The Periodic Table - Whitwell High School
... The atomic masses of its three stable isotopes, 8O (99.757 percent), 8O (0.038 percent),188O (0.205 percent), are 15.9949, 16.9991, and 17.9992 amu, respectively. Calculate the average atomic mass of oxygen using the relative abundances given in parentheses. Strategy Each isotope contributes to the ...
... The atomic masses of its three stable isotopes, 8O (99.757 percent), 8O (0.038 percent),188O (0.205 percent), are 15.9949, 16.9991, and 17.9992 amu, respectively. Calculate the average atomic mass of oxygen using the relative abundances given in parentheses. Strategy Each isotope contributes to the ...
Materials Required
... -Handout on common elemental isotopes and their abundancy -Post-assessment sheet (same as pre-assessment with additional conceptual questions) Activities Gaining Attention: The term Sub-atomic particles will be written on the board as the students take their seats. As class begins a bag of candy for ...
... -Handout on common elemental isotopes and their abundancy -Post-assessment sheet (same as pre-assessment with additional conceptual questions) Activities Gaining Attention: The term Sub-atomic particles will be written on the board as the students take their seats. As class begins a bag of candy for ...
for-unit-test-4-atomic-scientists-and-atoms
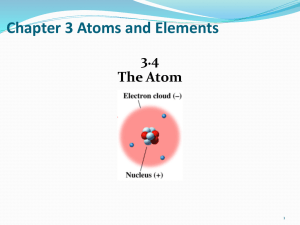
... • The Modern Atomic Theory According to the current theory, there are regions inside the atom where electrons are likely to found. These regions are called electron clouds, or orbitals. ...
... • The Modern Atomic Theory According to the current theory, there are regions inside the atom where electrons are likely to found. These regions are called electron clouds, or orbitals. ...
Document
... The following examples are designed to help you become more familiar with the size of atoms, which are very, very small! By working through these examples, you may better understand how the parts of the atom are related to one another. What is the size of one atom? 1. It is estimated that about 1 tr ...
... The following examples are designed to help you become more familiar with the size of atoms, which are very, very small! By working through these examples, you may better understand how the parts of the atom are related to one another. What is the size of one atom? 1. It is estimated that about 1 tr ...
Chapter 6 13edx
... This means that, for a set of orbitals in the same sublevel, there must be one electron in each orbital before pairing and the electrons have the same spin, as much as possible. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... This means that, for a set of orbitals in the same sublevel, there must be one electron in each orbital before pairing and the electrons have the same spin, as much as possible. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
atomic theory - chemistryatdulwich
... approximately one hundred thousand times greater than the radius of the nucleus. The nucleus has a very high density. This is because the protons, which all have ‘like’ charges are drawn very close together by very powerful nuclear forces. These forces need to be powerful as they Topic2atomictheory ...
... approximately one hundred thousand times greater than the radius of the nucleus. The nucleus has a very high density. This is because the protons, which all have ‘like’ charges are drawn very close together by very powerful nuclear forces. These forces need to be powerful as they Topic2atomictheory ...
Chapter 17 Resource: Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... a flat surface. Have the numbered columns of the microplate at the top and the lettered rows at the left. 2. Using the microtip pipette, place 15 drops of the aluminum nitrate solution in each of the wells A1–G1. Rinse the pipette with distilled water. 3. Place 15 drops of copper nitrate solution in ...
... a flat surface. Have the numbered columns of the microplate at the top and the lettered rows at the left. 2. Using the microtip pipette, place 15 drops of the aluminum nitrate solution in each of the wells A1–G1. Rinse the pipette with distilled water. 3. Place 15 drops of copper nitrate solution in ...
File
... The properties of mass and volume can be used to describe another important general property of matter called density. Density is the mass per unit volume of an object. Density is important property because it allows you to compare different types of matter. Suppose you were asked to determine wheth ...
... The properties of mass and volume can be used to describe another important general property of matter called density. Density is the mass per unit volume of an object. Density is important property because it allows you to compare different types of matter. Suppose you were asked to determine wheth ...
Elements, Mixtures and Compounds
... In ionic bonding electrons are lost (transferred) from metal atoms and gained by non-metal atoms to form charged particles called ions. Since electrons have a negative charge, metal atoms will be left with a positive charge and non-metal atoms will have gained a negative charge. These oppositely cha ...
... In ionic bonding electrons are lost (transferred) from metal atoms and gained by non-metal atoms to form charged particles called ions. Since electrons have a negative charge, metal atoms will be left with a positive charge and non-metal atoms will have gained a negative charge. These oppositely cha ...
