CHEMISTRY
... Smallest unit nucleus: center/core is most of the mass of the atom a. protons: + charge ...
... Smallest unit nucleus: center/core is most of the mass of the atom a. protons: + charge ...
Chem 400 Chem 150 REVIEW SHEET Amanda R
... o Most transition metals form cations of various charge Trends in Periodic Table – trends of elements to predict formation of bonds o Counting valence electrons, electron configuration o Atomic radii increases to the left and down o Electron Affinity/Ionization Energy and electronegativity increases ...
... o Most transition metals form cations of various charge Trends in Periodic Table – trends of elements to predict formation of bonds o Counting valence electrons, electron configuration o Atomic radii increases to the left and down o Electron Affinity/Ionization Energy and electronegativity increases ...
Chapter 6: Chemical Bonding
... • Bond Length – The distance between two bonded atoms at their minimum potential energy. AKA average distance between two bonded atoms. • Bond Energy – The energy required to break a chemical bond or form neutral isolated atoms. ...
... • Bond Length – The distance between two bonded atoms at their minimum potential energy. AKA average distance between two bonded atoms. • Bond Energy – The energy required to break a chemical bond or form neutral isolated atoms. ...
Fall Exam 3
... Orbital energies increase in the order 3s < 3p < 3d because orbital penetration decreases in the order 3s > 3p > 3d. Orbital energies increase in the order 3s < 3p < 3d because the Schrödinger equation predicts that orbital energy depends only on the angular momentum quantum number, l. Orbital energ ...
... Orbital energies increase in the order 3s < 3p < 3d because orbital penetration decreases in the order 3s > 3p > 3d. Orbital energies increase in the order 3s < 3p < 3d because the Schrödinger equation predicts that orbital energy depends only on the angular momentum quantum number, l. Orbital energ ...
Review Notes - Biochemistry
... 5. Chemical Formula: Where each _ELEMENT_ is represented by its chemical _SYMBOL_ and the _NUMBER__ of atoms is shown in __SUBSCRIPTS__. ...
... 5. Chemical Formula: Where each _ELEMENT_ is represented by its chemical _SYMBOL_ and the _NUMBER__ of atoms is shown in __SUBSCRIPTS__. ...
Molecular Orbital Theory
... between the 2 positive nuclei 2. A set of higher energy ANTI-BONDING orbitals are created Antibonding orbitals have most of the electron density on the opposite side from the region where the bond must be formed Nonbonding Orbital: the energy of which is essentially that of an atomic orbital ...
... between the 2 positive nuclei 2. A set of higher energy ANTI-BONDING orbitals are created Antibonding orbitals have most of the electron density on the opposite side from the region where the bond must be formed Nonbonding Orbital: the energy of which is essentially that of an atomic orbital ...
3: Many electrons
... For example, the ground state of the H2 molecule has an electron configuration 1σg2. The Pauli principle can only be satisfied if the electron spins are paired. The total wavefunction can be ...
... For example, the ground state of the H2 molecule has an electron configuration 1σg2. The Pauli principle can only be satisfied if the electron spins are paired. The total wavefunction can be ...
First Semester Honors Chemistry Exam Review (2011
... 38. A spherical electron cloud surrounding an atomic nucleus would best represent which orbital (s)? 39. How many orbital shapes are in the first energy level? Second? Third? Fourth? What are they? 40. Both copper (atomic number 29) and chromium (atomic number 24) appear to break the pattern in the ...
... 38. A spherical electron cloud surrounding an atomic nucleus would best represent which orbital (s)? 39. How many orbital shapes are in the first energy level? Second? Third? Fourth? What are they? 40. Both copper (atomic number 29) and chromium (atomic number 24) appear to break the pattern in the ...
Chapter 3
... finding an electron at various locations around the nucleus of. An atomic orbitals is represented pictorially as a region of space in which there is a high probably of finding an electron. ...
... finding an electron at various locations around the nucleus of. An atomic orbitals is represented pictorially as a region of space in which there is a high probably of finding an electron. ...
