•What makes up an atom? Draw an atom
... • Element - Pure substance that can’t be broken into other types of matter • Each element has its own symbol and specific number of protons ...
... • Element - Pure substance that can’t be broken into other types of matter • Each element has its own symbol and specific number of protons ...
Chapter 4 REVIEW
... 28. Chlorine is a very reactive element that forms stable compounds with most other elements. For each of the following chlorine compounds, draw Lewis and structural diagrams, and then predict the polarity of the molecules: (a) NCl3 (c) PCl5 (b) SiCl4 (d) SCl6 ...
... 28. Chlorine is a very reactive element that forms stable compounds with most other elements. For each of the following chlorine compounds, draw Lewis and structural diagrams, and then predict the polarity of the molecules: (a) NCl3 (c) PCl5 (b) SiCl4 (d) SCl6 ...
Chemistry of Life - juan-roldan
... and are called Valence Electrons Valence electrons occupy the valence shell (outermost shell) Changes in electron energy levels are important in energy conversions in organisms ...
... and are called Valence Electrons Valence electrons occupy the valence shell (outermost shell) Changes in electron energy levels are important in energy conversions in organisms ...
Chapter 7, 8, and 9 Exam 2014 Name I. 50% of your grade will come
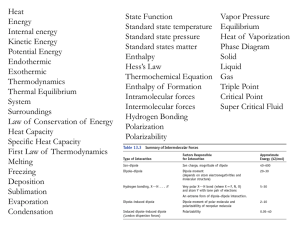
... The energy required to form the transition state in a chemical reaction. ...
... The energy required to form the transition state in a chemical reaction. ...
Quantum Number
... Atomic Orbitals A wave function with a given set of these three quantum numbers is called an atomic orbital ...
... Atomic Orbitals A wave function with a given set of these three quantum numbers is called an atomic orbital ...
electron configuration
... • States that atomic orbitals can have at most two electrons • Electrons paired within an orbital must have opposite spins (+1/2, -1/2) • Atomic orbital depicted as a box (or simply as a line or circle) • Electrons are depicted as arrows • An up arrow denotes an “up” spin • Down arrow denotes a “dow ...
... • States that atomic orbitals can have at most two electrons • Electrons paired within an orbital must have opposite spins (+1/2, -1/2) • Atomic orbital depicted as a box (or simply as a line or circle) • Electrons are depicted as arrows • An up arrow denotes an “up” spin • Down arrow denotes a “dow ...
Materials Science for Chemical Engineers
... one electron is places in all orbitals of equal energy before two electrons are placed in any one of these orbitals. Rule 3. Pauli Exclusion principle a maximum of two electrons can occupy an orbital. No two electrons can have the same four quantum numbers. ...
... one electron is places in all orbitals of equal energy before two electrons are placed in any one of these orbitals. Rule 3. Pauli Exclusion principle a maximum of two electrons can occupy an orbital. No two electrons can have the same four quantum numbers. ...
What do you know about light?
... • On its own the atomic number does not tell us the number of neutrons in an element. In order to determine the number of neutrons we need the mass number. ...
... • On its own the atomic number does not tell us the number of neutrons in an element. In order to determine the number of neutrons we need the mass number. ...
PS7aChemistryReviewRevised
... Instant coffee dissolves in water. Chocolate melts in a warm room ...
... Instant coffee dissolves in water. Chocolate melts in a warm room ...
Chem 101 notes review
... The symbol for the magnetic quantum number is m which defines the orbital. m = - , (- + 1), (- +2), .....0, ......., ( -2), ( -1), The last quantum number is the spin quantum number which has the symbol m s which characterizes the single electron. The spin quantum number only has two pos ...
... The symbol for the magnetic quantum number is m which defines the orbital. m = - , (- + 1), (- +2), .....0, ......., ( -2), ( -1), The last quantum number is the spin quantum number which has the symbol m s which characterizes the single electron. The spin quantum number only has two pos ...
CHAPTER 5 NOTES – ELECTRONS IN ATOMS
... to another energy level • Quantum Mechanical Model – the modern description of the electron in atoms – from the mathematical solutions to the Schrödinger equation – determines the allowed energies an electron can have and how likely it is to find the electron in various locations around the nucleus ...
