chemical change
... The evidence for a chemical reaction occurring, is the formation of a substance which is different from the original reactant or reactant, this is often accompanied by changes in energy, which are measured as temperature changes. Thus for the reaction of the silver metal sodium with the green/yellow ...
... The evidence for a chemical reaction occurring, is the formation of a substance which is different from the original reactant or reactant, this is often accompanied by changes in energy, which are measured as temperature changes. Thus for the reaction of the silver metal sodium with the green/yellow ...
Werner-type chromium compounds
... be described as Werner complex compounds acido groups containing an —XH radical, where characterized by having therein a nuclear triva X stands for oxygen or R-substituted nitrogen, lent chromium atom associated with an organic B being hydrogen or a hydrocarbon group, and acido group containing an — ...
... be described as Werner complex compounds acido groups containing an —XH radical, where characterized by having therein a nuclear triva X stands for oxygen or R-substituted nitrogen, lent chromium atom associated with an organic B being hydrogen or a hydrocarbon group, and acido group containing an — ...
Chem101 - Lecture 5 Introduction Introduction
... - Batteries work by using redox reactions that require the electrons flowing from the oxidation reaction to the reduction reaction to flow through a wire. ...
... - Batteries work by using redox reactions that require the electrons flowing from the oxidation reaction to the reduction reaction to flow through a wire. ...
2011 Assessment Report Chemistry 2
... concentration required its concentration to be as low as possible at the point of analysis. Question 8 required a unit conversion, but this was missed by many. Questions 15 and 16 assessed students’ ability to apply the supplied electrochemical data to the recharging of a secondary cell. Questions a ...
... concentration required its concentration to be as low as possible at the point of analysis. Question 8 required a unit conversion, but this was missed by many. Questions 15 and 16 assessed students’ ability to apply the supplied electrochemical data to the recharging of a secondary cell. Questions a ...
chapter 9: aqueous solutions
... 1. write the separate aqueous ions (including their correct charges) on the right side 2. write the formula of the compound followed by an arrow 3. balance using coefficients 4. add state symbols (state of pure substance on the left, ((s) usually), (aq) for ions on the right) Example 1: Solid Sodium ...
... 1. write the separate aqueous ions (including their correct charges) on the right side 2. write the formula of the compound followed by an arrow 3. balance using coefficients 4. add state symbols (state of pure substance on the left, ((s) usually), (aq) for ions on the right) Example 1: Solid Sodium ...
SAMPLE AP CHEMISTRY EXAM QUESTIONS
... (a) Liquid oxygen is attracted to a strong magnet, whereas liquid nitrogen is not. (b) The SO2 molecule has a dipole moment, whereas the C O2 molecule has no dipole moment. Include the Lewis (electron-dot) structures in your explanation. (c) Halides of cobalt(II) are colored, whereas halides of zinc ...
... (a) Liquid oxygen is attracted to a strong magnet, whereas liquid nitrogen is not. (b) The SO2 molecule has a dipole moment, whereas the C O2 molecule has no dipole moment. Include the Lewis (electron-dot) structures in your explanation. (c) Halides of cobalt(II) are colored, whereas halides of zinc ...
Mathematical Operations
... In these examples the common logarithm can be obtained by inspection. However, it is not possible to obtain the logarithm of a number such as 31.25 by inspection. The logarithm of 31.25 is the number x that satisfies the following ...
... In these examples the common logarithm can be obtained by inspection. However, it is not possible to obtain the logarithm of a number such as 31.25 by inspection. The logarithm of 31.25 is the number x that satisfies the following ...
Net Ionic Equations
... this step. Be sure the equation is balanced for both atoms and charge. • Write the net ionic equation by removing the spectators. Reduce coefficients to lowest terms. Be sure the equation is balanced for both atoms and charge. ...
... this step. Be sure the equation is balanced for both atoms and charge. • Write the net ionic equation by removing the spectators. Reduce coefficients to lowest terms. Be sure the equation is balanced for both atoms and charge. ...
