chapter
... in a Bohr model • Valence electrons participate in chemical reactions • An electron can move to a higher orbital by receiving more energy, or give up energy and sink to a lower orbital • Changes in electron energy levels are important in energy conversions in organisms ...
... in a Bohr model • Valence electrons participate in chemical reactions • An electron can move to a higher orbital by receiving more energy, or give up energy and sink to a lower orbital • Changes in electron energy levels are important in energy conversions in organisms ...
specimen
... and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (OCR) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included, the publisher will be pleased to make amends at the earliest opportunity. OCR is part of the Cambridge Assessment ...
... and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (OCR) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included, the publisher will be pleased to make amends at the earliest opportunity. OCR is part of the Cambridge Assessment ...
AP Chemistry Second Semester Notes
... 2. ions with the same # of e: isoelectronic 1. electrons fill from low to high energy (same for all atoms) b. transition metal ions a. n: 1 < 2 < 3 < 4 < 5 < 6 < 7 1. transition metal lose s electrons first b. l: s < p < next energy level < d < f 2. may lose d electrons if it eliminates sublevel c. ...
... 2. ions with the same # of e: isoelectronic 1. electrons fill from low to high energy (same for all atoms) b. transition metal ions a. n: 1 < 2 < 3 < 4 < 5 < 6 < 7 1. transition metal lose s electrons first b. l: s < p < next energy level < d < f 2. may lose d electrons if it eliminates sublevel c. ...
Bonding - Berkeley City College
... 2. Central atoms from periods 3, 4, 5, …may have more than 8 valence electrons (expanded octet) 3. Molecules with odd number of electrons will contain unpaired electrons. ...
... 2. Central atoms from periods 3, 4, 5, …may have more than 8 valence electrons (expanded octet) 3. Molecules with odd number of electrons will contain unpaired electrons. ...
makeup2
... (B) A precipitate of BaF2(s) is formed when the solutions are mixed (C) Undissolved BaCl2 solid dissolves when the solutions are mixed (D) The concentrations of all the ions in the final solution are 2 x 10¯6 M. 42. Which aqueous solution should be neutral? (A) NH4Cl (B) Na(ClO4)2 (C) KCN (D) NaHSO4 ...
... (B) A precipitate of BaF2(s) is formed when the solutions are mixed (C) Undissolved BaCl2 solid dissolves when the solutions are mixed (D) The concentrations of all the ions in the final solution are 2 x 10¯6 M. 42. Which aqueous solution should be neutral? (A) NH4Cl (B) Na(ClO4)2 (C) KCN (D) NaHSO4 ...
ATOMS, MOLECULES and IONS
... Chemical properties of elements depend on the atomic number of the element. A complete Periodic Table lists the elements, their symbols and atomic numbers as well as atomic masses. The Periodic Table is arranged into rows, called periods and columns, which are called groups. The first period consist ...
... Chemical properties of elements depend on the atomic number of the element. A complete Periodic Table lists the elements, their symbols and atomic numbers as well as atomic masses. The Periodic Table is arranged into rows, called periods and columns, which are called groups. The first period consist ...
Atomic number
... decay and thereby lose energy. Why would nucleii tend to fall apart?? (Think about what protons do to each other) These unstable elements are called RADIOACTIVE. All elements with more than 83 protons are RADIOACTIVE. ...
... decay and thereby lose energy. Why would nucleii tend to fall apart?? (Think about what protons do to each other) These unstable elements are called RADIOACTIVE. All elements with more than 83 protons are RADIOACTIVE. ...
honors chem 6 day review packet
... Draw the electron configuration for the following: Potassium Sulfur Cobalt P−3 Mg+2 Valence electrons are electrons in the outer shell. Draw the dot diagrams for the following: Potassium ...
... Draw the electron configuration for the following: Potassium Sulfur Cobalt P−3 Mg+2 Valence electrons are electrons in the outer shell. Draw the dot diagrams for the following: Potassium ...
Year End Chemistry Review
... 8. Atomic number = # of _____ Mass number = # of ________ Isotopes are atoms of the same element, therefore having the same number of __________, but different number of ____ and a different _______number. ...
... 8. Atomic number = # of _____ Mass number = # of ________ Isotopes are atoms of the same element, therefore having the same number of __________, but different number of ____ and a different _______number. ...
