A COMPUTATIONAL STUDY OF -SCN
... b. Determine how many unpaired electrons are present on the hydrogen atom. Enter that value in the Unpaired Electrons field of the Calculations window. c. Click Submit to exit Calculations window and start the calculation. 10. When the Save As window appears name the file and click on Save. Click OK ...
... b. Determine how many unpaired electrons are present on the hydrogen atom. Enter that value in the Unpaired Electrons field of the Calculations window. c. Click Submit to exit Calculations window and start the calculation. 10. When the Save As window appears name the file and click on Save. Click OK ...
A COMPUTATIONAL STUDY OF -SCN
... b. Determine how many unpaired electrons are present on the hydrogen atom. Enter that value in the Unpaired Electrons field of the Calculations window. c. Click Submit to exit Calculations window and start the calculation. 10. When the Save As window appears name the file and click on Save. Click OK ...
... b. Determine how many unpaired electrons are present on the hydrogen atom. Enter that value in the Unpaired Electrons field of the Calculations window. c. Click Submit to exit Calculations window and start the calculation. 10. When the Save As window appears name the file and click on Save. Click OK ...
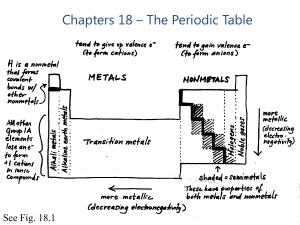
Chapters 18 – The Periodic Table
... Common Features: ns2p5 electron configuration (n = 2 to 6) All are non-metals Properties vary smoothly down the group, except for unexpectedly low E.A. of fluorine and small bond energy of F2 Highly reactive: not found as free elements in nature, but rather as halide ions (X-) in minerals an ...
... Common Features: ns2p5 electron configuration (n = 2 to 6) All are non-metals Properties vary smoothly down the group, except for unexpectedly low E.A. of fluorine and small bond energy of F2 Highly reactive: not found as free elements in nature, but rather as halide ions (X-) in minerals an ...
chapter 12: chemical bonding
... octet rule (rule of eight): atoms bond in a way that each atom has eight electrons (an octet) in its outer shell, except hydrogen which only needs 2 electrons – Atoms will bond to have the same # of valance electrons as the Noble gas in its period. GUIDELINES for Lewis Structures (or Electron Dot Di ...
... octet rule (rule of eight): atoms bond in a way that each atom has eight electrons (an octet) in its outer shell, except hydrogen which only needs 2 electrons – Atoms will bond to have the same # of valance electrons as the Noble gas in its period. GUIDELINES for Lewis Structures (or Electron Dot Di ...
Bonding and Nomenclature
... Energy is consumed Go from LOW energy (happy atoms) to HGHER energy (unhappy atoms) Ripping two atoms apart takes energy Energy is CONSUMED or needed as an ingredient to fuel the process A + energy → B + C ...
... Energy is consumed Go from LOW energy (happy atoms) to HGHER energy (unhappy atoms) Ripping two atoms apart takes energy Energy is CONSUMED or needed as an ingredient to fuel the process A + energy → B + C ...
power point notes
... result of differences in the size of tiny uncuttable particles. b. During the 4th century B.C. Artistole said NO WAY! He thought that only 4 elements actually exist: water, air, fire and earth ...
... result of differences in the size of tiny uncuttable particles. b. During the 4th century B.C. Artistole said NO WAY! He thought that only 4 elements actually exist: water, air, fire and earth ...
CHAPTER 2 THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 2.1 Chemical Elements
... between oppositely charged ions. It is formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another atom. For example, sodium loses an electron, forming a positive charge, and chlorine gains an electron to give it a negative charge. The ionic bond that forms between them results in the formation o ...
... between oppositely charged ions. It is formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another atom. For example, sodium loses an electron, forming a positive charge, and chlorine gains an electron to give it a negative charge. The ionic bond that forms between them results in the formation o ...
Fall Final 2009
... 20. Write the ground-state electron configuration of a Ni2+ ion. The Ni2+ ion is: a. diamagnetic b. paramagnetic with 1 unpaired electron c. paramagnetic with 2 unpaired electrons d. paramagnetic with 3 unpaired electrons e. paramagnetic with 4 unpaired electrons ...
... 20. Write the ground-state electron configuration of a Ni2+ ion. The Ni2+ ion is: a. diamagnetic b. paramagnetic with 1 unpaired electron c. paramagnetic with 2 unpaired electrons d. paramagnetic with 3 unpaired electrons e. paramagnetic with 4 unpaired electrons ...
PPT - George Mason University
... Lattice Energy – The atomic radius increases as you move down a group. Since the square of the distance is inversely proportional to the force of attraction, lattice energy decreases as the atomic radius increases ...
... Lattice Energy – The atomic radius increases as you move down a group. Since the square of the distance is inversely proportional to the force of attraction, lattice energy decreases as the atomic radius increases ...
Thursday, March 27, 2008
... Which statement is true about the properties of the elements in any one period of the Periodic Table? 1. They are determined by the number of neutrons. 2. They are determined by the number of electrons in the first shell. ...
