chapter2 - AlvarezHChem
... • Rays emitted were called cathode rays • Rays are composed of negatively charged particles called electrons • Electrons carry unit negative charge (-1) and have a very small mass (1/2000 the lightest atomic ...
... • Rays emitted were called cathode rays • Rays are composed of negatively charged particles called electrons • Electrons carry unit negative charge (-1) and have a very small mass (1/2000 the lightest atomic ...
Semester 2 Final Exam
... does the size change and why? (A) bigger / less electron-electron repulsion (B) bigger / more electron-electron repulsion (C) smaller / less electron-electron repulsion (D) smaller / more electron-electron repulsion 44. What type of bond is expected to form between N and O? (A) covalent (B) hydrogen ...
... does the size change and why? (A) bigger / less electron-electron repulsion (B) bigger / more electron-electron repulsion (C) smaller / less electron-electron repulsion (D) smaller / more electron-electron repulsion 44. What type of bond is expected to form between N and O? (A) covalent (B) hydrogen ...
Grade 9 Science Unit 1 Review.notebook
... Matter: anything that has mass and volume Theory: less well supported than a law. Element: substances that contain one type of matter and cannot be broken down or separated into simpler substances. Period: horizontal rows on the periodic table Valence Energy Level : the outter most energy level. Phy ...
... Matter: anything that has mass and volume Theory: less well supported than a law. Element: substances that contain one type of matter and cannot be broken down or separated into simpler substances. Period: horizontal rows on the periodic table Valence Energy Level : the outter most energy level. Phy ...
ScienceHelpNotes-UnitB3 - JA Williams High School
... Matter has been studied for many centuries. In the late 1800s, Dmitri Mendeleev organized the elements into the periodic table. The periodic table is separated by a staircase, with metals on the left of the staircase and nonmetals on the right. Metals have some similarities in their chemical prop ...
... Matter has been studied for many centuries. In the late 1800s, Dmitri Mendeleev organized the elements into the periodic table. The periodic table is separated by a staircase, with metals on the left of the staircase and nonmetals on the right. Metals have some similarities in their chemical prop ...
Advanced Placement (AP) Chemistry 2012 – 2013 Ramsay High
... 2. Relationships in the periodic table: horizontal, vertical, and diagonal with examples from alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, and the first series of transition elements. 3. Introduction to organic chemistry: hydrocarbons and functional groups (structure, nomenclature, chemical prope ...
... 2. Relationships in the periodic table: horizontal, vertical, and diagonal with examples from alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, and the first series of transition elements. 3. Introduction to organic chemistry: hydrocarbons and functional groups (structure, nomenclature, chemical prope ...
Chapter 2: Matter
... Ex. Hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen occur naturally as colorless gases but when combined they form Nylon which is a flexible solid. ...
... Ex. Hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen occur naturally as colorless gases but when combined they form Nylon which is a flexible solid. ...
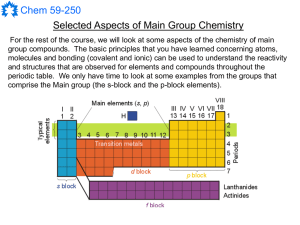
Main Group Notes 1
... The s-block metal hydrides are also very useful compounds that can usually be made by the reaction of the metal with H2(g); this does not work for BeH2 - you can use a BornHaber cycle to figure out why. The H atoms are hydrides (H-), which gives them a totally different kind of chemistry than proton ...
... The s-block metal hydrides are also very useful compounds that can usually be made by the reaction of the metal with H2(g); this does not work for BeH2 - you can use a BornHaber cycle to figure out why. The H atoms are hydrides (H-), which gives them a totally different kind of chemistry than proton ...
7. Molecular interactions
... A hydrogen bond is an attractive interaction between two species that arises from a link of the form A–H · · B , where A and B are highly electronegative elements and B possesses a lone pair of electrons. It is conventionally regarded as being limited to N, O, and F, but if B is an ionic species (su ...
... A hydrogen bond is an attractive interaction between two species that arises from a link of the form A–H · · B , where A and B are highly electronegative elements and B possesses a lone pair of electrons. It is conventionally regarded as being limited to N, O, and F, but if B is an ionic species (su ...
Sugárkémiai áttekintés Schiller Róbert
... One must know the activity of the source, then Delementary must be integrated over source and irradiated space. ...
... One must know the activity of the source, then Delementary must be integrated over source and irradiated space. ...
atoms - Alki Middle School
... the object. The Atomic - Molecular Theory of Matter is based upon a vast amount of indirect evidence gathered over a long period of time. Just like pieces being added to a puzzle, each new bit of information gives us a better understanding of atoms. ...
... the object. The Atomic - Molecular Theory of Matter is based upon a vast amount of indirect evidence gathered over a long period of time. Just like pieces being added to a puzzle, each new bit of information gives us a better understanding of atoms. ...
proteins - Small-Scale Chemistry
... one of the carbon sp2 orbitals to form a σ bond. We have also added dashed circles to represent the p orbitals on each of the three atoms which are directed out of the plane of the paper. See how the p orbital of the central carbon atom overlaps the p orbitals of both of the other atoms, forming π b ...
