Chem G 9
... neutrons will have different mass numbers and are called isotopes. Students should appreciate that a natural sample of an element is likely to contain a mixture of two or more isotopes. In determining the atomic mass of the element we must take into account that it is a mixture of isotopes with diff ...
... neutrons will have different mass numbers and are called isotopes. Students should appreciate that a natural sample of an element is likely to contain a mixture of two or more isotopes. In determining the atomic mass of the element we must take into account that it is a mixture of isotopes with diff ...
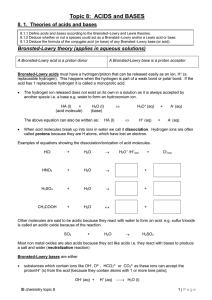
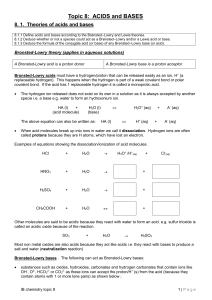
Topic 8: ACIDS and BASES
... positive ions like the H+ which never exists on its own and either reacts with water to form H3O+ or with a another base to form water. Other examples include CH3+ and Br+ (Hal+) which you will study in organic chemistry. molecules containing positive centres (mostly organic molecules) as a res ...
... positive ions like the H+ which never exists on its own and either reacts with water to form H3O+ or with a another base to form water. Other examples include CH3+ and Br+ (Hal+) which you will study in organic chemistry. molecules containing positive centres (mostly organic molecules) as a res ...
Chapter 14: Chemical Kinetics
... For example, compare the reaction between a solid and a gas with the reaction between two gases. The solid–gas reaction (for example, iron and oxygen reacting to form rust) will generally occur at a much slower rate than the gas–gas reaction (for example, oxygen and methane burning in a Bunsen burne ...
... For example, compare the reaction between a solid and a gas with the reaction between two gases. The solid–gas reaction (for example, iron and oxygen reacting to form rust) will generally occur at a much slower rate than the gas–gas reaction (for example, oxygen and methane burning in a Bunsen burne ...
The First Steps of Chemical Evolution towards the
... existence [2]. On the other hand, the mean life times of methane and ammonia are relatively short on an astronomic scale [4]. Therefore, they could have been only main components of the primitive atmosphere if they were continuously delivered to the atmosphere. For this assumption, we do not have an ...
... existence [2]. On the other hand, the mean life times of methane and ammonia are relatively short on an astronomic scale [4]. Therefore, they could have been only main components of the primitive atmosphere if they were continuously delivered to the atmosphere. For this assumption, we do not have an ...
5.1 questions - DrBravoChemistry
... Write an expression showing the relationship between free-energy change, ∆G, enthalpy change, ∆H, and entropy change, ∆S. ...
... Write an expression showing the relationship between free-energy change, ∆G, enthalpy change, ∆H, and entropy change, ∆S. ...
CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry Unit 2: Organic
... All brand names, product names, logos and related devices are used for identification purposes only and are trademarks, registered trademarks or service marks of their respective holders. ...
... All brand names, product names, logos and related devices are used for identification purposes only and are trademarks, registered trademarks or service marks of their respective holders. ...
Powerpoint
... Bond enthalpy is usually applied for gaseous molecules because molecules are isolated in gaseous state. In solid and liquid states, molecules are held by each other by intermolecular forces. The importance of bond enthalpy relies on the fact that it can be calculated accurately and there are some ex ...
... Bond enthalpy is usually applied for gaseous molecules because molecules are isolated in gaseous state. In solid and liquid states, molecules are held by each other by intermolecular forces. The importance of bond enthalpy relies on the fact that it can be calculated accurately and there are some ex ...
Chemical Equilibrium
... The equilibrium constant Kp for the reaction 2NO2 (g) 2NO (g) + O2 (g) is 158 at 1000K. What is the equilibrium pressure of O2 if the PNO2 = 0.400 atm and PNO = 0.270 atm? ...
... The equilibrium constant Kp for the reaction 2NO2 (g) 2NO (g) + O2 (g) is 158 at 1000K. What is the equilibrium pressure of O2 if the PNO2 = 0.400 atm and PNO = 0.270 atm? ...
Stoichiometry, Lab Basics, Reactions
... CaCl2. What is the minimum number of moles of AgNO3 that must be added to the solution in order to precipitate all of the Cl- as AgCl (s)? (Assume all AgCl is insoluble.) A) 0.10 mol B) 0.20 mol C) 0.30 mol D) 0.40 mol E) 0.60 mol ____ 21. A 40.0 mL sample of 0.25 M KOH is added to 60.0 mL of 0.15 M ...
... CaCl2. What is the minimum number of moles of AgNO3 that must be added to the solution in order to precipitate all of the Cl- as AgCl (s)? (Assume all AgCl is insoluble.) A) 0.10 mol B) 0.20 mol C) 0.30 mol D) 0.40 mol E) 0.60 mol ____ 21. A 40.0 mL sample of 0.25 M KOH is added to 60.0 mL of 0.15 M ...
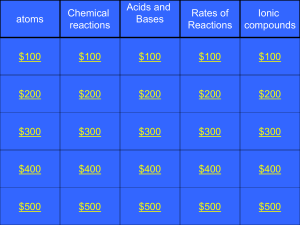
2P chem jeopardy 2011
... This NOT a chemical reaction. You can reverse it! (water vapour condenses to liquid water again). **Caution,bubbles DON’T ALWAYS mean a Chemical reaction! Category 2: $400: Q ...
... This NOT a chemical reaction. You can reverse it! (water vapour condenses to liquid water again). **Caution,bubbles DON’T ALWAYS mean a Chemical reaction! Category 2: $400: Q ...
chapter_14 Equilibr
... Side with fewest moles of gas Side with most moles of gas Side with most moles of gas Side with fewest moles of gas ...
... Side with fewest moles of gas Side with most moles of gas Side with most moles of gas Side with fewest moles of gas ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.