FINAL EXAM Review Sheet / Study Guide Honors Chemistry
... 18) A gas occupies 5.50 m3 at -53.0°C, exerting a pressure of 400.0 kPa. What volume (in liters) would the gas occupy at 272.0°C if the pressure is increased to 5.91 atm. ...
... 18) A gas occupies 5.50 m3 at -53.0°C, exerting a pressure of 400.0 kPa. What volume (in liters) would the gas occupy at 272.0°C if the pressure is increased to 5.91 atm. ...
34.) Write out the set of four quantum numbers for the last electron
... 11.) Potassium iodide completely dissolved in water 12.) Soil 13.) Chromium * Classify as chemical or physical changes. 14.) Shredding cheese 15.) Melting cheese 16.) Digesting cheese 17.) Making salt from sodium and chlorine 18.) Sprinkling salt on french fries * In what group (give number) are eac ...
... 11.) Potassium iodide completely dissolved in water 12.) Soil 13.) Chromium * Classify as chemical or physical changes. 14.) Shredding cheese 15.) Melting cheese 16.) Digesting cheese 17.) Making salt from sodium and chlorine 18.) Sprinkling salt on french fries * In what group (give number) are eac ...
ch-4-earth-chemistry
... Example: A neutral sodium atom has a charge of zero (equal # of protons and neutrons) and only 1 valence electron. Once it loses that valence electron, it will have 8 valence electrons and be stable and most likely, not gain or lose anymore electrons. What would be the charge on a sodium atom that l ...
... Example: A neutral sodium atom has a charge of zero (equal # of protons and neutrons) and only 1 valence electron. Once it loses that valence electron, it will have 8 valence electrons and be stable and most likely, not gain or lose anymore electrons. What would be the charge on a sodium atom that l ...
Chapter 2 2012
... Chemical formulas summarize the identity and number of atoms in a compound. The molecular formula of a compound specifies the number of each kind of atom present in a single molecular unit of a compound. • The number of atoms of each element is written as a subscript; when only a one atom of an elem ...
... Chemical formulas summarize the identity and number of atoms in a compound. The molecular formula of a compound specifies the number of each kind of atom present in a single molecular unit of a compound. • The number of atoms of each element is written as a subscript; when only a one atom of an elem ...
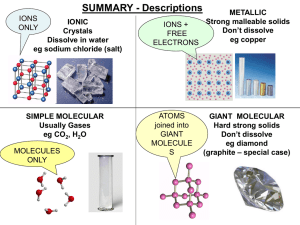
Earth Materials
... -Diamond and graphite are both made of carbon (C), but why is one the hardest substance on Earth and the other very soft ? ...
... -Diamond and graphite are both made of carbon (C), but why is one the hardest substance on Earth and the other very soft ? ...
NYS Regents Chemistry June 21, 2002
... 1: II. PERIODIC TABLE\1. Properties of Elements\A. Metals\1. Metals - (32) 2: II. PERIODIC TABLE\2. Valence Electrons\A. Electron / Ionic Configuration\2. Ionic Configuration - (10, 30) 2: II. PERIODIC TABLE\4. Properties of Periods\C. Electronegativity\1. Electronegativity - (11, 13) 1: II. PERIODI ...
... 1: II. PERIODIC TABLE\1. Properties of Elements\A. Metals\1. Metals - (32) 2: II. PERIODIC TABLE\2. Valence Electrons\A. Electron / Ionic Configuration\2. Ionic Configuration - (10, 30) 2: II. PERIODIC TABLE\4. Properties of Periods\C. Electronegativity\1. Electronegativity - (11, 13) 1: II. PERIODI ...
CHAPTER 1 Practice Exercises 1.1 12.3 g Cd 1.3 26.9814 u 1.5
... A chemical reaction is a process whereby one or more chemical species is/are transformed into different chemical species. This generally involves the making and/or breaking of chemical bonds. A product is the species formed in a chemical reaction. ...
... A chemical reaction is a process whereby one or more chemical species is/are transformed into different chemical species. This generally involves the making and/or breaking of chemical bonds. A product is the species formed in a chemical reaction. ...
Molecular orbital diagram
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of molecular orbitals, although the electrons involved may be redistributed among the orbitals. This tool is very well suited for simple diatomic molecules such as dihydrogen, dioxygen, and carbon monoxide but becomes more complex when discussing even comparatively simple polyatomic molecules, such as methane. MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. They can also predict bond strength, as well as the electronic transitions that can take place.