Kinetics Workbook - School District 67
... Even though there are more than four billion collisions per second between N and O the amount of product after a year is too small to detect. Using the collision theory, give two reasons why this reaction might be slow. i) ii) ...
... Even though there are more than four billion collisions per second between N and O the amount of product after a year is too small to detect. Using the collision theory, give two reasons why this reaction might be slow. i) ii) ...
Chemical Reactions
... Sometimes you are given quantities of more than one reactant, and asked to calculate the amount of product formed. The quantities of reactants might be such that both react completely, or one might react completely, and the other(s) might be in excess. These are called limiting reagent problems, sin ...
... Sometimes you are given quantities of more than one reactant, and asked to calculate the amount of product formed. The quantities of reactants might be such that both react completely, or one might react completely, and the other(s) might be in excess. These are called limiting reagent problems, sin ...
Common Curriculum Map Discipline: Science Course: Chemistry
... Chapters 1, 2 and 3 11.A.5a Formulate hypotheses referencing prior research and knowledge. 11.A.5b Design procedures to test the selected hypotheses. 11.A.4c Collect, organize and analyze data accurately and precisely. 12.C.4a Use kinetic theory, wave theory, quantum theory and the laws of thermo-dy ...
... Chapters 1, 2 and 3 11.A.5a Formulate hypotheses referencing prior research and knowledge. 11.A.5b Design procedures to test the selected hypotheses. 11.A.4c Collect, organize and analyze data accurately and precisely. 12.C.4a Use kinetic theory, wave theory, quantum theory and the laws of thermo-dy ...
____ 1. The energy required to convert a ground
... 45. The graph above shows the results of a study of the reaction of X with a large excess of Y to yield Z. The concentrations of X and Y were measured over a period of time. According to the results, which of the following can be concluded about the rate law for the reaction under the conditions stu ...
... 45. The graph above shows the results of a study of the reaction of X with a large excess of Y to yield Z. The concentrations of X and Y were measured over a period of time. According to the results, which of the following can be concluded about the rate law for the reaction under the conditions stu ...
IX Chemistry Chapter 02
... was sealed so that the material could not escape outside. The tube was weighed initially in a vertical position so that the solutions should not intermix with each other. The reactants were mixed by inverting and shaking the tube. The tube was weighed after mixing on the formation of white precipita ...
... was sealed so that the material could not escape outside. The tube was weighed initially in a vertical position so that the solutions should not intermix with each other. The reactants were mixed by inverting and shaking the tube. The tube was weighed after mixing on the formation of white precipita ...
Chemical reaction
... Solid sodium plus liquid water react to yield hydrogen gas plus a solution of sodium hydroxide and heat. 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) Æ 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) + heat ...
... Solid sodium plus liquid water react to yield hydrogen gas plus a solution of sodium hydroxide and heat. 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) Æ 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) + heat ...
elements of chemistry unit
... CLASS NOTES REDOX REACTIONS One type of chemical reaction involves the transfer of electrons from one species (species means atoms or groups of atoms) to another. These reactions are called oxidation reduction reactions. REDOX REACTIONS The species that loses electrons is oxidized and the species ga ...
... CLASS NOTES REDOX REACTIONS One type of chemical reaction involves the transfer of electrons from one species (species means atoms or groups of atoms) to another. These reactions are called oxidation reduction reactions. REDOX REACTIONS The species that loses electrons is oxidized and the species ga ...
Stoichiometry Notes
... In this chapter we will discuss the calculations based on chemical equations. It has been classified into two parts : ...
... In this chapter we will discuss the calculations based on chemical equations. It has been classified into two parts : ...
Order date : 24-07-2010
... energy, Born- Haber cycle, structure of AX, AX2, AO2, AO3, A2, O3, ABO3, AB2O4 type crystal defects, non- stoichiometry, sharing of polyhedra, structure of silicates, aluminosilicates, molecular sieves, polyoxyanions. Electronic properties of solids, band theory, k- space, Brillouin zones, band stru ...
... energy, Born- Haber cycle, structure of AX, AX2, AO2, AO3, A2, O3, ABO3, AB2O4 type crystal defects, non- stoichiometry, sharing of polyhedra, structure of silicates, aluminosilicates, molecular sieves, polyoxyanions. Electronic properties of solids, band theory, k- space, Brillouin zones, band stru ...
Final Exam Review Packet
... with than if you use grams or pounds. Also, you can compare two quantities of moles to each other, but you cannot compare grams and pounds. 7. Hydrates are compounds formed by the union of water with some other substance, generally forming a neutral body, as certain crystallized salts. 8. The concen ...
... with than if you use grams or pounds. Also, you can compare two quantities of moles to each other, but you cannot compare grams and pounds. 7. Hydrates are compounds formed by the union of water with some other substance, generally forming a neutral body, as certain crystallized salts. 8. The concen ...
