Document
... The thermochemical equation is the chemical equation for a reaction (including phase labels) in which the equation is given a molar interpretation, and the enthalpy of reaction for these molar amounts is written directly after the equation. For the reaction of sodium metal with water, the thermochem ...
... The thermochemical equation is the chemical equation for a reaction (including phase labels) in which the equation is given a molar interpretation, and the enthalpy of reaction for these molar amounts is written directly after the equation. For the reaction of sodium metal with water, the thermochem ...
Chemical Reactions - Effingham County Schools
... Propane burns in excess oxygen according to the following reaction. ...
... Propane burns in excess oxygen according to the following reaction. ...
Biology 251 Fall 2015 1 TOPIC 23: ACID BASE BALANCE I
... H+ in the tubular system is buffered before it is excreted. First it combines with the filtered HCO3- in the tubular system to produce water until all HCO3- is used up. Next the H+ combines with filtered phosphate in the tubules and the H2PO4- so produced is ...
... H+ in the tubular system is buffered before it is excreted. First it combines with the filtered HCO3- in the tubular system to produce water until all HCO3- is used up. Next the H+ combines with filtered phosphate in the tubules and the H2PO4- so produced is ...
Learning Outcomes
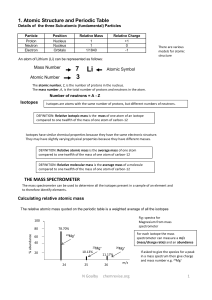
... (f) define relative atomic mass, Ar .............................................................................................. 18 (g) define relative molecular mass, Mr, and calculate relative molecular mass (and relative formula mass) as the sum of relative atomic masses........................ ...
... (f) define relative atomic mass, Ar .............................................................................................. 18 (g) define relative molecular mass, Mr, and calculate relative molecular mass (and relative formula mass) as the sum of relative atomic masses........................ ...
Name_________________________________________
... 3. If the actual yield is 4.95 g Pb, what is the percent yield? [ANS = 0.415 g, 5.69 g, 87%] Benzocaine is a compound containing carbon, oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen. When a sample of benzocaine weighing 3.54 g is burned in excess oxygen, 8.49 g of CO2 and 2.14 g of H2O are formed. In a separate ex ...
... 3. If the actual yield is 4.95 g Pb, what is the percent yield? [ANS = 0.415 g, 5.69 g, 87%] Benzocaine is a compound containing carbon, oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen. When a sample of benzocaine weighing 3.54 g is burned in excess oxygen, 8.49 g of CO2 and 2.14 g of H2O are formed. In a separate ex ...
Word - icho39.chem.msu.ru
... Since the total pressure is increased P > P, the right side of equation (6) is negative, G < 0. The increase of the total pressure will push the reaction towards formation of additional amounts of ammonia. The reaction will proceed predominantly in the forward direction (a product-favored reaction ...
... Since the total pressure is increased P > P, the right side of equation (6) is negative, G < 0. The increase of the total pressure will push the reaction towards formation of additional amounts of ammonia. The reaction will proceed predominantly in the forward direction (a product-favored reaction ...
Thermodynamics ppt
... q < 0 ⇒ exothermic ⇒ heat is flowing out of the system to the surroundings w > 0 ⇒ work is being done on the system by the surroundings when a gas is getting compressed by an external pressure w < 0 ⇒ the system is doing work on the surroundings when a gas is expanding against an external pressure ∆ ...
... q < 0 ⇒ exothermic ⇒ heat is flowing out of the system to the surroundings w > 0 ⇒ work is being done on the system by the surroundings when a gas is getting compressed by an external pressure w < 0 ⇒ the system is doing work on the surroundings when a gas is expanding against an external pressure ∆ ...
Chemical Reaction Equations
... In order to make sure this happens, more of the other reactant must be present than is required An excess reagent is the reactant whose entities are present in surplus amounts, so that some remain after the reaction ends.. In our reaction: much more copper was used than needed (evidenced by the unre ...
... In order to make sure this happens, more of the other reactant must be present than is required An excess reagent is the reactant whose entities are present in surplus amounts, so that some remain after the reaction ends.. In our reaction: much more copper was used than needed (evidenced by the unre ...
Photosynthesis in Hydrogen-Dominated Atmospheres
... is to estimate the energy of the photons necessary to provide that energy, given the nature of the specific chemicals involved. Lastly we map these requirements of chemical input, energy input and photon wavelength onto possible planetary environments. We now describe the methods for each of these s ...
... is to estimate the energy of the photons necessary to provide that energy, given the nature of the specific chemicals involved. Lastly we map these requirements of chemical input, energy input and photon wavelength onto possible planetary environments. We now describe the methods for each of these s ...
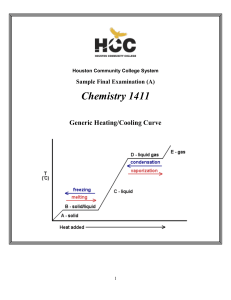
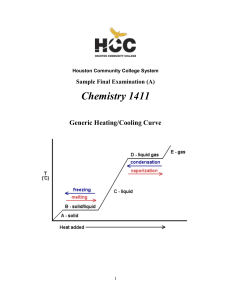
1411FINALSAMPLE+KEY - Houston Community College
... sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizations that allow more than an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electron ...
... sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizations that allow more than an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electron ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.