... to another energy level • Quantum Mechanical Model – the modern description of the electron in atoms – from the mathematical solutions to the Schrödinger equation – determines the allowed energies an electron can have and how likely it is to find the electron in various locations around the nucleus ...
Ch8.Periodic properties
... Electron configurations Configuration shows which orbitals are occupied Aufbau principle: e– takes lowest available energy Hund’s rule: if there are 2 or more orbitals of equal energy (degenerate orbitals), e– will occupy all orbitals singly before pairing ...
... Electron configurations Configuration shows which orbitals are occupied Aufbau principle: e– takes lowest available energy Hund’s rule: if there are 2 or more orbitals of equal energy (degenerate orbitals), e– will occupy all orbitals singly before pairing ...
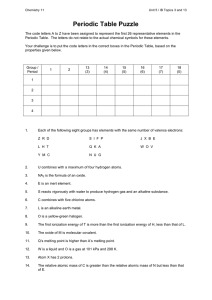
Periodic Table Puzzle
... The code letters A to Z have been assigned to represent the first 26 representative elements in the Periodic Table. The letters do not relate to the actual chemical symbols for these elements. Your challenge is to put the code letters in the correct boxes in the Periodic Table, based on the properti ...
... The code letters A to Z have been assigned to represent the first 26 representative elements in the Periodic Table. The letters do not relate to the actual chemical symbols for these elements. Your challenge is to put the code letters in the correct boxes in the Periodic Table, based on the properti ...
Unit 1, Lecture 1
... The properties of electrons They are negatively charged. They have a spin (either up or down). The shapes of s and p orbitals s orbitals are spherically symmetric (“round”). p orbitals have two lobes with opposite sign along the axes. p orbitals are also triply degenerate. Atomic energy levels and e ...
... The properties of electrons They are negatively charged. They have a spin (either up or down). The shapes of s and p orbitals s orbitals are spherically symmetric (“round”). p orbitals have two lobes with opposite sign along the axes. p orbitals are also triply degenerate. Atomic energy levels and e ...
Transition metal compounds have interesting magnetic properties.
... The observed color is related to the amount of energy required to promote an electron. Compare " to energy absorbed. ...
... The observed color is related to the amount of energy required to promote an electron. Compare " to energy absorbed. ...
File - Science With BLT
... What is the formula for the compound formed by calcium ions and chloride ions? a. CaCl c. CaCl3 b. Ca2Cl d. CaCl2 What is the formula for the compound formed by lead(II) ions and chromate ions? a. PbCrO4 c. Pb2(CrO4)3 b. Pb2CrO4 d. Pb(CrO4)2 What is the formula for aluminum sulfate? a. AlSO4 c. Al2( ...
... What is the formula for the compound formed by calcium ions and chloride ions? a. CaCl c. CaCl3 b. Ca2Cl d. CaCl2 What is the formula for the compound formed by lead(II) ions and chromate ions? a. PbCrO4 c. Pb2(CrO4)3 b. Pb2CrO4 d. Pb(CrO4)2 What is the formula for aluminum sulfate? a. AlSO4 c. Al2( ...
Atomic Structure, Molecular Structure & Bonding
... – H is never central; C is often central 3. Draw in electrons to fulfill octet and duet rules – C “likes” 8 electrons; H “likes” 2 electrons 4. Count ve-’s and compare to #2 5. If too many e-’s, make a double bond 6. Calculate formal charge (FC) to double check structure – No or low FCs (e.g. +1) mo ...
... – H is never central; C is often central 3. Draw in electrons to fulfill octet and duet rules – C “likes” 8 electrons; H “likes” 2 electrons 4. Count ve-’s and compare to #2 5. If too many e-’s, make a double bond 6. Calculate formal charge (FC) to double check structure – No or low FCs (e.g. +1) mo ...
Molecular orbital diagram
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of molecular orbitals, although the electrons involved may be redistributed among the orbitals. This tool is very well suited for simple diatomic molecules such as dihydrogen, dioxygen, and carbon monoxide but becomes more complex when discussing even comparatively simple polyatomic molecules, such as methane. MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. They can also predict bond strength, as well as the electronic transitions that can take place.