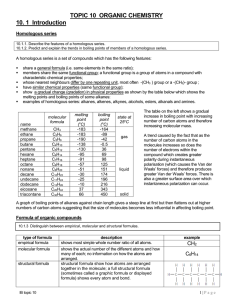
name chemistry final review
... d. 0.821g of BF3 0.0121 moles of BF3 e. 11.6g of Na2CO3 0.109 moles of Na2CO3 f. 68g of Al2(SO4)3 0.20 moles of Al2(SO4)3 g. 275g of NaCl 4.71 moles of NaCl ...
... d. 0.821g of BF3 0.0121 moles of BF3 e. 11.6g of Na2CO3 0.109 moles of Na2CO3 f. 68g of Al2(SO4)3 0.20 moles of Al2(SO4)3 g. 275g of NaCl 4.71 moles of NaCl ...
Name: (1 of 2) Math Set # 13 Protons,
... now has a charge. For example, if a hydrogen atom has one proton (+) and one electron (-‐) the two charges cancel each other out. When the electron is lost the hydrogen atom is only a ...
... now has a charge. For example, if a hydrogen atom has one proton (+) and one electron (-‐) the two charges cancel each other out. When the electron is lost the hydrogen atom is only a ...
Document
... 74. A column of elements in the periodic table is known as a ___________________. 75. What type of ions have names ending in –ide? ...
... 74. A column of elements in the periodic table is known as a ___________________. 75. What type of ions have names ending in –ide? ...
organic chemistry - Peoria Public Schools
... As they are unsaturated alkenes are reactive. The second bond of the double bond is weaker than a single carbon-carbon bond and is broken much easier. It is because of this greater reactivity that alkenes, especially ethene, are important starting materials in organic synthesis of useful chemicals. ...
... As they are unsaturated alkenes are reactive. The second bond of the double bond is weaker than a single carbon-carbon bond and is broken much easier. It is because of this greater reactivity that alkenes, especially ethene, are important starting materials in organic synthesis of useful chemicals. ...
Chemistry exam review
... Atoms must give away electrons to reach a stable octet. Atoms share valence electrons only with neighboring atoms to reach a stable octet. Delocalized electrons move among many atoms creating a sea of electrons. ...
... Atoms must give away electrons to reach a stable octet. Atoms share valence electrons only with neighboring atoms to reach a stable octet. Delocalized electrons move among many atoms creating a sea of electrons. ...
Chapter 2 – Atoms and Elements
... In 1794, Joseph Proust (1754-1826) demonstrated the law of definite proportions (aka law of constant composition): In a given chemical compound, the proportions by mass of the elements that compose it are fixed, independent of the origin of the compound or its mode of preparation. In 1808, John Dalt ...
... In 1794, Joseph Proust (1754-1826) demonstrated the law of definite proportions (aka law of constant composition): In a given chemical compound, the proportions by mass of the elements that compose it are fixed, independent of the origin of the compound or its mode of preparation. In 1808, John Dalt ...
Unit 3 Atomic Structure
... energy as __________. e.g., a- or b-particles, g rays half-life: the time needed for ½ of a radioactive sample to decay into stable matter e.g., C–14: -- half-life is 5,730 years -- decays into stable N–14 ...
... energy as __________. e.g., a- or b-particles, g rays half-life: the time needed for ½ of a radioactive sample to decay into stable matter e.g., C–14: -- half-life is 5,730 years -- decays into stable N–14 ...
Introduction to Computational Chemistry
... • Conformational energies accurate to 1–2 kcal/mol. • Vibrational frequencies for most covalent bonds systematically too high by 10–12% • Zero point vibrational energies: ~1-2 kcal/mol • Isodesmic reaction energies accurate to 2–5 kcal/mol. • Entropies accurate to 0.5 cal/K mol. • Protonation/Deprot ...
... • Conformational energies accurate to 1–2 kcal/mol. • Vibrational frequencies for most covalent bonds systematically too high by 10–12% • Zero point vibrational energies: ~1-2 kcal/mol • Isodesmic reaction energies accurate to 2–5 kcal/mol. • Entropies accurate to 0.5 cal/K mol. • Protonation/Deprot ...
