Chapter 1: Quiz Review - Wetaskiwin Composite High School
... you make about this substance from the formula. A. A is a metal and B is a non-metal C. B is a metal and A is a non-metal B. The name will contain the prefixes di and mono D. The compound contains a polyatomic ion 5. What statement about binary compounds is FALSE? A. Binary compounds are formed from ...
... you make about this substance from the formula. A. A is a metal and B is a non-metal C. B is a metal and A is a non-metal B. The name will contain the prefixes di and mono D. The compound contains a polyatomic ion 5. What statement about binary compounds is FALSE? A. Binary compounds are formed from ...
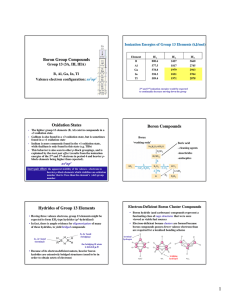
Boron Group Compounds Oxidation States Boron
... Indium is more commonly found in the +1 oxidation state, while thallium is only found in this state (e.g. TlBr) This behavior is also seen in other p-block groupings, and is explained by the inert pair effect (results from the ionization energies of the 2nd and 3rd electrons in period 4 and heavier ...
... Indium is more commonly found in the +1 oxidation state, while thallium is only found in this state (e.g. TlBr) This behavior is also seen in other p-block groupings, and is explained by the inert pair effect (results from the ionization energies of the 2nd and 3rd electrons in period 4 and heavier ...
AP CHEMISTRY – Source: 1999 AP Exam CHAPTER 8 TEST
... Directions: Each set of lettered choice below refers to the numbered statement immediately following it. Select the one lettered choice that best fits each statement and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. A choice may be used once, more than once, or not at all in each set. ...
... Directions: Each set of lettered choice below refers to the numbered statement immediately following it. Select the one lettered choice that best fits each statement and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. A choice may be used once, more than once, or not at all in each set. ...
Cumulative Review, entire quarter
... For positive ions, remove electrons from the outer shell or period first. On the filling diagram , this would be row by row, from the top down. ...
... For positive ions, remove electrons from the outer shell or period first. On the filling diagram , this would be row by row, from the top down. ...
Part II - American Chemical Society
... Part II of this test requires that student answers be written in a response booklet of blank pages. Only this “Blue Book” is graded for a score on Part II. Testing materials, scratch paper, and the “Blue Book” should be made available to the student only during the examination period. All testing ma ...
... Part II of this test requires that student answers be written in a response booklet of blank pages. Only this “Blue Book” is graded for a score on Part II. Testing materials, scratch paper, and the “Blue Book” should be made available to the student only during the examination period. All testing ma ...
Key
... iii. What would you predict for N–O bond order, and how does this compare to the answer you get from Lewis electron structures? There is a σ bond between the N and each O, and one π bonding pair (in orbital A) distributed among all three N–O bonds. The bond order is 4/3, which is also what you get f ...
... iii. What would you predict for N–O bond order, and how does this compare to the answer you get from Lewis electron structures? There is a σ bond between the N and each O, and one π bonding pair (in orbital A) distributed among all three N–O bonds. The bond order is 4/3, which is also what you get f ...
SC 119 PRACTICE Assessment:
... interparticle forces between two molecules of propane and interparticle forces between two molecules of water and use these analyses to support your answer. ...
... interparticle forces between two molecules of propane and interparticle forces between two molecules of water and use these analyses to support your answer. ...
Chemistry 2011-2012
... SC1 Students will analyze the nature of matter and its classifications. SC1a. Relate the role of nuclear fusion in producing essentially all elements heavier than helium. SC1b. Identify substances based on chemical and physical properties. SC2 Students will relate how the Law of Conservation of Matt ...
... SC1 Students will analyze the nature of matter and its classifications. SC1a. Relate the role of nuclear fusion in producing essentially all elements heavier than helium. SC1b. Identify substances based on chemical and physical properties. SC2 Students will relate how the Law of Conservation of Matt ...
V. Chemical reactions
... iii.Catalysts- affect reactions without being part of the reaction iv. Concentration- how much of a material is in a given area ...
... iii.Catalysts- affect reactions without being part of the reaction iv. Concentration- how much of a material is in a given area ...
halogen compounds organic chemistry
... The contribution of structures III, IV and V imparts a partial double bond character to the carbon-chlorine bond. The shortening of bond length imparts stability to aryl halides and as a result, the bond cleavage becomes rather difficult. The aryl halides are, therefore, less reactive than alkyl hal ...
... The contribution of structures III, IV and V imparts a partial double bond character to the carbon-chlorine bond. The shortening of bond length imparts stability to aryl halides and as a result, the bond cleavage becomes rather difficult. The aryl halides are, therefore, less reactive than alkyl hal ...
