Matter - Moodle
... help to ___________________and ______________________ substances • Characteristic Properties are the _______________or _____________________ characteristics the substance is known for Example: • Helium is light and non-flammable so it is good for _____________________ element A substance that cannot ...
... help to ___________________and ______________________ substances • Characteristic Properties are the _______________or _____________________ characteristics the substance is known for Example: • Helium is light and non-flammable so it is good for _____________________ element A substance that cannot ...
Things to Know to Pass the Chemistry Regents
... 15. Rutherford’s gold foil showed atoms small (+) nucleus & mostly empty space with e*few deflections = small (+) nucleus, most through = mostly empty space 16. Bohr’s model e- in orbits like planets around sun (orbit does NOT equal orbital) 17. Modern, wave-mechanical model e- in orbitals (most pro ...
... 15. Rutherford’s gold foil showed atoms small (+) nucleus & mostly empty space with e*few deflections = small (+) nucleus, most through = mostly empty space 16. Bohr’s model e- in orbits like planets around sun (orbit does NOT equal orbital) 17. Modern, wave-mechanical model e- in orbitals (most pro ...
Practice Multiple Choice Questions for the Chemistry Final Exam
... 93. What is the boiling point of water at standard pressure? a) 100 C b) 112 C c) 212 C d) 200 C 94. Which of the following is a pure substance? a) water b) milk c) soil d) concrete 95. Sugar in water is an example of which solute-solvent combination? a) gas-liquid b) liquid-liquid c) solid-liquid ...
... 93. What is the boiling point of water at standard pressure? a) 100 C b) 112 C c) 212 C d) 200 C 94. Which of the following is a pure substance? a) water b) milk c) soil d) concrete 95. Sugar in water is an example of which solute-solvent combination? a) gas-liquid b) liquid-liquid c) solid-liquid ...
- gst boces
... 15. Rutherford’s gold foil showed atoms small (+) nucleus & mostly empty space with e*few deflections = small (+) nucleus, most through = mostly empty space 16. Bohr’s model e- in orbits like planets around sun (orbit does NOT equal orbital) 17. Modern, wave-mechanical model e- in orbitals (most pro ...
... 15. Rutherford’s gold foil showed atoms small (+) nucleus & mostly empty space with e*few deflections = small (+) nucleus, most through = mostly empty space 16. Bohr’s model e- in orbits like planets around sun (orbit does NOT equal orbital) 17. Modern, wave-mechanical model e- in orbitals (most pro ...
File
... A) Their metallic properties decrease and their atomic radii decrease. B) Their metallic properties decrease and their atomic radii increase. C) Their metallic properties increase and their atomic radii decrease. D) Their metallic properties increase and their atomic radii increase. 39. An ion of wh ...
... A) Their metallic properties decrease and their atomic radii decrease. B) Their metallic properties decrease and their atomic radii increase. C) Their metallic properties increase and their atomic radii decrease. D) Their metallic properties increase and their atomic radii increase. 39. An ion of wh ...
Syracuse Syllabus
... understanding of math and algebra, including an understanding of decimals, exponents, logarithms, quadratics, and algebraic equations, is essential to success in this course (calculus is not required). You should not be taking remedial algebra concurrently with this course. Topics included are atomi ...
... understanding of math and algebra, including an understanding of decimals, exponents, logarithms, quadratics, and algebraic equations, is essential to success in this course (calculus is not required). You should not be taking remedial algebra concurrently with this course. Topics included are atomi ...
chem481chp
... 24 electrons would be needed to satisfy the valencies independently. 24-17 = 7. The odd number of electrons is a signal that there will be a place where we would normally expect to find another electron. When you have some experience with these situations, you probably will have no problem in assign ...
... 24 electrons would be needed to satisfy the valencies independently. 24-17 = 7. The odd number of electrons is a signal that there will be a place where we would normally expect to find another electron. When you have some experience with these situations, you probably will have no problem in assign ...
Biol 1020 Ch. 2 Chemistry
... http://serc.carleton.edu/images/usingdata/nasaimages/periodic-table.gif ...
... http://serc.carleton.edu/images/usingdata/nasaimages/periodic-table.gif ...