... one of the carbon sp2 orbitals to form a σ bond. We have also added dashed circles to represent the p orbitals on each of the three atoms which are directed out of the plane of the paper. See how the p orbital of the central carbon atom overlaps the p orbitals of both of the other atoms, forming π b ...
1 Chem 1: Chapter # 11: Theories of Covalent Bonding: VALENCE
... F to F: the picture looks like a 2p orbital on one F is overlapping with a 2p orbital on the other F atom, but actually each F is sp3 hybridized & electrons are localized between two atomic nuclei We cannot use this direct overlap picture for CH4’s bonding. The 2s and the three 2p orbitals on each C ...
... F to F: the picture looks like a 2p orbital on one F is overlapping with a 2p orbital on the other F atom, but actually each F is sp3 hybridized & electrons are localized between two atomic nuclei We cannot use this direct overlap picture for CH4’s bonding. The 2s and the three 2p orbitals on each C ...
NGSS Ps1. 1 Targets 1 and 2- Atoms, Elements, Molecules, and
... (+), neutrons (no chargeneutral), and electrons (-). •The number of protons determines which elements can be formed from the atoms •Remember, the atomic number of an element tells you the number of protons in that element ...
... (+), neutrons (no chargeneutral), and electrons (-). •The number of protons determines which elements can be formed from the atoms •Remember, the atomic number of an element tells you the number of protons in that element ...
NGSS Ps1. 1 Targets 1 and 2- Atoms, Elements, Molecules, and
... (+), neutrons (no chargeneutral), and electrons (-). •The number of protons determines which elements can be formed from the atoms •Remember, the atomic number of an element tells you the number of protons in that element ...
... (+), neutrons (no chargeneutral), and electrons (-). •The number of protons determines which elements can be formed from the atoms •Remember, the atomic number of an element tells you the number of protons in that element ...
Atomic Structure: SOL Review #1 Name: Historical Developments 1
... The electrons are not “singly before pairing.” Electrons repel each other, so they do want not pair until there is no more “space” left in the sublevel. Periodic Table and Periodic Trends 27) Which elements would have similar properties to Na? ...
... The electrons are not “singly before pairing.” Electrons repel each other, so they do want not pair until there is no more “space” left in the sublevel. Periodic Table and Periodic Trends 27) Which elements would have similar properties to Na? ...
C2 Knowledge PowerPoint
... •In graphite, only three of the four electrons in the outer shell of each carbon atom (2.4) are involved in covalent bonds. •Graphite is soft and slippery – layers can easily slide over each other because the weak forces of attraction are easily broken. This is why graphite is used as a lubricant. • ...
... •In graphite, only three of the four electrons in the outer shell of each carbon atom (2.4) are involved in covalent bonds. •Graphite is soft and slippery – layers can easily slide over each other because the weak forces of attraction are easily broken. This is why graphite is used as a lubricant. • ...
Document
... •In graphite, only three of the four electrons in the outer shell of each carbon atom (2.4) are involved in covalent bonds. •Graphite is soft and slippery – layers can easily slide over each other because the weak forces of attraction are easily broken. This is why graphite is used as a lubricant. • ...
... •In graphite, only three of the four electrons in the outer shell of each carbon atom (2.4) are involved in covalent bonds. •Graphite is soft and slippery – layers can easily slide over each other because the weak forces of attraction are easily broken. This is why graphite is used as a lubricant. • ...
Final Exam - Dawson College
... A transition metal ion with a charge of 1+ having 5 unpaired “4d” electrons The element with the highest first ionization energy in period 4 The excited electron configuration is 1s22s22p63s13p1 The halogen with the smallest electron affinity (less exothermic) The noble gas with electrons occupying ...
... A transition metal ion with a charge of 1+ having 5 unpaired “4d” electrons The element with the highest first ionization energy in period 4 The excited electron configuration is 1s22s22p63s13p1 The halogen with the smallest electron affinity (less exothermic) The noble gas with electrons occupying ...
Ms - cloudfront.net
... 43. Use the following equation to answer the questions below: N2 + 3H2 2NH3 a. How many moles of NH3 are in 1.75 moles of N2? b. How many moles of N2 are in 5.23 moles of H2? c. How many moles of H2 are in 3.02 moles of NH3? 44. Determine the mass of carbon dioxide produced when 0.85 grams of but ...
... 43. Use the following equation to answer the questions below: N2 + 3H2 2NH3 a. How many moles of NH3 are in 1.75 moles of N2? b. How many moles of N2 are in 5.23 moles of H2? c. How many moles of H2 are in 3.02 moles of NH3? 44. Determine the mass of carbon dioxide produced when 0.85 grams of but ...
Regents questions
... Arranging the elements by atomic weight leads to an order slightly different from that in a modern periodic table, where the arrangement is by atomic number. Why does this happen? ...
... Arranging the elements by atomic weight leads to an order slightly different from that in a modern periodic table, where the arrangement is by atomic number. Why does this happen? ...