theodore l. brown h. eugene lemay, jr. bruce e. bursten catherine j
... system, or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or likewise. To obtain permission(s) to use material from this work, please submit a written request to Pearson Education, Inc., Permissions Department, 1900 E. Lake Ave., Glenview, IL 60025. Many o ...
... system, or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or likewise. To obtain permission(s) to use material from this work, please submit a written request to Pearson Education, Inc., Permissions Department, 1900 E. Lake Ave., Glenview, IL 60025. Many o ...
Chapter 5
... atoms, molecules are relatively stable, and enthalpy is low. In contrast, when electrons are only weakly attracted to nuclei, there are weak bonds between atoms, molecules are relatively unstable, and enthalpy is high. You might wonder if this means that breaking chemical bonds releases energy. It d ...
... atoms, molecules are relatively stable, and enthalpy is low. In contrast, when electrons are only weakly attracted to nuclei, there are weak bonds between atoms, molecules are relatively unstable, and enthalpy is high. You might wonder if this means that breaking chemical bonds releases energy. It d ...
Question Bank - Edudel.nic.in
... Why should a solution of a non volatile solute boil at a higher temperature? Explain with the help of a diagram. Derive the relationship between molar mass and elevation in boiling point. ...
... Why should a solution of a non volatile solute boil at a higher temperature? Explain with the help of a diagram. Derive the relationship between molar mass and elevation in boiling point. ...
Practice Exam 4
... Ne and Ar are both atoms so they should have less entropy than a molecular substance, which has more complexity. Ar will have a higher entropy than Ne because it has a larger mass and more fundamental particles. The correct order is H2 O(ℓ) < Ne(g) < Ar(g) < CO2 (g). 017 10.0 points Consider the fol ...
... Ne and Ar are both atoms so they should have less entropy than a molecular substance, which has more complexity. Ar will have a higher entropy than Ne because it has a larger mass and more fundamental particles. The correct order is H2 O(ℓ) < Ne(g) < Ar(g) < CO2 (g). 017 10.0 points Consider the fol ...
paper - General Atomics Fusion Group
... Combustion of fossil fuels, used to power transportation, generate electricity, heat homes, and fuel industry, provides 86% of the world’s energy [1, 2]. Drawbacks to fossil fuel utilization include limited supply, pollution, and carbon dioxide emissions. Carbon dioxide emissions, thought to be resp ...
... Combustion of fossil fuels, used to power transportation, generate electricity, heat homes, and fuel industry, provides 86% of the world’s energy [1, 2]. Drawbacks to fossil fuel utilization include limited supply, pollution, and carbon dioxide emissions. Carbon dioxide emissions, thought to be resp ...
Acids - Beck-Shop
... 1 Add a measured volume of one solution to a conical flask using a pipette. 2 Add the other solution to a burette, and record the initial burette reading to the nearest 0.05 cm3. 3 Add a few drops of an indicator to the solution in the conical flask. 4 Run the solution in the burette into the so ...
... 1 Add a measured volume of one solution to a conical flask using a pipette. 2 Add the other solution to a burette, and record the initial burette reading to the nearest 0.05 cm3. 3 Add a few drops of an indicator to the solution in the conical flask. 4 Run the solution in the burette into the so ...
chem 102 class notes - Louisiana Tech University
... completion, that is, until one of the reactants runs out. Many reactions do proceed . For such reactions essentially to completion: complete reactions are indicated by it can be assumed that the reactants are quantitatively converted to products and that the amount of limiting reactant that remains ...
... completion, that is, until one of the reactants runs out. Many reactions do proceed . For such reactions essentially to completion: complete reactions are indicated by it can be assumed that the reactants are quantitatively converted to products and that the amount of limiting reactant that remains ...
Document
... Direction of Net Chemical Change in Established Equilibrium KC = 1 at 1100 ºC; Starting amounts are 1 mol each of CO and H2O as well as 2 mols each of CO2 and H2. Which substance will be present in greater amounts and which in lesser amounts once the equilibrium has been established? ...
... Direction of Net Chemical Change in Established Equilibrium KC = 1 at 1100 ºC; Starting amounts are 1 mol each of CO and H2O as well as 2 mols each of CO2 and H2. Which substance will be present in greater amounts and which in lesser amounts once the equilibrium has been established? ...
K c
... 1. The concentrations of the reacting species in the condensed phase are expressed in mol/L (M). In the gaseous phase, the concentrations can be expressed in M. 2. The concentrations of pure solids, pure liquids and solvents do not appear in the equilibrium constant expressions. 3. The equilibrium c ...
... 1. The concentrations of the reacting species in the condensed phase are expressed in mol/L (M). In the gaseous phase, the concentrations can be expressed in M. 2. The concentrations of pure solids, pure liquids and solvents do not appear in the equilibrium constant expressions. 3. The equilibrium c ...
1.24 calculations and chemical reactions
... Step 2 use balanced equation to work out which reactant is in excess Using 1TiCl4 :4 Na ratio we can see that 0.527mol of TiCl4 should react with 2.108 mol of Na. We actually have 3.48 mole of Na which is an excess of 1.372 moles. We can complete calculation using the limiting reactant of TiCl4 Step ...
... Step 2 use balanced equation to work out which reactant is in excess Using 1TiCl4 :4 Na ratio we can see that 0.527mol of TiCl4 should react with 2.108 mol of Na. We actually have 3.48 mole of Na which is an excess of 1.372 moles. We can complete calculation using the limiting reactant of TiCl4 Step ...
Chemical Reactions Q3U3
... The concentration of reactants and products no longer change, A state of Chemical equilibrium has been established. Ex. N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) <----> 2 NH3 (g) + energy ...
... The concentration of reactants and products no longer change, A state of Chemical equilibrium has been established. Ex. N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) <----> 2 NH3 (g) + energy ...
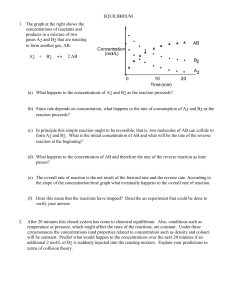
EQUILIBRIUM - SCH4U1-CCVI
... After 20 minutes this closed system has come to chemical equilibrium. Also, conditions such as temperature or pressure, which might affect the rates of the reactions, are constant. Under these circumstances the concentrations (and properties related to concentration such as density and colour) will ...
... After 20 minutes this closed system has come to chemical equilibrium. Also, conditions such as temperature or pressure, which might affect the rates of the reactions, are constant. Under these circumstances the concentrations (and properties related to concentration such as density and colour) will ...
PREPARMACY PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY THERMOCHEMISTRY
... Heat of reaction or enthalpy of reaction The heat (enthalpy) of reaction is simply the amount of heat absorbed or evolved in the reaction. Its value depends upon the number of moles of the reactants which have reacted in the given chemical reactions. Thus, Heat of reaction may be defined as the amo ...
... Heat of reaction or enthalpy of reaction The heat (enthalpy) of reaction is simply the amount of heat absorbed or evolved in the reaction. Its value depends upon the number of moles of the reactants which have reacted in the given chemical reactions. Thus, Heat of reaction may be defined as the amo ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.