Need
... electron arrangement in elements, compounds and ions. Electrons in Lewis structures are arranged by their orbitals. The first two electrons are placed together in the “s” orbital. The remaining electrons are spread among the 3 “p” orbitals. The “s” orbital must be filled first. Then each “p” ...
... electron arrangement in elements, compounds and ions. Electrons in Lewis structures are arranged by their orbitals. The first two electrons are placed together in the “s” orbital. The remaining electrons are spread among the 3 “p” orbitals. The “s” orbital must be filled first. Then each “p” ...
Unit 3 Test - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... ___ Combustibility is the ability of a substance to react with acids ___ Sugar disappearing in water is an example of a solution ___ Raisins in Raisin Bran are an example of a solution ___ Lighting a test tube of acetylene gas is an example of a reaction with acid ___ Lighting a test tube of acetyle ...
... ___ Combustibility is the ability of a substance to react with acids ___ Sugar disappearing in water is an example of a solution ___ Raisins in Raisin Bran are an example of a solution ___ Lighting a test tube of acetylene gas is an example of a reaction with acid ___ Lighting a test tube of acetyle ...
Atoms and Elements
... putting electrons into orbitals that have the same energy as each other. Put one electron into each orbital before pairing them up. Whichever way the first arrow (electron) points, the others must point the same way until they pair up, then they point in opposite directions. ...
... putting electrons into orbitals that have the same energy as each other. Put one electron into each orbital before pairing them up. Whichever way the first arrow (electron) points, the others must point the same way until they pair up, then they point in opposite directions. ...
(null): 110.ReactionsIntro
... 2) Old bonds are broken and new bonds are made … 3) So, new substance must be made (chem change) 4) Ex: Zn + HCl ZnCl2 + H2 a) label each chemical with bond type (metallic, covalent, ionic, covalent) b) Have to break e.g. metallic zinc bond so Cl can steal an electron and form ionic bond c) Zn los ...
... 2) Old bonds are broken and new bonds are made … 3) So, new substance must be made (chem change) 4) Ex: Zn + HCl ZnCl2 + H2 a) label each chemical with bond type (metallic, covalent, ionic, covalent) b) Have to break e.g. metallic zinc bond so Cl can steal an electron and form ionic bond c) Zn los ...
Unit 3: Bonding and Nomenclature Content Outline: Chemical
... For example: H20 (water) or O2 (Oxygen gas) or C6H12O6 (Glucose) B. This term is usually used with molecules that are bound together using covalent bonds. C. These molecules can possess single bonds (-), double bonds (=), or even triple bonds (Ξ). 1. The purpose of “creating” the bonds is to achieve ...
... For example: H20 (water) or O2 (Oxygen gas) or C6H12O6 (Glucose) B. This term is usually used with molecules that are bound together using covalent bonds. C. These molecules can possess single bonds (-), double bonds (=), or even triple bonds (Ξ). 1. The purpose of “creating” the bonds is to achieve ...
Chapter 4 Review, pages 262–267
... Carbon also forms a covalent bond. It will share its 4 valence electrons with electrons from other atoms it bonds with. If carbon were to gain 4 electrons, it would be very difficult for carbon’s 6 protons to hold onto 10 electrons. For carbon to lose 4 electrons would require a large quantity of en ...
... Carbon also forms a covalent bond. It will share its 4 valence electrons with electrons from other atoms it bonds with. If carbon were to gain 4 electrons, it would be very difficult for carbon’s 6 protons to hold onto 10 electrons. For carbon to lose 4 electrons would require a large quantity of en ...
3 molecules
... follow the OCTET RULE; they obtain an inert gas valence (outer) shell that contains 8 electrons • Metals - lose # electrons = group number e.g. Ca Ca2+ + 2e- (Ar outer shell) • Nonmetals - gain electrons = 8 - group # e.g. N + 3e N3- (Ne outer shell) ...
... follow the OCTET RULE; they obtain an inert gas valence (outer) shell that contains 8 electrons • Metals - lose # electrons = group number e.g. Ca Ca2+ + 2e- (Ar outer shell) • Nonmetals - gain electrons = 8 - group # e.g. N + 3e N3- (Ne outer shell) ...
