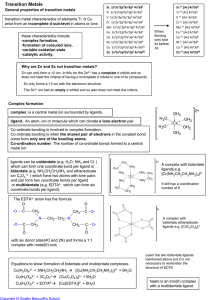
Equilibrium Booklet - mrstorie
... 3. Chemists have determined the equilibrium constants for several reactions. In which of these reactions are the products favoured over the reactants? a. KC = 1.0×102 ...
... 3. Chemists have determined the equilibrium constants for several reactions. In which of these reactions are the products favoured over the reactants? a. KC = 1.0×102 ...
CHEMICAL EQUATIONS - Clayton State University
... Consider the following Sodium (Na) has an atomic mass of 22.99 u This implies that the mass of 1 mole of Na = 22.99 g Molar mass of Na = 22.99 g/mol Formula mass of NaCl = 58.44 u The mass of 1 mole of NaCl = 58.44 g Molar mass of NaCl = 58.88 g/mol Formula mass of CaCO3 = 100.09 u The mass of 1 mol ...
... Consider the following Sodium (Na) has an atomic mass of 22.99 u This implies that the mass of 1 mole of Na = 22.99 g Molar mass of Na = 22.99 g/mol Formula mass of NaCl = 58.44 u The mass of 1 mole of NaCl = 58.44 g Molar mass of NaCl = 58.88 g/mol Formula mass of CaCO3 = 100.09 u The mass of 1 mol ...
document
... are written as separate ions in the solution. Other reactants and products are written in molecular form. State symbols are included: (s), (l), (g), (aq). For example: AgNO3(aq) + NaCl(aq) AgCl(s) + NaNO3(aq) In ionic form: Ag+(aq) + NO3−(aq) + Na+(aq)Cl−(aq) AgCl(s) + Na+(aq) + NO3−(aq) Copyrigh ...
... are written as separate ions in the solution. Other reactants and products are written in molecular form. State symbols are included: (s), (l), (g), (aq). For example: AgNO3(aq) + NaCl(aq) AgCl(s) + NaNO3(aq) In ionic form: Ag+(aq) + NO3−(aq) + Na+(aq)Cl−(aq) AgCl(s) + Na+(aq) + NO3−(aq) Copyrigh ...
Worked out problems
... Analyze: We are given an incomplete, unbalanced (skeleton) equation for a redox reaction occurring in acidic solution and asked to complete and balance it. Plan: We use the half-reaction procedure we just learned. Solve: Step 1: We divide the equation into two halfreactions: Step 2:We balance each h ...
... Analyze: We are given an incomplete, unbalanced (skeleton) equation for a redox reaction occurring in acidic solution and asked to complete and balance it. Plan: We use the half-reaction procedure we just learned. Solve: Step 1: We divide the equation into two halfreactions: Step 2:We balance each h ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
... expressing the extent of ionization of water in quantitative terms. A brief review of some properties of reversible chemical reactions shows how this can be done. The position of equilibrium of any chemical reaction is given by its equilibrium constant, Keq (sometimes expressed simply as K ). For th ...
... expressing the extent of ionization of water in quantitative terms. A brief review of some properties of reversible chemical reactions shows how this can be done. The position of equilibrium of any chemical reaction is given by its equilibrium constant, Keq (sometimes expressed simply as K ). For th ...
Higher Chemistry Resources Guide - Glow Blogs
... dropping a strip of magnesium into various concentrations of hydrochloric acid and recording the time taken for the effervescence to stop. An unusual experiment demonstrating the effect of concentration on reaction rate is provided in the decolourisation of permanganate using rhubarb as described in ...
... dropping a strip of magnesium into various concentrations of hydrochloric acid and recording the time taken for the effervescence to stop. An unusual experiment demonstrating the effect of concentration on reaction rate is provided in the decolourisation of permanganate using rhubarb as described in ...
Syllabus - Chemistry
... Application of reterosynthetic approach in the synthesis of camphor, longifoline, cortisone. Reserpine, Vitamin D, juvabione, Aphidicolin Fredericamycin A. or examples of other complex molecules. Unit-IV 13 hrs Oxidation:Introduction, Different oxidative processes. Hydrocarbons: Alkenes, aromatic ri ...
... Application of reterosynthetic approach in the synthesis of camphor, longifoline, cortisone. Reserpine, Vitamin D, juvabione, Aphidicolin Fredericamycin A. or examples of other complex molecules. Unit-IV 13 hrs Oxidation:Introduction, Different oxidative processes. Hydrocarbons: Alkenes, aromatic ri ...
Higher Chemistry Resources Guide - Glow Blogs
... The following pages show the Mandatory Course key areas table from the SQA Higher Chemistry Course and Unit Support Notes. An additional fourth column has been included which contains hyperlinks to useful resources. Please note: Practitioners are not required to use the resources listed – they are o ...
... The following pages show the Mandatory Course key areas table from the SQA Higher Chemistry Course and Unit Support Notes. An additional fourth column has been included which contains hyperlinks to useful resources. Please note: Practitioners are not required to use the resources listed – they are o ...
Mnemonic Devices - Free WonderKids-e
... - is another weak oxidizing agent. Its mode of action is to decompose into water and atomic oxygen (O). Atomic oxygen normally combines to form molecular . However, in the brief time that is available, atomic oxygen acts as a very good oxidizing agent if it encounters a suitable reactant. Hydrogen p ...
... - is another weak oxidizing agent. Its mode of action is to decompose into water and atomic oxygen (O). Atomic oxygen normally combines to form molecular . However, in the brief time that is available, atomic oxygen acts as a very good oxidizing agent if it encounters a suitable reactant. Hydrogen p ...
theodore l. brown h. eugene lemay, jr. bruce e. bursten catherine j
... system, or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or likewise. To obtain permission(s) to use material from this work, please submit a written request to Pearson Education, Inc., Permissions Department, 1900 E. Lake Ave., Glenview, IL 60025. Many o ...
... system, or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or likewise. To obtain permission(s) to use material from this work, please submit a written request to Pearson Education, Inc., Permissions Department, 1900 E. Lake Ave., Glenview, IL 60025. Many o ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.