Magnetic Susceptibility Synthesis of Mn(acac)3
... • The energy ‘gap’ between the two sets of orbitals depends on the ligands. – I-
... • The energy ‘gap’ between the two sets of orbitals depends on the ligands. – I-
Exam 3 Key
... a. What is the hybridization for the left oxygen atom? sp3 b. What is the hybridization for the right oxygen atom? sp2 c. What is the hybridization for the top oxygen atom? sp2 d. What is the hybridization for the nitrogen atom? sp2 e. Write a description of the bonding, stating whether each bond is ...
... a. What is the hybridization for the left oxygen atom? sp3 b. What is the hybridization for the right oxygen atom? sp2 c. What is the hybridization for the top oxygen atom? sp2 d. What is the hybridization for the nitrogen atom? sp2 e. Write a description of the bonding, stating whether each bond is ...
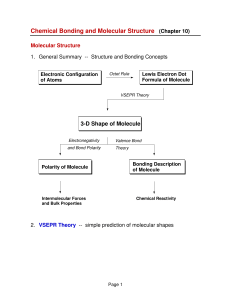
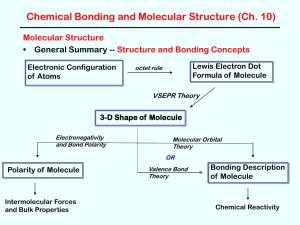
3-D Shape of Molecule
... 2. Molecular Orbitals for simple diatomic molecules (H2 and He2) in H2 the 1s atomic orbitals on the two H atoms are combined into: a bonding MO -- σ1s and an antibonding MO -- σ*1s MO energy level diagram for H2 (only the bonding MO is filled): ...
... 2. Molecular Orbitals for simple diatomic molecules (H2 and He2) in H2 the 1s atomic orbitals on the two H atoms are combined into: a bonding MO -- σ1s and an antibonding MO -- σ*1s MO energy level diagram for H2 (only the bonding MO is filled): ...
AP Chapter 9 Molecular Shapes
... π bonds • π bonds must lie in the same plane, therefore, the presence of π bonds makes the molecule slightly rigid. ...
... π bonds • π bonds must lie in the same plane, therefore, the presence of π bonds makes the molecule slightly rigid. ...
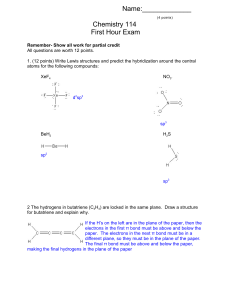
Name:______ Chemistry 114 First Hour Exam
... electrons in the first ð bond must be above and below the paper. The electrons in the next ð bond must be in a different plane, so they must be in the plane of the paper. The final ð bond must be above and below the paper, making the final hydrogens in the plane of the paper ...
... electrons in the first ð bond must be above and below the paper. The electrons in the next ð bond must be in a different plane, so they must be in the plane of the paper. The final ð bond must be above and below the paper, making the final hydrogens in the plane of the paper ...
Chem 101A Exam 4 Concepts Chapter 7 – Modern Atomic Theory
... Chem 101A Exam 4 Concepts Chapter 7 – Modern Atomic Theory Use formulas that relate energy of photon, frequency, wavelength, speed of light, and the Rydberg Equation Notable scientists and their contributions: Rutherford, Bohr, Planc, de Broglie, Heisenberg, Schrödinger. The four Quantum ...
... Chem 101A Exam 4 Concepts Chapter 7 – Modern Atomic Theory Use formulas that relate energy of photon, frequency, wavelength, speed of light, and the Rydberg Equation Notable scientists and their contributions: Rutherford, Bohr, Planc, de Broglie, Heisenberg, Schrödinger. The four Quantum ...
Chapter 2 - Speedway High School
... Chemical reactions make and break chemical bonds • The starting molecules of a chemical reaction are called reactants • The final molecules of a chemical reaction are called products ...
... Chemical reactions make and break chemical bonds • The starting molecules of a chemical reaction are called reactants • The final molecules of a chemical reaction are called products ...
Molecular orbital diagram
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of molecular orbitals, although the electrons involved may be redistributed among the orbitals. This tool is very well suited for simple diatomic molecules such as dihydrogen, dioxygen, and carbon monoxide but becomes more complex when discussing even comparatively simple polyatomic molecules, such as methane. MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. They can also predict bond strength, as well as the electronic transitions that can take place.