Covalent Bonding and Molecular Structures
... able to form four equivalent covalent bonds to hydrogen atoms, (2) explain why all the bond angles are about 120°, (3) with reference to the valence bond model, explain how the double bond between carbon atoms forms, and (4) explain why one bond in the double bond is weaker than the other. 21. Descr ...
... able to form four equivalent covalent bonds to hydrogen atoms, (2) explain why all the bond angles are about 120°, (3) with reference to the valence bond model, explain how the double bond between carbon atoms forms, and (4) explain why one bond in the double bond is weaker than the other. 21. Descr ...
Semester 1 Final Review Powerpoint
... compound CO2. This compound is considered a molecule because it contains one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms (both are non-metals). ...
... compound CO2. This compound is considered a molecule because it contains one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms (both are non-metals). ...
work-schedule-gr-11-caps-2017
... Describe a covalent chemical bond (a shared pair of electrons) Apply simple rules to deduce bond formation: different atoms each with valence electrons that are: o unpaired - can share these electrons to form a chemical bond o paired (called lone pairs of electrons) - cannot share these four ele ...
... Describe a covalent chemical bond (a shared pair of electrons) Apply simple rules to deduce bond formation: different atoms each with valence electrons that are: o unpaired - can share these electrons to form a chemical bond o paired (called lone pairs of electrons) - cannot share these four ele ...
What are atoms? - Riverdale Middle School
... found that the rays were made of particles. He called these particles electrons. • electron is a particle with a negative ...
... found that the rays were made of particles. He called these particles electrons. • electron is a particle with a negative ...
Average Atomic Mass
... Molecular Formula 62. Calculate the molar mass of magnesium phosphate. 63. How many moles are in 7.23 grams of strontium oxide? 64. How many moles are in 3.02 x 1023 atoms of zinc? 65. How many grams are in 7.2 x 1046 molecules of copper (II) sulfate? 66. How many grams are in 1.00 moles of sodium o ...
... Molecular Formula 62. Calculate the molar mass of magnesium phosphate. 63. How many moles are in 7.23 grams of strontium oxide? 64. How many moles are in 3.02 x 1023 atoms of zinc? 65. How many grams are in 7.2 x 1046 molecules of copper (II) sulfate? 66. How many grams are in 1.00 moles of sodium o ...
3. chemical bonding and molecular structure
... Ionic compounds dissolve in polar solvents like H2O due to ion-dipole interactions. Ionic compounds are generally insoluble in non-polar solvents like CHCl3, CCl4, CH3OH, C6H6, etc. Covalent bond: It was proposed by Lewis. The bond formed by sharing of electron pair is called covalent bond. In coval ...
... Ionic compounds dissolve in polar solvents like H2O due to ion-dipole interactions. Ionic compounds are generally insoluble in non-polar solvents like CHCl3, CCl4, CH3OH, C6H6, etc. Covalent bond: It was proposed by Lewis. The bond formed by sharing of electron pair is called covalent bond. In coval ...
2009-10 Chemistry 1st Semester Final Exam Topics and Review
... Matter- elements and compounds, mixtures and pure substances Elements, atoms, atomic structure- parts, location, charges, and masses. For any atom, ion, or isotope be able to identify: atomic number, mass number (atomic mass), # protons, # electrons, # neutrons 10. Periodic Table: what is found wher ...
... Matter- elements and compounds, mixtures and pure substances Elements, atoms, atomic structure- parts, location, charges, and masses. For any atom, ion, or isotope be able to identify: atomic number, mass number (atomic mass), # protons, # electrons, # neutrons 10. Periodic Table: what is found wher ...
PREP Chemistry 2008 Final Exam Review Problems
... 62. The volume of a gas is 0.668 L at 66.8ºC. At what Celsius temperature will the gas have a volume of 0.942 L, assuming the pressure remains constant? 63. Air in a tightly sealed bottle has a pressure of 0.978 atm at 25.0 ºC. What will the pressure be if the temperature is raised to 46.0ºC? 64. Ca ...
... 62. The volume of a gas is 0.668 L at 66.8ºC. At what Celsius temperature will the gas have a volume of 0.942 L, assuming the pressure remains constant? 63. Air in a tightly sealed bottle has a pressure of 0.978 atm at 25.0 ºC. What will the pressure be if the temperature is raised to 46.0ºC? 64. Ca ...