- Palisades School District
... compounds M(OH)2 and MCO3 , where M represents an unidentified metal. (a) Identify the charge of the M ion in the ionic compounds above. (b) At 25°C, a saturated solution of M(OH)2 has a pH of 9.15. Calculate the molar concentration of OH-(aq) in the saturated solution. 2. Zinc metal is added to a h ...
... compounds M(OH)2 and MCO3 , where M represents an unidentified metal. (a) Identify the charge of the M ion in the ionic compounds above. (b) At 25°C, a saturated solution of M(OH)2 has a pH of 9.15. Calculate the molar concentration of OH-(aq) in the saturated solution. 2. Zinc metal is added to a h ...
Document
... 3. Divide each of the individual moles by the smallest number of moles to gain the molar ratios for each element in the compound. These are the formula subscripts. (X2Y3 etc…) Subscript for C ...
... 3. Divide each of the individual moles by the smallest number of moles to gain the molar ratios for each element in the compound. These are the formula subscripts. (X2Y3 etc…) Subscript for C ...
4.IonicCompounds - Gleneaglesunit1and2chemistry2012
... • Ionic bonds formed when metal atoms combined with non-metal atoms • Metallic bonds formed when metal atoms combined with metal atoms. • Covalent bonds formed when non-metal atoms combined with non-metal atoms. ...
... • Ionic bonds formed when metal atoms combined with non-metal atoms • Metallic bonds formed when metal atoms combined with metal atoms. • Covalent bonds formed when non-metal atoms combined with non-metal atoms. ...
24 Sept 08 - Seattle Central College
... simple ratio of whole numbers. What this means at the particulate level is that when elements combine, they do so in the ratio of small whole numbers. For example: carbon and oxygen react to form CO or CO2, but not CO1.8. ...
... simple ratio of whole numbers. What this means at the particulate level is that when elements combine, they do so in the ratio of small whole numbers. For example: carbon and oxygen react to form CO or CO2, but not CO1.8. ...
Chapter 3: Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... Use VSEPR theory to predict the shapes of molecules. Explain how hybridization relates the shape of molecules to the orbitals occupied by the electrons. Predict the polarity of molecules Describe the types of intermolecular forces of attraction: London dispersion, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen ...
... Use VSEPR theory to predict the shapes of molecules. Explain how hybridization relates the shape of molecules to the orbitals occupied by the electrons. Predict the polarity of molecules Describe the types of intermolecular forces of attraction: London dispersion, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen ...
Chemistry: Chemical Reactions Notes STOP
... of the products. Remember positive ions keep the same name as their neutral element (Ca2+ is calcium) and negative ions end in –ide (Cl1-‐ is chloride). The exception to this rule is polyatomic ...
... of the products. Remember positive ions keep the same name as their neutral element (Ca2+ is calcium) and negative ions end in –ide (Cl1-‐ is chloride). The exception to this rule is polyatomic ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... The rules for naming oxoanions, anions of oxoacids, are as follows: 1. When all the H ions are removed from the “-ic” acid, the anion’s name ends with “-ate.” For example, the anion CO32- derived from H2CO3 is called carbonate. 2. When all the H ions are removed from the “-ous” acid, the anion’s na ...
... The rules for naming oxoanions, anions of oxoacids, are as follows: 1. When all the H ions are removed from the “-ic” acid, the anion’s name ends with “-ate.” For example, the anion CO32- derived from H2CO3 is called carbonate. 2. When all the H ions are removed from the “-ous” acid, the anion’s na ...
electron configuration
... make its 3d sublevel HALF FULL Copper steals a 4s electron to FILL its 3d sublevel ...
... make its 3d sublevel HALF FULL Copper steals a 4s electron to FILL its 3d sublevel ...
atomic number
... Neutron numbers are able to change the mass of atoms, because they weigh about as much as a proton and electron together. If there are many atoms of an element that are isotopes, the average atomic mass for that element will change. We have spoken about carbon (C) having an average mass of 12.01. It ...
... Neutron numbers are able to change the mass of atoms, because they weigh about as much as a proton and electron together. If there are many atoms of an element that are isotopes, the average atomic mass for that element will change. We have spoken about carbon (C) having an average mass of 12.01. It ...
File first semester final study guide key
... 10. Compare and contrast ionic and covalent compounds in terms of their properties and the elements that make up the compounds. Be specific and detailed in your answer. Ionic – metal and nonmetal; electrons are transferred; brittle; high melting points; conduct electricity in water. Covalent – nonme ...
... 10. Compare and contrast ionic and covalent compounds in terms of their properties and the elements that make up the compounds. Be specific and detailed in your answer. Ionic – metal and nonmetal; electrons are transferred; brittle; high melting points; conduct electricity in water. Covalent – nonme ...