Matter
... Consists of only one kind of atom, • Cannot be broken down into a simpler type of matter by either physical or chemical means • Can exist as either atoms or molecules. ...
... Consists of only one kind of atom, • Cannot be broken down into a simpler type of matter by either physical or chemical means • Can exist as either atoms or molecules. ...
study guide for atoms/periodic table quiz
... table—just know how to read it. You will need to know that elements in a family have similar properties. You will not need to memorize the family names or tell me specifics about different families, but you will need to be able to tell me if an element is likely to be reactive, based on where its fa ...
... table—just know how to read it. You will need to know that elements in a family have similar properties. You will not need to memorize the family names or tell me specifics about different families, but you will need to be able to tell me if an element is likely to be reactive, based on where its fa ...
The four elements: fire, water, wind, and earth.
... A dense nucleus of positive charge with the electrons circling around it Size scale: if the nucleus of the atom was the size of a tennis ball, the atom would have a diameter over 1 mile. The nearest electron would be .25 mi from the nucleus! If the nucleus was the size of a quarter, the diameter of ...
... A dense nucleus of positive charge with the electrons circling around it Size scale: if the nucleus of the atom was the size of a tennis ball, the atom would have a diameter over 1 mile. The nearest electron would be .25 mi from the nucleus! If the nucleus was the size of a quarter, the diameter of ...
Chapter 2 Early philosophy of Matter Revolution
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory • 1. Each element is composed of tiny, indestructible particles called atoms • 2. All atoms of a given element have the same mass and other properties that distinguish them from other elements • 3. Atom combine in small whole number ratios to form molecules of compounds • 4. ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory • 1. Each element is composed of tiny, indestructible particles called atoms • 2. All atoms of a given element have the same mass and other properties that distinguish them from other elements • 3. Atom combine in small whole number ratios to form molecules of compounds • 4. ...
ch3 B - Manasquan Public Schools
... Later on, the discovery of protons and neutrons were discovered in the nucleus. And it was later concluded that all atoms are neutral in charge. The number of protons and electrons in any atom are always equal. ...
... Later on, the discovery of protons and neutrons were discovered in the nucleus. And it was later concluded that all atoms are neutral in charge. The number of protons and electrons in any atom are always equal. ...
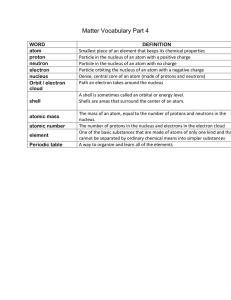
Matter Vocab Part 4
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
CHAPTER 3 sec 1 - Leon County Schools
... the first to suggest that all things were made up of small indivisible and indestructible particles, he called atoms. He had no scientific support, so what makes him right? ...
... the first to suggest that all things were made up of small indivisible and indestructible particles, he called atoms. He had no scientific support, so what makes him right? ...
ChemFinalgeocities
... 89. To complete the list, calculate the density for carbon dioxide if 250.0 mL of the gas has a mass of 0.4997 g. Look at each of the electron dot structures shown below. In each case, decide: how many valence electrons are present; whether or not the particle is reactive; and if it is reactive, wha ...
... 89. To complete the list, calculate the density for carbon dioxide if 250.0 mL of the gas has a mass of 0.4997 g. Look at each of the electron dot structures shown below. In each case, decide: how many valence electrons are present; whether or not the particle is reactive; and if it is reactive, wha ...
Matter on Earth and in the universe is made of atoms that have
... 20. Vertical columns on the periodic table are called _groups_ or _families_. Horizontal rows on the periodic table are called _periods_. How can you tell which elements will have similar properties? Why do they have similar properties? Elements with similar properties have the same number of valenc ...
... 20. Vertical columns on the periodic table are called _groups_ or _families_. Horizontal rows on the periodic table are called _periods_. How can you tell which elements will have similar properties? Why do they have similar properties? Elements with similar properties have the same number of valenc ...
ATOMS, MOLECULES and IONS
... elements are called noble, or inert (ie; unreactive) gases. Elements belonging to a certain group all exhibit similar chemical properties. ...
... elements are called noble, or inert (ie; unreactive) gases. Elements belonging to a certain group all exhibit similar chemical properties. ...
Models of the Atom: A Historical perspective
... • Most particles passed through • So, atoms are mostly empty space ...