Balancing reaction equations, oxidation state, and reduction
... Reduce coefficients to lowest terms. Be sure the equation is balanced for both atoms and charge. ...
... Reduce coefficients to lowest terms. Be sure the equation is balanced for both atoms and charge. ...
MSTA WOW Chemistry
... • The cylinder will get hot, so let it cool before handling. • This demonstration can be easily and safely scaled up for larger audiences. A 500-mL or 1-L Pyrex® graduated cylinder works well in this case. You may have heard of this demonstration also referred to as elephant toothpaste. • The sligh ...
... • The cylinder will get hot, so let it cool before handling. • This demonstration can be easily and safely scaled up for larger audiences. A 500-mL or 1-L Pyrex® graduated cylinder works well in this case. You may have heard of this demonstration also referred to as elephant toothpaste. • The sligh ...
Stoichiometry Notes
... accurately the volume of a solution of unknown concentration and react with a solution of known concentration. The volume of the known solution is determined by finding what is called the EQUIVALENCE POINT (stoichiometric point). This equivalence point occurs when all the ratio of moles of each spec ...
... accurately the volume of a solution of unknown concentration and react with a solution of known concentration. The volume of the known solution is determined by finding what is called the EQUIVALENCE POINT (stoichiometric point). This equivalence point occurs when all the ratio of moles of each spec ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... compounds are molecular. Two, HNO3 and HCHO2 , are acids. Nitric acid, HNO3 is a common strong acid, as shown in Table 4.2, and therefore is a strong electrolyte. Because most acids are weak acids, our best guess would be that HCHO2 is a weak acid (weak electrolyte). This is correct. The remaining m ...
... compounds are molecular. Two, HNO3 and HCHO2 , are acids. Nitric acid, HNO3 is a common strong acid, as shown in Table 4.2, and therefore is a strong electrolyte. Because most acids are weak acids, our best guess would be that HCHO2 is a weak acid (weak electrolyte). This is correct. The remaining m ...
chapter 4 - reactions in solution
... attractions of the ions for each other and the interactions of the ions for water molecules. If ion-dipole interactions are strong, compounds will not dissolve in water. Salt does not dissolve in nonpolar solvent, such as gasoline, because interactions between solvent molecules and ions are very w ...
... attractions of the ions for each other and the interactions of the ions for water molecules. If ion-dipole interactions are strong, compounds will not dissolve in water. Salt does not dissolve in nonpolar solvent, such as gasoline, because interactions between solvent molecules and ions are very w ...
chapter 7-Chemical Bonding
... Ionic Compounds • Small ions with high ionic charges have large Coulombic forces of attraction. • Large ions with small ionic charges have small Coulombic forces of attraction. • Use this information, plus the periodicity rules from Chapter 6, to arrange these compounds in order of increasing attrac ...
... Ionic Compounds • Small ions with high ionic charges have large Coulombic forces of attraction. • Large ions with small ionic charges have small Coulombic forces of attraction. • Use this information, plus the periodicity rules from Chapter 6, to arrange these compounds in order of increasing attrac ...
Homo-coupling of terminal alkynes on a noble metal surface
... coordinates. We expect to find transition states yielding smaller barriers by optimizing the tautomer geometry, for example, with respect to its conformation, the position of the H atoms or its registry with the substrate, which has not yet been done due to the related substantial computational effor ...
... coordinates. We expect to find transition states yielding smaller barriers by optimizing the tautomer geometry, for example, with respect to its conformation, the position of the H atoms or its registry with the substrate, which has not yet been done due to the related substantial computational effor ...
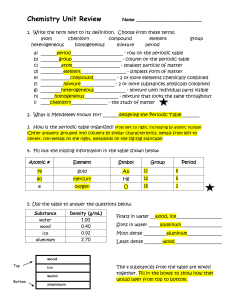
Classification of
... 2 other elements in this same group: _H, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr________ 8. Examine the pictures of substances shown below. Label each substance as an element, compound or mixture. ...
