Chemistry Standard Outline
... SC2b. Experimentally determine indicators of a chemical reaction specifically precipitation, gas evolution, water production, and changes in energy to the system. SC5. Students will understand that the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs can be affected by changing concentration, temperature, o ...
... SC2b. Experimentally determine indicators of a chemical reaction specifically precipitation, gas evolution, water production, and changes in energy to the system. SC5. Students will understand that the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs can be affected by changing concentration, temperature, o ...
AJR Ch10 Molecular Geometry.docx Slide 1 Chapter 10 Molecular
... Molecular shape is only discussed when there are three or more atoms connected (diatomic shape is obvious). ...
... Molecular shape is only discussed when there are three or more atoms connected (diatomic shape is obvious). ...
File
... - Transition metals are often found in ores. Ores are minerals containing relatively large amounts of metal compounds. - Transition metals make up most metal objects. Some form colorful compounds. 4.The Inner Transition Metals - the 14 inner transition metals between lanthanium (atomic no. 57) and h ...
... - Transition metals are often found in ores. Ores are minerals containing relatively large amounts of metal compounds. - Transition metals make up most metal objects. Some form colorful compounds. 4.The Inner Transition Metals - the 14 inner transition metals between lanthanium (atomic no. 57) and h ...
sample - Bright Red Publishing
... So knowing the states of the reactants and products in a chemical reaction should allow us to predict whether the reaction is accompanied by an increase or a decrease in entropy. Consider, for example, the reaction 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(s). We know that the entropies of solids are very much smalle ...
... So knowing the states of the reactants and products in a chemical reaction should allow us to predict whether the reaction is accompanied by an increase or a decrease in entropy. Consider, for example, the reaction 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(s). We know that the entropies of solids are very much smalle ...
Module 3 Exam Review 1. Organic chemistry is the study of which
... acids joined together by peptide bonds is the ____ structure. 41. The simplest amino acid is glycine because it only has a _____ as its side chain. 42. Hydrogen bonds form the ______________ structure of proteins. 43. A protein that has been denatured is said to have lost its __________. 44. What le ...
... acids joined together by peptide bonds is the ____ structure. 41. The simplest amino acid is glycine because it only has a _____ as its side chain. 42. Hydrogen bonds form the ______________ structure of proteins. 43. A protein that has been denatured is said to have lost its __________. 44. What le ...
Final Exam Review Day 1
... Subatomic Particles and their Jobs # protons = atomic number (identifies the element) neutrons define the mass of the atom ...
... Subatomic Particles and their Jobs # protons = atomic number (identifies the element) neutrons define the mass of the atom ...
PPT - kimscience.com
... All matter is made of indivisible atoms; they can be neither created nor destroyed during chemical reactions All atoms of a given element are identical in their physical and chemical properties; they differ from atoms of every other element Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-numb ...
... All matter is made of indivisible atoms; they can be neither created nor destroyed during chemical reactions All atoms of a given element are identical in their physical and chemical properties; they differ from atoms of every other element Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-numb ...
Chemistry Syllabus
... 2a. Describe and classify matter based on physical and chemical properties and interactions between molecules or atoms. (DOK 1) Physical properties (e.g., melting points, densities, boiling points) of a variety of substances Substances and mixtures Three states of matter in terms of internal e ...
... 2a. Describe and classify matter based on physical and chemical properties and interactions between molecules or atoms. (DOK 1) Physical properties (e.g., melting points, densities, boiling points) of a variety of substances Substances and mixtures Three states of matter in terms of internal e ...
Chemistry Syllabus - Madison County Schools
... 2a. Describe and classify matter based on physical and chemical properties and interactions between molecules or atoms. (DOK 1) Physical properties (e.g., melting points, densities, boiling points) of a variety of substances Substances and mixtures Three states of matter in terms of internal e ...
... 2a. Describe and classify matter based on physical and chemical properties and interactions between molecules or atoms. (DOK 1) Physical properties (e.g., melting points, densities, boiling points) of a variety of substances Substances and mixtures Three states of matter in terms of internal e ...
Fall 2013 Final practice questions w/o solution
... A) B has electrons in p orbitals, so it is lower in energy. B) Li does not want to gain an electron because it already has a half-full s orbital. C) B is a smaller atom, so its valence electrons are more tightly held. D) B is farther to the right in the same row as Li. E) The gain of an electron fil ...
... A) B has electrons in p orbitals, so it is lower in energy. B) Li does not want to gain an electron because it already has a half-full s orbital. C) B is a smaller atom, so its valence electrons are more tightly held. D) B is farther to the right in the same row as Li. E) The gain of an electron fil ...
Sem 1 Final
... • Anions are produced when a neutral atom…. • gains electrons; • thus causing anions to have a negative ______________ charge? ...
... • Anions are produced when a neutral atom…. • gains electrons; • thus causing anions to have a negative ______________ charge? ...
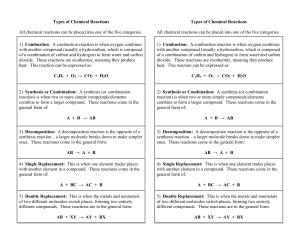
Types of Chemical Reactions
... of a combination of carbon and hydrogen) to form water and carbon dioxide. These reactions are exothermic, meaning they produce heat. This reaction can be expressed as: ...
... of a combination of carbon and hydrogen) to form water and carbon dioxide. These reactions are exothermic, meaning they produce heat. This reaction can be expressed as: ...
Unit 1: Sig. Figs, Compounds, Elements, Homo/Hetero mixtures
... d. e- = 4, p+= 2, n0= 5 11. How many electrons, protons, and neutrons does an ion of 32 P have? a. e- = 15, p+= 15, n0= 17 b. e- = 15, p+= 17, n0= 15 c. e- = 18, p+= 15, n0= 16 d. e- = 18, p+= 15, n0= 17 12. When an atom of gallium forms a gallium ion, its charge becomes ______ because it _______ el ...