... • Most particles passed through • So, atoms are mostly empty space ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table Test
... a. Speed in mph b. stopping distance c. same car, same road conditions, same driver 2) An experiment is run to see if a new type of salt will melt ice better then sodium chloride. The salt is sprinkled on 30 sheets of ice and the time it takes for the ice to melt is recorded. a. What is the experime ...
... a. Speed in mph b. stopping distance c. same car, same road conditions, same driver 2) An experiment is run to see if a new type of salt will melt ice better then sodium chloride. The salt is sprinkled on 30 sheets of ice and the time it takes for the ice to melt is recorded. a. What is the experime ...
TEST REVIEW S Valence Electrons TEST REVIEW SHEET 2017
... NOTE: If an element has <4 valence electrons it will give them away during an ionic bond and become a positive ion. If >4, it will take them and become a negative ion For the most part…. metals will give away their valence electrons and nonmetals will take enough valence electrons to fill their oute ...
... NOTE: If an element has <4 valence electrons it will give them away during an ionic bond and become a positive ion. If >4, it will take them and become a negative ion For the most part…. metals will give away their valence electrons and nonmetals will take enough valence electrons to fill their oute ...
Chemistry--Chapter 5: Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... 1) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms (we know now atoms are divisible!). 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3) Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemic ...
... 1) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms (we know now atoms are divisible!). 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3) Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemic ...
Atomic Structure Notes
... Has no electrical charge (neutral). Found in the nucleus of an atom. More massive than electrons. Protons + Neutrons = Atomic Mass ...
... Has no electrical charge (neutral). Found in the nucleus of an atom. More massive than electrons. Protons + Neutrons = Atomic Mass ...
Bohr Model & Lewis Dot Diagrams
... (atomic mass – atomic number) Then determine the number of electrons (atomic number) ...
... (atomic mass – atomic number) Then determine the number of electrons (atomic number) ...
COS 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, 1.3
... • region in an atom where there is a high probability of finding electrons ...
... • region in an atom where there is a high probability of finding electrons ...
Development of atomic theory
... energy and spiral into the nucleus. This difficulty was solved by Niels Bohr (1913), who applied the quantum theory developed by Max Planck and Albert Einstein to the problem of atomic structure. Bohr proposed that electrons could circle a nucleus without radiating energy only in orbits for which th ...
... energy and spiral into the nucleus. This difficulty was solved by Niels Bohr (1913), who applied the quantum theory developed by Max Planck and Albert Einstein to the problem of atomic structure. Bohr proposed that electrons could circle a nucleus without radiating energy only in orbits for which th ...
unit plan template
... PS-2.2 Illustrate the fact that the atoms of elements exist as stable or unstable isotopes. PS-2.3 Explain the trends of the periodic table based on the elements’ valence electrons and atomic numbers. PS-2.4 Use the atomic number and the mass number to calculate the number of protons, neutrons, and/ ...
... PS-2.2 Illustrate the fact that the atoms of elements exist as stable or unstable isotopes. PS-2.3 Explain the trends of the periodic table based on the elements’ valence electrons and atomic numbers. PS-2.4 Use the atomic number and the mass number to calculate the number of protons, neutrons, and/ ...
Chapter 2 Lect. 1
... atoms of other elements c. Atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds d. Atoms of one element can’t change into another element e. In chemical reactions, the atoms don’t change, but the way they are bound together does ...
... atoms of other elements c. Atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds d. Atoms of one element can’t change into another element e. In chemical reactions, the atoms don’t change, but the way they are bound together does ...
Early Models of Atom
... 1. Each element is composed of indivisible particles called atoms 2. In an element, all of the atoms are identical. Atoms of different elements have different properties, such as mass. 3. In chemical reactions atoms are neither created nor destroyed. 4. In compounds atoms of more then one element co ...
... 1. Each element is composed of indivisible particles called atoms 2. In an element, all of the atoms are identical. Atoms of different elements have different properties, such as mass. 3. In chemical reactions atoms are neither created nor destroyed. 4. In compounds atoms of more then one element co ...
Classifying Matter and the Periodic Table
... Dalton’s atomic theory of matter • each element is composed of extremely small particles called atoms • all atoms of a given element are identical, but they differ from those of other any other element ...
... Dalton’s atomic theory of matter • each element is composed of extremely small particles called atoms • all atoms of a given element are identical, but they differ from those of other any other element ...