... Figure 1.11: Formaldehyde H—C—H and H—C—O angles are close to 120° trigonal planar geometry ...
... Figure 1.11: Formaldehyde H—C—H and H—C—O angles are close to 120° trigonal planar geometry ...
Summary from Organic Chemistry Packet:
... – Alkenes: C=C double bonds as well as single bonds – Alkynes: carbon-carbon triple bonds as well as single bonds. – Aromatic: hydrocarbons containing benzene rings. ...
... – Alkenes: C=C double bonds as well as single bonds – Alkynes: carbon-carbon triple bonds as well as single bonds. – Aromatic: hydrocarbons containing benzene rings. ...
Atoms and Molecules
... Key Concepts • Matter is made of atoms • Atoms are made of protons, neutrons and electrons • Elements are determined by the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom ...
... Key Concepts • Matter is made of atoms • Atoms are made of protons, neutrons and electrons • Elements are determined by the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Life Atoms
... • An atom whose outer electron shell is full cannot interact with other atoms and is called inert. • Atoms is reactive when its outer electron shell is only partially full and it can react with other atoms. ...
... • An atom whose outer electron shell is full cannot interact with other atoms and is called inert. • Atoms is reactive when its outer electron shell is only partially full and it can react with other atoms. ...
ap chemistry chapter 8 bonding
... suggests that electrons are delocalized. That is, they are not associated with a particular atom in a molecule. ...
... suggests that electrons are delocalized. That is, they are not associated with a particular atom in a molecule. ...
2-1 Chemistry of life
... When we total the monetary value of the elements in our bodies and the value of the average person's skin, we arrive at a net worth of $4.50 Our most valuable asset is our skin. The method the Imperial State Institute for Nutrition at Tokyo developed for measuring the amount of a person's skin is to ...
... When we total the monetary value of the elements in our bodies and the value of the average person's skin, we arrive at a net worth of $4.50 Our most valuable asset is our skin. The method the Imperial State Institute for Nutrition at Tokyo developed for measuring the amount of a person's skin is to ...
ViewpointAPBiology
... Atoms combine by chemical bonding to form molecules Weak chemical bonds play important roles in chemistry of life A molecule’s biological function is related to its ...
... Atoms combine by chemical bonding to form molecules Weak chemical bonds play important roles in chemistry of life A molecule’s biological function is related to its ...
Ch 4 Review PowerPoint ch4jeopardy_review1
... periodic table forms no stable compounds? • What are Noble Gases? ...
... periodic table forms no stable compounds? • What are Noble Gases? ...
semester 1 study guide 2015 - slater science
... o Write electron configurations, including noble gas abbreviations (no exceptions to the general rules). Included here are extended arrangements showing electrons in orbitals. o Identify s, p, d, and f blocks on Periodic Table. o Identify an element based on its electron configuration. ( be able to ...
... o Write electron configurations, including noble gas abbreviations (no exceptions to the general rules). Included here are extended arrangements showing electrons in orbitals. o Identify s, p, d, and f blocks on Periodic Table. o Identify an element based on its electron configuration. ( be able to ...
EOC Review - Dorman Freshman Campus
... the pollution and other gases emitted from the environment which is surrounded by dust and dirt in clouds….the dust and dirt fall as rain bringing with it the pollution which is ...
... the pollution and other gases emitted from the environment which is surrounded by dust and dirt in clouds….the dust and dirt fall as rain bringing with it the pollution which is ...
Chapter 10
... • Make predictions about O2 molecule and ions • Which has the strongest bond: O2,O2+, or O2-? ...
... • Make predictions about O2 molecule and ions • Which has the strongest bond: O2,O2+, or O2-? ...
Valence electrons and Lewis Dot Structures
... A _______________ can be a single atom, 2 or more atoms of the same element, or a group of atoms of different elements that have combined to form a compound. ...
... A _______________ can be a single atom, 2 or more atoms of the same element, or a group of atoms of different elements that have combined to form a compound. ...
Name: Date: Chemistry 1 – Midterm Review Sheet Unit 1 – Scientific
... 6. How many lone pairs of electrons are in the Lewis structure for ammonia, NH3? a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3 e) 4 7. Choose the correct Lewis structure for the OH- ion. a) c) b) ...
... 6. How many lone pairs of electrons are in the Lewis structure for ammonia, NH3? a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3 e) 4 7. Choose the correct Lewis structure for the OH- ion. a) c) b) ...
Electron Arrangement
... bonding): Hydrogen (H2), Oxygen (O2), Nitrogen (N2) and all of the Group 7 elements (Halogens). In molecular compounds When non-metal atoms join! Eg. Water (H2O), ammonia (NH3), Methane (CH4). These have specific shapes because of the covalent bonds. Covalent molecular substances tend to have low me ...
... bonding): Hydrogen (H2), Oxygen (O2), Nitrogen (N2) and all of the Group 7 elements (Halogens). In molecular compounds When non-metal atoms join! Eg. Water (H2O), ammonia (NH3), Methane (CH4). These have specific shapes because of the covalent bonds. Covalent molecular substances tend to have low me ...
Properties of Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
... Atomic Masses: What is the difference between the mass number for Carbon–14 and carbon’s atomic mass of 12.011 amu? ...
... Atomic Masses: What is the difference between the mass number for Carbon–14 and carbon’s atomic mass of 12.011 amu? ...