The Elements and the Periodic Table
... each are best described with a wave model, and some properties are best described by a particle model. • Quantum mechanics, which unifies the wave and particle models of light, arose from a combination of the attempts by physicists and chemists to understand both the structure of the atom, and their ...
... each are best described with a wave model, and some properties are best described by a particle model. • Quantum mechanics, which unifies the wave and particle models of light, arose from a combination of the attempts by physicists and chemists to understand both the structure of the atom, and their ...
Bonding Notes
... The two are bonded because of the opposite charges of the two ions that attract for one another. Notice that a total number of eight valence electrons are used . This is called the octet rule! The octet rule means that each atom participating in a ionic bond must achieve eight electrons in its outer ...
... The two are bonded because of the opposite charges of the two ions that attract for one another. Notice that a total number of eight valence electrons are used . This is called the octet rule! The octet rule means that each atom participating in a ionic bond must achieve eight electrons in its outer ...
AP Chemistry MC Review Questions
... (A) Atoms have equal numbers of positive and negative charges. (B) Electrons in atoms are arranged in shells. (C) Neutrons are at the center of an atom. (D) Neutrons and protons in atoms have nearly equal mass. (E) The positive charge of an atom is concentrated in a small region. 23. _____The emissi ...
... (A) Atoms have equal numbers of positive and negative charges. (B) Electrons in atoms are arranged in shells. (C) Neutrons are at the center of an atom. (D) Neutrons and protons in atoms have nearly equal mass. (E) The positive charge of an atom is concentrated in a small region. 23. _____The emissi ...
CHEMISTRY 123-07 Midterm #1 – Answer key October 14, 2010
... 31. Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute per volume of solution in liters. 32. Ions that contain atoms of more than one element are called polyatomic ions. 33. Proton donors are known as Brønsted acids. 34. A compound that forms between a non-metal and a non-metal is a molecular comp ...
... 31. Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute per volume of solution in liters. 32. Ions that contain atoms of more than one element are called polyatomic ions. 33. Proton donors are known as Brønsted acids. 34. A compound that forms between a non-metal and a non-metal is a molecular comp ...
atoms
... In a nuclear equation, the element symbols represent only the nuclei of atoms Rather than the entire neutral atoms, so the subscript represents only the number of nuclear charges (protons). An emitted electron is written as 0-1e , where the superscript o indicates that the mass of an electron is ess ...
... In a nuclear equation, the element symbols represent only the nuclei of atoms Rather than the entire neutral atoms, so the subscript represents only the number of nuclear charges (protons). An emitted electron is written as 0-1e , where the superscript o indicates that the mass of an electron is ess ...
Redox Balancing Worksheet
... The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to its charge. Thus the oxidation number of Cl in the Clion is -1, that for Mg in the Mg+2 ion is +2, and that for oxygen in O2- ion is -2. The sum of the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero if neutral, or equal to the charge if an ion. The oxidat ...
... The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to its charge. Thus the oxidation number of Cl in the Clion is -1, that for Mg in the Mg+2 ion is +2, and that for oxygen in O2- ion is -2. The sum of the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero if neutral, or equal to the charge if an ion. The oxidat ...
Final Exam Review
... 65. Which pair of atoms is most likely to form a covalent chemical bond? (Ch. 12) a. H and H d. Na and Cl b. He and Ne e. Li and Br c. Na and Na 66. Which of the following is likely to have the largest radius? (Ch. 11) a. H d. Rb b. Mn e. Ag c. Cl 67. Which property is not a characteristic of the al ...
... 65. Which pair of atoms is most likely to form a covalent chemical bond? (Ch. 12) a. H and H d. Na and Cl b. He and Ne e. Li and Br c. Na and Na 66. Which of the following is likely to have the largest radius? (Ch. 11) a. H d. Rb b. Mn e. Ag c. Cl 67. Which property is not a characteristic of the al ...
Foundations of Atomic Theory
... identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds In chemical reactions, atoms are comb ...
... identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds In chemical reactions, atoms are comb ...
Isotopes
... all of the atoms of a given element were identical. This idea persisted for over 100 years, until James Chadwick discovered that the nuclei of most atoms contain neutrons as well as protons. (This is a good example of how a theory changes as new observations are made.) After the discovery of the neu ...
... all of the atoms of a given element were identical. This idea persisted for over 100 years, until James Chadwick discovered that the nuclei of most atoms contain neutrons as well as protons. (This is a good example of how a theory changes as new observations are made.) After the discovery of the neu ...