PS 2 - Purdyphysicalscience
... Found in the center of the nucleus Gives the nucleus its positive charge Proton number never changes All elements are placed by increasing atomic numbers on the periodic table (IDs the element) Protons (positive) are equal to Electrons (negative) so all elements are neutral Protons do not change dur ...
... Found in the center of the nucleus Gives the nucleus its positive charge Proton number never changes All elements are placed by increasing atomic numbers on the periodic table (IDs the element) Protons (positive) are equal to Electrons (negative) so all elements are neutral Protons do not change dur ...
Chem Course Desc2. New
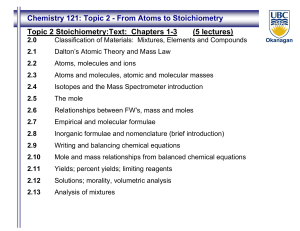
... 2.4 Use the Periodic table to identify metals, semimetals (metalloids), nonmetals, alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens and transition metals. (C. S. 1. b, c ) 2.5 Relate the position of an element in the periodic table to its quantum electron configuration. ( C.S. 1.g ) ...
... 2.4 Use the Periodic table to identify metals, semimetals (metalloids), nonmetals, alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens and transition metals. (C. S. 1. b, c ) 2.5 Relate the position of an element in the periodic table to its quantum electron configuration. ( C.S. 1.g ) ...
48th CHEMISTRY OLYMPIAD CHEMISTRY
... 1. A plate of the metal X was brought for analysis to a laboratory. A lab assistant has cut two pieces of the same weight from a plate and placed one of them into a solution of a lead salt, the second one – into the solution of copper salt. After the certain time the weight of the first piece has in ...
... 1. A plate of the metal X was brought for analysis to a laboratory. A lab assistant has cut two pieces of the same weight from a plate and placed one of them into a solution of a lead salt, the second one – into the solution of copper salt. After the certain time the weight of the first piece has in ...
CH_3 IN TOTO - WordPress.com
... Atomic mass is the • weighted average of all naturally occurring isotopes of that element • number on the periodic table below the chemical symbol with two decimal places ...
... Atomic mass is the • weighted average of all naturally occurring isotopes of that element • number on the periodic table below the chemical symbol with two decimal places ...
Document
... Na < Ca < Al < Sn Na < Al < Ca < Sn Na < Al < Sn < Ca Ca < Na < Sn < Al Dr.Laila Al-Harbi ...
... Na < Ca < Al < Sn Na < Al < Ca < Sn Na < Al < Sn < Ca Ca < Na < Sn < Al Dr.Laila Al-Harbi ...
Devillez (ld2653) – Test 1 Review – Devillez – (99998)
... deflected, they were deflected at all angles, including some very wide angles! The wide deflections suggested a very hard (dense) positively charged core in the atom. However, this core, or nucleus, must be small in relation to the overall size of the atom, since so few of the α particles were defle ...
... deflected, they were deflected at all angles, including some very wide angles! The wide deflections suggested a very hard (dense) positively charged core in the atom. However, this core, or nucleus, must be small in relation to the overall size of the atom, since so few of the α particles were defle ...
Chapter 3
... 1. Write the correct formula(s) for the reactants on the left side and the correct formula(s) for the product(s) on the right side of the equation. 2. Change the numbers in front of the formulas (coefficients) to make the number of atoms of each element the same on both sides of the equation. Do not ...
... 1. Write the correct formula(s) for the reactants on the left side and the correct formula(s) for the product(s) on the right side of the equation. 2. Change the numbers in front of the formulas (coefficients) to make the number of atoms of each element the same on both sides of the equation. Do not ...
Syllabus Cambridge International A & AS Level Chemistry Syllabus code 9701
... Candidates can take the course either as an AS Level, A Level or staged assessment to A Level. Practice of experimental skills Candidates should be directed towards the practice of experimental skills throughout the whole period of their course of study. Candidates’ experimental skills will be teste ...
... Candidates can take the course either as an AS Level, A Level or staged assessment to A Level. Practice of experimental skills Candidates should be directed towards the practice of experimental skills throughout the whole period of their course of study. Candidates’ experimental skills will be teste ...
Exam Review
... 9. Which of the following ideas of the Bohr model is not retained in the modern theory of ...
... 9. Which of the following ideas of the Bohr model is not retained in the modern theory of ...