... 2 other elements in this same group: _H, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr________ 8. Examine the pictures of substances shown below. Label each substance as an element, compound or mixture. ...
ch14
... states. They may lose either the np electron only, or both the np and ns electrons. The lower oxidation state becomes increasingly prominent down the group, since the ns2 electrons form an inert pair. Oxides of the element in the lower oxidation state are more basic than oxides in the higher oxidati ...
... states. They may lose either the np electron only, or both the np and ns electrons. The lower oxidation state becomes increasingly prominent down the group, since the ns2 electrons form an inert pair. Oxides of the element in the lower oxidation state are more basic than oxides in the higher oxidati ...
General Chemistry Stoichiometry Notes
... Important Vocabulary Terms Theoretical yield- the maximum amount of product that can be produced from a given amount of reactant. ...
... Important Vocabulary Terms Theoretical yield- the maximum amount of product that can be produced from a given amount of reactant. ...
Slide 1
... The observations and deductions come in pairs of activities. One involves inorganic chemistry and the other organic chemistry. The inorganic exercise typically involves the analysis of a so-called “Double Salt”. One of the ions in these mixed salts is common to both salts in most cases. Here are so ...
... The observations and deductions come in pairs of activities. One involves inorganic chemistry and the other organic chemistry. The inorganic exercise typically involves the analysis of a so-called “Double Salt”. One of the ions in these mixed salts is common to both salts in most cases. Here are so ...
Chemistry 1B General Chemistry Exp 1 Spring 2017
... labels. Don’t forget your units when showing an example calculation. Since many calculations are repetitive, you can continue to work them out on a separate piece of white paper to include with your report. Observations: These are a crucial part of your scientific endeavors. Depending on the experim ...
... labels. Don’t forget your units when showing an example calculation. Since many calculations are repetitive, you can continue to work them out on a separate piece of white paper to include with your report. Observations: These are a crucial part of your scientific endeavors. Depending on the experim ...
Table of contents
... ◦ Halogens are highly reactive nonmetals (form -1 anions). Highly variable physical properties. Low boiling points. Gases at room temperature. ◦ Transition elements – very hard, very high melting and boiling points. Very malleable and conducts electricity since d electrons are loose. Low ionization ...
... ◦ Halogens are highly reactive nonmetals (form -1 anions). Highly variable physical properties. Low boiling points. Gases at room temperature. ◦ Transition elements – very hard, very high melting and boiling points. Very malleable and conducts electricity since d electrons are loose. Low ionization ...
Unit 13: Electrochemistry (Link to Prentice Hall Text: Chapters 22
... A car battery powers the car through a spontaneous reaction, but what can you do if the battery dies? (c) To coat one metal on top of another one, as with jewelry, or exhaust pipes. a. To make something look more expensive or shinier b. To improve corrosion resistance ...
... A car battery powers the car through a spontaneous reaction, but what can you do if the battery dies? (c) To coat one metal on top of another one, as with jewelry, or exhaust pipes. a. To make something look more expensive or shinier b. To improve corrosion resistance ...
Syracuse University
... INTRODUCTION AND LEARNING GOALS - Whether we like it or not, we live in a dynamic chemical universe. Chemical properties and reactions influence our every action (and reaction). We rely upon chemical properties and reactions to both sustain and cultivate our lives. This course is intended to provide ...
... INTRODUCTION AND LEARNING GOALS - Whether we like it or not, we live in a dynamic chemical universe. Chemical properties and reactions influence our every action (and reaction). We rely upon chemical properties and reactions to both sustain and cultivate our lives. This course is intended to provide ...
Which notation represents an atom of sodium
... a) The equation represents a physical change, with the product and reactants having different chemical properties. b) The equation represents a physical change, with the product and reactants having identical chemical properties. c) The equation represents a chemical change, with the product and rea ...
... a) The equation represents a physical change, with the product and reactants having different chemical properties. b) The equation represents a physical change, with the product and reactants having identical chemical properties. c) The equation represents a chemical change, with the product and rea ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.