... d. e- = 4, p+= 2, n0= 5 11. How many electrons, protons, and neutrons does an ion of 32 P have? a. e- = 15, p+= 15, n0= 17 b. e- = 15, p+= 17, n0= 15 c. e- = 18, p+= 15, n0= 16 d. e- = 18, p+= 15, n0= 17 12. When an atom of gallium forms a gallium ion, its charge becomes ______ because it _______ el ...
Presentation
... compounds are composed of individual covalently bonded units, or molecules. • Covalent compounds are formed between nonmetals. • Prefixes are used to indicate number of each type of element in the compound. • Write the prefixes as indicated on the next slide…. ...
... compounds are composed of individual covalently bonded units, or molecules. • Covalent compounds are formed between nonmetals. • Prefixes are used to indicate number of each type of element in the compound. • Write the prefixes as indicated on the next slide…. ...
File
... C. The rate of formation of products is the same as the rate of decomposition of the reactants D. Matter is neither created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction. (74-76) The reaction of propane with oxygen is: C3H8 + 5O2 ⇄ 3CO2 +4H2O + 2043 kJ 114. Which direction will the reaction shift if the ...
... C. The rate of formation of products is the same as the rate of decomposition of the reactants D. Matter is neither created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction. (74-76) The reaction of propane with oxygen is: C3H8 + 5O2 ⇄ 3CO2 +4H2O + 2043 kJ 114. Which direction will the reaction shift if the ...
Periodic Table Trends - Magoffin County Schools
... • When an atom loses electrons, the ionic radius decreases for two reasons. • First, lost electrons will almost always be valence electrons, so they can leave an empty outer shell, which makes the radius smaller. • Second, the positively-charged nucleus exerts the same amount of pull but on fewer e ...
... • When an atom loses electrons, the ionic radius decreases for two reasons. • First, lost electrons will almost always be valence electrons, so they can leave an empty outer shell, which makes the radius smaller. • Second, the positively-charged nucleus exerts the same amount of pull but on fewer e ...
Chemistry 110 Lab
... position which is occupied by a lone pair. The molecular geometry of AX2E1 is then bent, because one position is missing a ligand in the trigonal planar orbital geometry. To understand why the bond angle in this molecule is not 120°, one needs to study a more subtle difference which arises from the ...
... position which is occupied by a lone pair. The molecular geometry of AX2E1 is then bent, because one position is missing a ligand in the trigonal planar orbital geometry. To understand why the bond angle in this molecule is not 120°, one needs to study a more subtle difference which arises from the ...
Final Review 2
... 78) Why do covalent compounds usually have lower melting and boiling points than ionic compounds? a) No bonds need to be broken to melt a covalent compound. b) The intermolecular forces in ionic compounds are stronger than those in covalent compounds. c) Covalent molecules have higher electron affin ...
... 78) Why do covalent compounds usually have lower melting and boiling points than ionic compounds? a) No bonds need to be broken to melt a covalent compound. b) The intermolecular forces in ionic compounds are stronger than those in covalent compounds. c) Covalent molecules have higher electron affin ...
Lecture 2
... Some schematic diagrams showing how p bonding occurs with a ligand having a d orbital (P), a p* orbital, and a vacant p orbital. ...
... Some schematic diagrams showing how p bonding occurs with a ligand having a d orbital (P), a p* orbital, and a vacant p orbital. ...
Electrons
... first period) has one orbital for its electrons. All of the elements in the second row (the second period) have two orbitals for their electrons. It goes down the periodic table like that. At this time, the maximum number of electron orbitals or electron shells for any element is seven. ...
... first period) has one orbital for its electrons. All of the elements in the second row (the second period) have two orbitals for their electrons. It goes down the periodic table like that. At this time, the maximum number of electron orbitals or electron shells for any element is seven. ...
Metals and non-metals III IMPORTANT POINTS Non-metals
... 1. a. Magnesium, chromium and sodium are all metals, hence, they react with oxygen to form basic oxides b. Chromium, as it is a transition metal. Metals have high density and coloured compounds are formed by transition metals. c. Bromine - the formula is Br2, that is, two atoms of bromine. d. Bromin ...
... 1. a. Magnesium, chromium and sodium are all metals, hence, they react with oxygen to form basic oxides b. Chromium, as it is a transition metal. Metals have high density and coloured compounds are formed by transition metals. c. Bromine - the formula is Br2, that is, two atoms of bromine. d. Bromin ...
The d-block elements are commonly known as transition
... Ligand-to-Metal Charge-Transfer (LMCT) Transition Color in transition-series metal compounds is generally due to the electronic transitions of two principal types of charge transfer transitions. An electron may jump from a predominantly ligand orbital to a predominantly metal orbital, giving rise t ...
... Ligand-to-Metal Charge-Transfer (LMCT) Transition Color in transition-series metal compounds is generally due to the electronic transitions of two principal types of charge transfer transitions. An electron may jump from a predominantly ligand orbital to a predominantly metal orbital, giving rise t ...
Chapter 1: Quiz Review - Wetaskiwin Composite High School
... you make about this substance from the formula. A. A is a metal and B is a non-metal C. B is a metal and A is a non-metal B. The name will contain the prefixes di and mono D. The compound contains a polyatomic ion 5. What statement about binary compounds is FALSE? A. Binary compounds are formed from ...
... you make about this substance from the formula. A. A is a metal and B is a non-metal C. B is a metal and A is a non-metal B. The name will contain the prefixes di and mono D. The compound contains a polyatomic ion 5. What statement about binary compounds is FALSE? A. Binary compounds are formed from ...