Principles of Chemistry 1 and 2 Notes
... (treat single, double and triple bonds as the same). 3 sets (no lone pair) ----> geometry is trigonal planar. ------------------------------------------------------b. BeF2 (beryllium is underlined as a central atom) Lewis structure is as follows: :::F - Be - F::: There are two single bonds of beryll ...
... (treat single, double and triple bonds as the same). 3 sets (no lone pair) ----> geometry is trigonal planar. ------------------------------------------------------b. BeF2 (beryllium is underlined as a central atom) Lewis structure is as follows: :::F - Be - F::: There are two single bonds of beryll ...
Pirogov National Medical Univercity of Vinnitsa
... - the excess reagent does not spill and poured into dishes, from which it was taken to prevent contamination of reagents - concentrated solutions of acids and alkalis, toxic substances are in reserved closet, where they are worked with. Work with acids and base 1. While working with concentrated aci ...
... - the excess reagent does not spill and poured into dishes, from which it was taken to prevent contamination of reagents - concentrated solutions of acids and alkalis, toxic substances are in reserved closet, where they are worked with. Work with acids and base 1. While working with concentrated aci ...
Chapter 4
... good electrical conductors, that is, they transmit electric current with relatively little > Many of the chemical reactions that we study take place in aqueous solution. Seawater is a solution of ions, principally Na+ and Cl-, but it also contains dissolved CO2 and other gases from the atmosphere.Th ...
... good electrical conductors, that is, they transmit electric current with relatively little > Many of the chemical reactions that we study take place in aqueous solution. Seawater is a solution of ions, principally Na+ and Cl-, but it also contains dissolved CO2 and other gases from the atmosphere.Th ...
A Few Things You Might Want To Know
... Bond and molecule polarities are not discrete properties, i.e., they change gradually. The EN differences serve as rough guidelines only for the determination of bind polarity. ...
... Bond and molecule polarities are not discrete properties, i.e., they change gradually. The EN differences serve as rough guidelines only for the determination of bind polarity. ...
thermodynamics
... Chemical energy stored by molecules can be released as heat during chemical reactions when a fuel like methane, cooking gas or coal burns in air. The chemical energy may also be used to do mechanical work when a fuel burns in an engine or to provide electrical energy through a galvanic cell like dry ...
... Chemical energy stored by molecules can be released as heat during chemical reactions when a fuel like methane, cooking gas or coal burns in air. The chemical energy may also be used to do mechanical work when a fuel burns in an engine or to provide electrical energy through a galvanic cell like dry ...
- Angelo State University
... • If the total mass of a sample of small objects is known, and the average mass of each small object is known, the number of objects in the sample can be ...
... • If the total mass of a sample of small objects is known, and the average mass of each small object is known, the number of objects in the sample can be ...
Chapter 15 Acids and Bases
... the H+ from the acid combines with the OH- from the base to make a molecule of H2O it is often helpful to think of H2O as H-OH the cation from the base combines with the anion from the acid to make a salt acid + base → salt + water HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) H+(aq)+Cl-(aq)+Na+(aq)+ ...
... the H+ from the acid combines with the OH- from the base to make a molecule of H2O it is often helpful to think of H2O as H-OH the cation from the base combines with the anion from the acid to make a salt acid + base → salt + water HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) H+(aq)+Cl-(aq)+Na+(aq)+ ...
- sartep.com
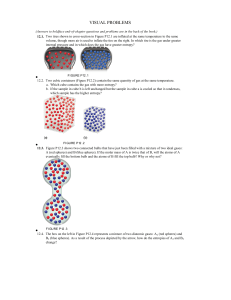
... 68._______________Which of the molecules has four sp3 hybrid bonds? 69._______________Which substance would have the greatest melting point? 70._______________In which of the choices is there polar double bonding in a non-polar molecule? 71. ________________. . .C10H12O4S(s) + . . O2(g) . . . CO2( ...
... 68._______________Which of the molecules has four sp3 hybrid bonds? 69._______________Which substance would have the greatest melting point? 70._______________In which of the choices is there polar double bonding in a non-polar molecule? 71. ________________. . .C10H12O4S(s) + . . O2(g) . . . CO2( ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.