2015_Final Exam Study Guide
... All of the following compounds are exceptions to the octet rule except a. BCl3. c. Br2. b. NO. d. SI4. A bond is classified as nonpolar covalent if the difference in the electronegativities between the 2 atoms is a. 2.1 or more. c. less than 0.4. b. between 0.5 and 2. d. less than zero. Which of the ...
... All of the following compounds are exceptions to the octet rule except a. BCl3. c. Br2. b. NO. d. SI4. A bond is classified as nonpolar covalent if the difference in the electronegativities between the 2 atoms is a. 2.1 or more. c. less than 0.4. b. between 0.5 and 2. d. less than zero. Which of the ...
Organic Chemistry II
... the presence of an acid to give an alcohol. Hence, we should be mindful of LeChatelier’s principle in order to move the equilibrium in the direction we want. If you look at the balanced equation it becomes obvious that water must be avoided to minimize the undesired reverse reaction. This is why con ...
... the presence of an acid to give an alcohol. Hence, we should be mindful of LeChatelier’s principle in order to move the equilibrium in the direction we want. If you look at the balanced equation it becomes obvious that water must be avoided to minimize the undesired reverse reaction. This is why con ...
19_Worked_Examples
... liquid. Thus, the number of molecules of gas has decreased significantly during the reaction. By using the general rules discussed in Section 19.3, we expect a decrease in the number of gas molecules to lead to a decrease in the entropy of the system—the products have fewer possible microstates than ...
... liquid. Thus, the number of molecules of gas has decreased significantly during the reaction. By using the general rules discussed in Section 19.3, we expect a decrease in the number of gas molecules to lead to a decrease in the entropy of the system—the products have fewer possible microstates than ...
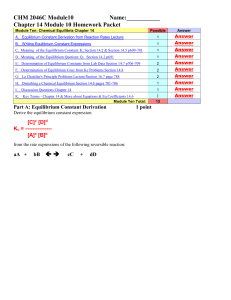
CHEM 1212 Module Ten-Chapter 16 Name
... __________________ 2. If at least one of the reactants or one of the products is not in the same phase, then we say the system is in __________________ equilibrium. __________________ 3. The state where the concentrations of the reactants and the products remain constant with time , it is said that ...
... __________________ 2. If at least one of the reactants or one of the products is not in the same phase, then we say the system is in __________________ equilibrium. __________________ 3. The state where the concentrations of the reactants and the products remain constant with time , it is said that ...
Future perspectives in catalysis - NRSC
... merged. Experts have found common tools to study reactions and now share a common understanding of the molecular foundations of catalysis. This facilitates more rapid progress. A good catalyst is stable enough to survive many process cycles. That is why noble metals – that are intrinsically very sta ...
... merged. Experts have found common tools to study reactions and now share a common understanding of the molecular foundations of catalysis. This facilitates more rapid progress. A good catalyst is stable enough to survive many process cycles. That is why noble metals – that are intrinsically very sta ...
Thermodynamics and Equilibrium
... – This inequality implies that for a reaction to be spontaneous, H-TS must be negative. – If H-TS is positive, the reverse reaction is spontaneous. If H-TS=0, the reaction is at equilibrium Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company.All rights reserved. ...
... – This inequality implies that for a reaction to be spontaneous, H-TS must be negative. – If H-TS is positive, the reverse reaction is spontaneous. If H-TS=0, the reaction is at equilibrium Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company.All rights reserved. ...
Ch 10 - Enrico Fermi High School
... 1. What effect (increase, decrease, no change) will a decrease in temperature have on K? 2. What effect (inc, dec, none) will removing H2 have on the equilibrium constant, K? 3. In which direction will the reaction shift if gaseous H2 is removed from the system? 4. Adding a catalyst (a gold surface) ...
... 1. What effect (increase, decrease, no change) will a decrease in temperature have on K? 2. What effect (inc, dec, none) will removing H2 have on the equilibrium constant, K? 3. In which direction will the reaction shift if gaseous H2 is removed from the system? 4. Adding a catalyst (a gold surface) ...
〈541〉 TITRIMETRY
... In most cases, however, the use of an appropriate redox indicator will yield a much sharper endpoint. It may be necessary to adjust the oxidation state of the analyte prior to titration through use of an appropriate oxidizing or reducing agent; the excess reagent must then be removed, e.g., through ...
... In most cases, however, the use of an appropriate redox indicator will yield a much sharper endpoint. It may be necessary to adjust the oxidation state of the analyte prior to titration through use of an appropriate oxidizing or reducing agent; the excess reagent must then be removed, e.g., through ...
Chemistry
... the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) that set forth a vision for science education where the Science and Engineering Practices (SEPs), Disciplinary Core Ideas (DCIs) of science, and Crosscutting Concepts ...
... the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) that set forth a vision for science education where the Science and Engineering Practices (SEPs), Disciplinary Core Ideas (DCIs) of science, and Crosscutting Concepts ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.