Bio 102 Lecture - chapter 2 The Chemical Basis of Life
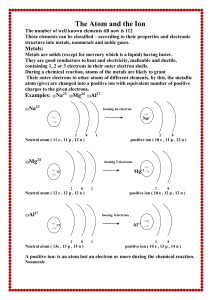
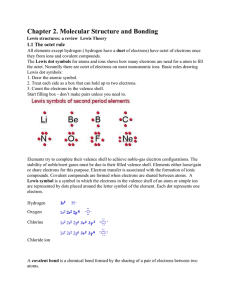
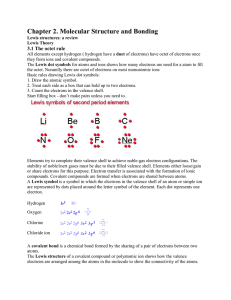
... If 3 or less electrons in the outer most shell – Tendency to donate electrons. If 5 or more electrons in the outer most shell – Tendency to receive electrons. A ‘chemical bond’ the force of attraction between atoms to attain stability. ...
... If 3 or less electrons in the outer most shell – Tendency to donate electrons. If 5 or more electrons in the outer most shell – Tendency to receive electrons. A ‘chemical bond’ the force of attraction between atoms to attain stability. ...
Cumulative Review, entire quarter
... 8. If needed, the formal charge on an atom is calculated as the number of valence (outer s & p) electrons in the neutral atom minus the number of electrons the atom has in the structure, counting one electron for each bond. The formal charges add to give the total charge on the structure. The most s ...
... 8. If needed, the formal charge on an atom is calculated as the number of valence (outer s & p) electrons in the neutral atom minus the number of electrons the atom has in the structure, counting one electron for each bond. The formal charges add to give the total charge on the structure. The most s ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 2
... The Energy Levels of Electrons • Energy is the capacity to cause change • Potential energy is the energy that matter has because of its location or structure • The electrons of an atom differ in their amounts of potential energy • An electron’s state of potential energy is called its energy level, ...
... The Energy Levels of Electrons • Energy is the capacity to cause change • Potential energy is the energy that matter has because of its location or structure • The electrons of an atom differ in their amounts of potential energy • An electron’s state of potential energy is called its energy level, ...
Name: (1 of 2) Math Set # 13 Protons, Neutrons, Electrons Proton
... An ionic bond is created between metals and nonmetals. This is because a metal in group 1 or 2 gives up electrons easily and nonmetals in groups 16 through 18 accept electrons easily. An ionic bond results in two or more ions being attracted to each other. The total charge of the molecule must be ze ...
... An ionic bond is created between metals and nonmetals. This is because a metal in group 1 or 2 gives up electrons easily and nonmetals in groups 16 through 18 accept electrons easily. An ionic bond results in two or more ions being attracted to each other. The total charge of the molecule must be ze ...
CHAPTER 1 Practice Exercises 1.1 x = 12.3 g Cd 1.3 2.24845 ×12 u
... A chemical reaction is a process whereby one or more chemical species is/are transformed into different chemical species. This generally involves the making and/or breaking of chemical ...
... A chemical reaction is a process whereby one or more chemical species is/are transformed into different chemical species. This generally involves the making and/or breaking of chemical ...
Biology\Ch 2 Chemistry
... A structural formula shows which atoms bond where and by sharing or “stealing” how many electrons. Ex: Chemical formula: CO2 Structural formula: O = C = O This shows carbon is between the two oxygen atoms and that 2 electrons are shared between each oxygen and the carbon. All atoms (except Helium a ...
... A structural formula shows which atoms bond where and by sharing or “stealing” how many electrons. Ex: Chemical formula: CO2 Structural formula: O = C = O This shows carbon is between the two oxygen atoms and that 2 electrons are shared between each oxygen and the carbon. All atoms (except Helium a ...
Molecular orbital diagram
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of molecular orbitals, although the electrons involved may be redistributed among the orbitals. This tool is very well suited for simple diatomic molecules such as dihydrogen, dioxygen, and carbon monoxide but becomes more complex when discussing even comparatively simple polyatomic molecules, such as methane. MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. They can also predict bond strength, as well as the electronic transitions that can take place.