... Which statement is true about the properties of the elements in any one period of the Periodic Table? 1. They are determined by the number of neutrons. 2. They are determined by the number of electrons in the first shell. ...
History of Atom Notes
... J.J. Thomson (England, late 1890s) Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) expts.: --Cathode ray was attracted to positive magnet **Atoms have negative particles...ELECTRONS --Since atoms are neutral, must also have positive particles...PROTONS ...
... J.J. Thomson (England, late 1890s) Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) expts.: --Cathode ray was attracted to positive magnet **Atoms have negative particles...ELECTRONS --Since atoms are neutral, must also have positive particles...PROTONS ...
Chapter 3 Power Point
... known as chemical bonding The atoms combine according to certain rules – Determined by the number of electrons that surround the atomic nucleus Each energy level in an atom can hold only a certain number of electrons – 1st – 2 electrons – 2nd – 8 electrons – 3rd – 8 electrons When the outermost ener ...
... known as chemical bonding The atoms combine according to certain rules – Determined by the number of electrons that surround the atomic nucleus Each energy level in an atom can hold only a certain number of electrons – 1st – 2 electrons – 2nd – 8 electrons – 3rd – 8 electrons When the outermost ener ...
Physical Science CP Seton Hall Preparatory School Mr. Greene
... Atomic Mass Units (AMU) Isotopes Calculation of the number of neutrons/protons contained in an isotope Ions; cations vs. anions Periodic Table: Period Group Properties of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids Periodic trends; atomic radius, electronegativity, and metallic character Major groups; alkali ...
... Atomic Mass Units (AMU) Isotopes Calculation of the number of neutrons/protons contained in an isotope Ions; cations vs. anions Periodic Table: Period Group Properties of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids Periodic trends; atomic radius, electronegativity, and metallic character Major groups; alkali ...
Year End Chemistry Review
... 4. Density as measured by water displacement: Find the density of a metal if its mass = 5.0 grams, the initial volume of water without metal = 10.0 mL and the final volume of water with metal = 12.5 mL. 5. Significant figures: How many significant figures are in each of the following: a) 0.003 g b) ...
... 4. Density as measured by water displacement: Find the density of a metal if its mass = 5.0 grams, the initial volume of water without metal = 10.0 mL and the final volume of water with metal = 12.5 mL. 5. Significant figures: How many significant figures are in each of the following: a) 0.003 g b) ...
Semester 1 Study Guide – Chemistry
... meaning that only certain discrete energy levels are allowed. ...
... meaning that only certain discrete energy levels are allowed. ...
(EXAMPLES: DNA and RNA) NUCLEIC ACIDS contain atoms of
... contain ___________ hydrogens these are more "heart-healthy"! food scientists can use a process called "hydrogenation" to artificially add hydrogens so that these molecules are more solid such as corn oil margarine, which makes them less healthy. ...
... contain ___________ hydrogens these are more "heart-healthy"! food scientists can use a process called "hydrogenation" to artificially add hydrogens so that these molecules are more solid such as corn oil margarine, which makes them less healthy. ...
Lewis Structures - Moore Public Schools
... The double bonded O atom has 6 electrons: 4 non-bonding and 2 bonding (one electron for each bond). Since O should have 6 electrons, the formal charge is 0. The two singly bonded O atoms each have 7 electrons: 6 non-bonding and 1 bonding electron. Since O should have 6 electrons, and there is one ex ...
... The double bonded O atom has 6 electrons: 4 non-bonding and 2 bonding (one electron for each bond). Since O should have 6 electrons, the formal charge is 0. The two singly bonded O atoms each have 7 electrons: 6 non-bonding and 1 bonding electron. Since O should have 6 electrons, and there is one ex ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... 2. Conduct heat and electricity. 3. Malleable (can be shaped) and ductile (pulled into wires). 4. Form cations (lose electrons to form positive ions). Nonmetals are on the right side of the periodic table (with the exception of H). Found in all three states. 1. Poor conductors of heat and electricit ...
... 2. Conduct heat and electricity. 3. Malleable (can be shaped) and ductile (pulled into wires). 4. Form cations (lose electrons to form positive ions). Nonmetals are on the right side of the periodic table (with the exception of H). Found in all three states. 1. Poor conductors of heat and electricit ...
Name: Midterm Review (Part II) Fill in the blanks (Chapter 6.1 – 6.3
... How do nonmetals obey the octet rule when reacting to form ionic compounds? How do nonmetals obey the octet rule when reacting to form covalent compounds? How many valence electrons there are in S-2 ion? S-2 anion has a larger/smaller radius than a neutral Sulfur (S) atom. A covalent bond is a bond ...
... How do nonmetals obey the octet rule when reacting to form ionic compounds? How do nonmetals obey the octet rule when reacting to form covalent compounds? How many valence electrons there are in S-2 ion? S-2 anion has a larger/smaller radius than a neutral Sulfur (S) atom. A covalent bond is a bond ...