Atomic Theory - WaylandHighSchoolChemistry
... Schrödinger and Heisenberg, and many, many more. Used their brains to venture in the realm of inner space and found the world of the atom was a weird and wondrous place. ...
... Schrödinger and Heisenberg, and many, many more. Used their brains to venture in the realm of inner space and found the world of the atom was a weird and wondrous place. ...
AS specification - word format File
... e use chemical equations to calculate reacting masses and vice versa using the concepts of amount of substance and molar mass f use chemical equations to calculate volumes of gases and vice versa using the concepts of amount of substance and molar volume of gases, eg calculation of the mass or volum ...
... e use chemical equations to calculate reacting masses and vice versa using the concepts of amount of substance and molar mass f use chemical equations to calculate volumes of gases and vice versa using the concepts of amount of substance and molar volume of gases, eg calculation of the mass or volum ...
Chapter 2
... COVALENT BONDING (I) • Requires shared electrons • Example: CH4 C: has 4 valence e, needs 4 more H: has 1 valence e, needs 1 more Electronegativities are comparable. Adapted from Fig. 2.10, Callister 6e. ...
... COVALENT BONDING (I) • Requires shared electrons • Example: CH4 C: has 4 valence e, needs 4 more H: has 1 valence e, needs 1 more Electronegativities are comparable. Adapted from Fig. 2.10, Callister 6e. ...
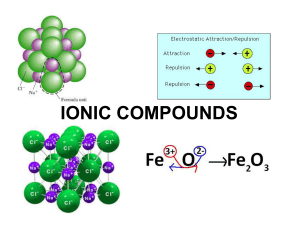
Section 8.3 Names and Formulas of Ionic Compounds Formula Unit
... • 1. a force that holds two atoms together • 2. Atoms gain more stable electron configurations by losing or gaining electrons. • 3. Noble gases are relatively unreactive because they have eight electrone I n their outermost energy ...
... • 1. a force that holds two atoms together • 2. Atoms gain more stable electron configurations by losing or gaining electrons. • 3. Noble gases are relatively unreactive because they have eight electrone I n their outermost energy ...
Basic Atomic Theory
... • An element is a class of substances that contain the same number of protons in all its atoms. • They all have names and abbreviations ...
... • An element is a class of substances that contain the same number of protons in all its atoms. • They all have names and abbreviations ...
Chem152
... 49. What is the molecular formula for lactic acid if the percent composition is 40.00% C, 6.71% H, 53.29% O, and the approximate molar mass is 90 g/mol? A) CHO B) CH2O C) CHO2 D) C3H6O3 E) C6HO8 50. How many atoms of nickel equal a mass of 58.69 g? A) 1 B) 27 C) 58.69 D) 59 E) 6.02 × 1023 51. How ma ...
... 49. What is the molecular formula for lactic acid if the percent composition is 40.00% C, 6.71% H, 53.29% O, and the approximate molar mass is 90 g/mol? A) CHO B) CH2O C) CHO2 D) C3H6O3 E) C6HO8 50. How many atoms of nickel equal a mass of 58.69 g? A) 1 B) 27 C) 58.69 D) 59 E) 6.02 × 1023 51. How ma ...
Semester 2 Review WS
... b.) When hydrochloric acid is added to sodium bicarbonate, it produces water, sodium chloride and carbon dioxide. If 20.0 grams of sodium bicarbonate reacts and 6.75 g of CO2 is produced, what is the percent yield of the carbon dioxide? ...
... b.) When hydrochloric acid is added to sodium bicarbonate, it produces water, sodium chloride and carbon dioxide. If 20.0 grams of sodium bicarbonate reacts and 6.75 g of CO2 is produced, what is the percent yield of the carbon dioxide? ...
final exam practice test - Clayton State University
... e. By careful experimentation, a scientist can measure the dipole moment for each individual bond of a complex molecule. ...
... e. By careful experimentation, a scientist can measure the dipole moment for each individual bond of a complex molecule. ...