2014 Syllabus - Cambridge International Examinations
... This syllabus is examined in the May/June examination series and the October/November examination series. This syllabus is available to private candidates. However, it is expected that private candidates learn in an environment where practical work is an integral part of the course. Candidates will ...
... This syllabus is examined in the May/June examination series and the October/November examination series. This syllabus is available to private candidates. However, it is expected that private candidates learn in an environment where practical work is an integral part of the course. Candidates will ...
Final Exam - KFUPM Faculty List
... Se is in representative group VI, thus it has 6 s,p valence electrons ns2np4 It is in period 4, thus n = 4 and (n-1)d is filled: ns2(n-1)d10np4 The next smaller noble gas to Se is Ar, thus Se has an [Ar] core: [Ar]4s23d104p4 Sec# 7-11 Grade# 65 Q18. Given the following 1st, 2nd, and 3rd ionization e ...
... Se is in representative group VI, thus it has 6 s,p valence electrons ns2np4 It is in period 4, thus n = 4 and (n-1)d is filled: ns2(n-1)d10np4 The next smaller noble gas to Se is Ar, thus Se has an [Ar] core: [Ar]4s23d104p4 Sec# 7-11 Grade# 65 Q18. Given the following 1st, 2nd, and 3rd ionization e ...
c00kieee - Ritter Illustration
... f-block elements, actinides (5f ) and lanthanides (4f ) are separated from the other elements. This modern placement as well as their name is attributed to Prof. Glenn T. Seaborg, who in the 1930s proposed the actinide theory. As a result of this concept, the actinides were removed from their origin ...
... f-block elements, actinides (5f ) and lanthanides (4f ) are separated from the other elements. This modern placement as well as their name is attributed to Prof. Glenn T. Seaborg, who in the 1930s proposed the actinide theory. As a result of this concept, the actinides were removed from their origin ...
GCSE Chemistry Specification Specification for exams from 2014 2014
... Subject Content 3.1 Introduction to Subject Content ...
... Subject Content 3.1 Introduction to Subject Content ...
ch03 - Atoms and Elements
... Atomic mass is the • weighted average of all naturally occurring isotopes of that element • number on the periodic table below the chemical symbol with two decimal places ...
... Atomic mass is the • weighted average of all naturally occurring isotopes of that element • number on the periodic table below the chemical symbol with two decimal places ...
Chemistry Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 2.1 Multiple
... B) Rutherford's gold foil experiment. C) Thomson's cathode ray tube experiment. D) None of these Answer: B Topic: Section 2.4 Atomic Structure: Protons and Neutrons 18) The existence of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom was demonstrated by A) Millikan's oil drop experiment. B) Rutherford's gold foi ...
... B) Rutherford's gold foil experiment. C) Thomson's cathode ray tube experiment. D) None of these Answer: B Topic: Section 2.4 Atomic Structure: Protons and Neutrons 18) The existence of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom was demonstrated by A) Millikan's oil drop experiment. B) Rutherford's gold foi ...
Chemistry Essentials For Dummies
... Breaking Elements Apart with Nuclear Fission .................... 52 Mass defect: Where does all that energy come from? .................................................... 52 Chain reactions and critical mass ............................... 53 Coming Together with Nuclear Fusion.................... ...
... Breaking Elements Apart with Nuclear Fission .................... 52 Mass defect: Where does all that energy come from? .................................................... 52 Chain reactions and critical mass ............................... 53 Coming Together with Nuclear Fusion.................... ...
08 Redox Reactions
... “The charge which an atom appears to have, when all other atoms are removed from it as ions is known as oxidation number.” OR “The oxidation number or oxidation state of an atom in a molecule or ion is defined as the number of charges it would carry if electrons were completely transferred.” Metals ...
... “The charge which an atom appears to have, when all other atoms are removed from it as ions is known as oxidation number.” OR “The oxidation number or oxidation state of an atom in a molecule or ion is defined as the number of charges it would carry if electrons were completely transferred.” Metals ...
Chapters 1 to 5 - Lakeland Regional High School
... ____ 35. The main energy level that can hold only two electrons is the a. first. c. third. b. second. d. fourth. ____ 36. "Orbitals of equal energy are each occupied by one electron before any is occupied by a second electron, and all electrons in singly occupied orbitals must have the same spin" i ...
... ____ 35. The main energy level that can hold only two electrons is the a. first. c. third. b. second. d. fourth. ____ 36. "Orbitals of equal energy are each occupied by one electron before any is occupied by a second electron, and all electrons in singly occupied orbitals must have the same spin" i ...