What are atoms? - Riverdale Middle School
... found that the rays were made of particles. He called these particles electrons. • electron is a particle with a negative ...
... found that the rays were made of particles. He called these particles electrons. • electron is a particle with a negative ...
Practice Multiple Choice Questions for the Chemistry Final Exam
... 93. What is the boiling point of water at standard pressure? a) 100 C b) 112 C c) 212 C d) 200 C 94. Which of the following is a pure substance? a) water b) milk c) soil d) concrete 95. Sugar in water is an example of which solute-solvent combination? a) gas-liquid b) liquid-liquid c) solid-liquid ...
... 93. What is the boiling point of water at standard pressure? a) 100 C b) 112 C c) 212 C d) 200 C 94. Which of the following is a pure substance? a) water b) milk c) soil d) concrete 95. Sugar in water is an example of which solute-solvent combination? a) gas-liquid b) liquid-liquid c) solid-liquid ...
Chemistry exam review
... Atoms must give away electrons to reach a stable octet. Atoms share valence electrons only with neighboring atoms to reach a stable octet. Delocalized electrons move among many atoms creating a sea of electrons. ...
... Atoms must give away electrons to reach a stable octet. Atoms share valence electrons only with neighboring atoms to reach a stable octet. Delocalized electrons move among many atoms creating a sea of electrons. ...
Chemistry exam review
... Atoms must give away electrons to reach a stable octet. Atoms share valence electrons only with neighboring atoms to reach a stable octet. Delocalized electrons move among many atoms creating a sea of electrons. ...
... Atoms must give away electrons to reach a stable octet. Atoms share valence electrons only with neighboring atoms to reach a stable octet. Delocalized electrons move among many atoms creating a sea of electrons. ...
127 - Chimica
... (CO),] (compound 4), identified spectroscopically (IR and 'H NMR), which was previously synthesized'" by photochemical hydrogenation of [Re2(CO)lo].The new method parallels that recently discovered8for the transformation of [Re4H6(CO)12]2into the unsaturated [Re4H5(CO),,]-. As in that case, the proc ...
... (CO),] (compound 4), identified spectroscopically (IR and 'H NMR), which was previously synthesized'" by photochemical hydrogenation of [Re2(CO)lo].The new method parallels that recently discovered8for the transformation of [Re4H6(CO)12]2into the unsaturated [Re4H5(CO),,]-. As in that case, the proc ...
C1 Revision Fundamental ideas adapted CS
... Complete the following using the periodic table to help: H2O: ........... atoms of h.......................... .......... atoms of o....................... ...
... Complete the following using the periodic table to help: H2O: ........... atoms of h.......................... .......... atoms of o....................... ...
Synthesis of Alum Lab
... 2Al(s) + 2K+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) + 6H2O(l) 2[Al(OH)4]-(aq) + 2K+(aq) + 3H2(g) The oxidation and reduction half reactions: ...
... 2Al(s) + 2K+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) + 6H2O(l) 2[Al(OH)4]-(aq) + 2K+(aq) + 3H2(g) The oxidation and reduction half reactions: ...
key
... 127) Classify these statements as being either true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make it true. a) A 3f orbital can hold a maximum of 14 electrons False; no 3f orbital b) The ground state electron configuration of a sulfur atom is 1s22s22p63s23p4. True c) A ground state sulfur ato ...
... 127) Classify these statements as being either true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make it true. a) A 3f orbital can hold a maximum of 14 electrons False; no 3f orbital b) The ground state electron configuration of a sulfur atom is 1s22s22p63s23p4. True c) A ground state sulfur ato ...
AP Chemistry - Chagrin Falls Schools
... The electromagnetic spectrum, Quanta and Photons, photoelectric effect, Bohr’s model and the Bright Line Spectrum, DeBroglie, Heisenberg, Schrodinger, The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom, effective nuclear charge, electron configurations, relationship between configurations and periodicity. Stu ...
... The electromagnetic spectrum, Quanta and Photons, photoelectric effect, Bohr’s model and the Bright Line Spectrum, DeBroglie, Heisenberg, Schrodinger, The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom, effective nuclear charge, electron configurations, relationship between configurations and periodicity. Stu ...