Chemistry Review Module Chapter 1
... • The Modern Model of the Atom – Of course, the Rutherford-Bohr model and the Simplified Model do not perfectly represent what happens inside the atom. No model can! – A more complete model, The Modern or ElectronCloud model exists, but is more complicated and extremely difficult to draw. – The Mode ...
... • The Modern Model of the Atom – Of course, the Rutherford-Bohr model and the Simplified Model do not perfectly represent what happens inside the atom. No model can! – A more complete model, The Modern or ElectronCloud model exists, but is more complicated and extremely difficult to draw. – The Mode ...
Atomic Theory Quiz A
... That’s the most common isotope, Sr-88. Watch your rounding to the nearest whole number work. 6. Name all seven metalloids and write their symbols next to their names (size order, small to large) Boron (B), Silicon (Si), Germanium (Ge), Arsenic (As), Antimony (Sb), Tellurium (Te), and Astatine (At). ...
... That’s the most common isotope, Sr-88. Watch your rounding to the nearest whole number work. 6. Name all seven metalloids and write their symbols next to their names (size order, small to large) Boron (B), Silicon (Si), Germanium (Ge), Arsenic (As), Antimony (Sb), Tellurium (Te), and Astatine (At). ...
Matter
... of varying density surrounding the nucleus. • The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. ...
... of varying density surrounding the nucleus. • The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. ...
Chapter 17
... of varying density surrounding the nucleus. • The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. ...
... of varying density surrounding the nucleus. • The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. ...
Chapter 4 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and
... of varying density surrounding the nucleus. • The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. ...
... of varying density surrounding the nucleus. • The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. ...
Hi Guys. Today we are going to be talking about the smallest part of
... You should go ahead and practice doing your dot diagrams and Bohr structures for all of the elements from hydrogen to argon. Since argon is the last one, let’s go ahead and practice the dot diagram and Bohr structure together. Argon has an atomic number of 18 and an atomic mass of let’s go ahead and ...
... You should go ahead and practice doing your dot diagrams and Bohr structures for all of the elements from hydrogen to argon. Since argon is the last one, let’s go ahead and practice the dot diagram and Bohr structure together. Argon has an atomic number of 18 and an atomic mass of let’s go ahead and ...
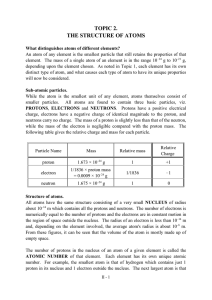
TOPIC 2. THE STRUCTURE OF ATOMS
... Note how the electron arrangement in the Na+ ion is the same as for the Ne atom which has atomic number 10, one smaller than the Na atom. All the other members of the first group of elements in Table 2 (the alkali metals) also have just one more electron than a noble gas atom, and they all behave as ...
... Note how the electron arrangement in the Na+ ion is the same as for the Ne atom which has atomic number 10, one smaller than the Na atom. All the other members of the first group of elements in Table 2 (the alkali metals) also have just one more electron than a noble gas atom, and they all behave as ...
AQA GCSE Chemistry My Revision Notes
... (c) There are some advantages of drinking hard water. Give one of them. (1 mark) (d) What happens if you use temporarily hard water in a kettle? (2 marks) (e) Explain how an ion-exchange column softens hard water. (2 marks) (f) Another way of softening hard water is to use sodium carbonate. Explain ...
... (c) There are some advantages of drinking hard water. Give one of them. (1 mark) (d) What happens if you use temporarily hard water in a kettle? (2 marks) (e) Explain how an ion-exchange column softens hard water. (2 marks) (f) Another way of softening hard water is to use sodium carbonate. Explain ...
Unit 10: Structure and Bonding
... Radioactive and Non radioactive isotopes Do NOT assume the word isotope means the atom it is radioactive, this depends on the stability of the nucleus i.e. unstable atoms (radioactive) might be referred to as radioisotopes. Many isotopes are extremely stable in the nuclear sense and NOT radioactive ...
... Radioactive and Non radioactive isotopes Do NOT assume the word isotope means the atom it is radioactive, this depends on the stability of the nucleus i.e. unstable atoms (radioactive) might be referred to as radioisotopes. Many isotopes are extremely stable in the nuclear sense and NOT radioactive ...
UNIT 2 ATOMS, MATTER, AND THE MOLE
... there are two atoms of hydrogen. 2. H2O2 is not water. It is called hydrogen peroxide, has two atoms of hydrogen for every two atoms of oxygen and behaves much differently that water. This brings us to the next law. F. LAW OF MULTIPLE PROPORTIONS-states that there can exist two or more compounds wit ...
... there are two atoms of hydrogen. 2. H2O2 is not water. It is called hydrogen peroxide, has two atoms of hydrogen for every two atoms of oxygen and behaves much differently that water. This brings us to the next law. F. LAW OF MULTIPLE PROPORTIONS-states that there can exist two or more compounds wit ...
electrons - Science Department
... fundamental, meaning that they cannot be broken up into smaller particles. ...
... fundamental, meaning that they cannot be broken up into smaller particles. ...
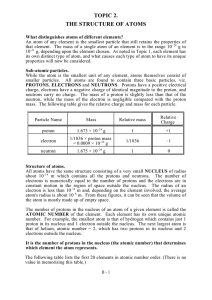
TOPIC 2. THE STRUCTURE OF ATOMS
... whose atomic number is 1 less than that of the first group element. Some other elements have atoms which only require one more electron in order to obtain the noble gas arrangement. These atoms are F, Cl, Br and I, all of which are just one electron short of having a filled outer level. In chemical ...
... whose atomic number is 1 less than that of the first group element. Some other elements have atoms which only require one more electron in order to obtain the noble gas arrangement. These atoms are F, Cl, Br and I, all of which are just one electron short of having a filled outer level. In chemical ...
Electrons
... a. an electron circles the nucleus only in fixed energy ranges called orbits; b. an electron can neither gain or lose energy inside this orbit, but could move up or down to another orbit; c. that the lowest energy orbit is closest to the nucleus. Describe the wave/particle duality of electrons. Writ ...
... a. an electron circles the nucleus only in fixed energy ranges called orbits; b. an electron can neither gain or lose energy inside this orbit, but could move up or down to another orbit; c. that the lowest energy orbit is closest to the nucleus. Describe the wave/particle duality of electrons. Writ ...