Syracuse University
... INTRODUCTION AND LEARNING GOALS - Whether we like it or not, we live in a dynamic chemical universe. Chemical properties and reactions influence our every action (and reaction). We rely upon chemical properties and reactions to both sustain and cultivate our lives. This course is intended to provide ...
... INTRODUCTION AND LEARNING GOALS - Whether we like it or not, we live in a dynamic chemical universe. Chemical properties and reactions influence our every action (and reaction). We rely upon chemical properties and reactions to both sustain and cultivate our lives. This course is intended to provide ...
Study Modules XII Chemistry 2017
... Interstitial defects: - i) some constituent particles occupy the interstitial sites of the crystal. ii) This defect increases the density of the crystal. Ionic solids show Stoichiometric defects as Frenkel and Schottky defects Frenkel Defect: The ion (smaller ion, usually cation) is dislocated (move ...
... Interstitial defects: - i) some constituent particles occupy the interstitial sites of the crystal. ii) This defect increases the density of the crystal. Ionic solids show Stoichiometric defects as Frenkel and Schottky defects Frenkel Defect: The ion (smaller ion, usually cation) is dislocated (move ...
PAGE PROOFS
... Chemists make sense out of the huge number of chemical reactions by classifying them into groups. Examples of such groupings are polymerisation reactions, which you have already studied in Unit 1, and precipitation reactions, which you met in chapter 000. Often these groups are so large that they ar ...
... Chemists make sense out of the huge number of chemical reactions by classifying them into groups. Examples of such groupings are polymerisation reactions, which you have already studied in Unit 1, and precipitation reactions, which you met in chapter 000. Often these groups are so large that they ar ...
Strumenti tutor LIM
... A chemical transformation takes place when....................(atoms in the reactants are rearranged to form new substabces)(old bonds are broken and new bonds are formed)( at least one new substance is formed) We can realize that a chemical reaction is taking place when...........( there is a chang ...
... A chemical transformation takes place when....................(atoms in the reactants are rearranged to form new substabces)(old bonds are broken and new bonds are formed)( at least one new substance is formed) We can realize that a chemical reaction is taking place when...........( there is a chang ...
Stoichiometry – AP - Waukee Community School District Blogs
... making ammonia for fertilizer production from the nitrogen in the air reacted with hydrogen gas. The hydrogen gas is obtained from the reaction of methane with water vapor. This process has saved millions from starvation. Suppose 25.0 kg of nitrogen reacts with 5.00 kg of hydrogen to form ammonia. W ...
... making ammonia for fertilizer production from the nitrogen in the air reacted with hydrogen gas. The hydrogen gas is obtained from the reaction of methane with water vapor. This process has saved millions from starvation. Suppose 25.0 kg of nitrogen reacts with 5.00 kg of hydrogen to form ammonia. W ...
fahad h. ahmad - Fahad`s Academy
... 3. The strong forces holding ionic compounds prevents them to evaporate easily. Hence, ionic compounds have no smell. 4. Solid ionic compounds don’t conduct electricity but they do when they are aqueous or molten. This is because in liquid/aqueous state the ions which conduct electricity are free to ...
... 3. The strong forces holding ionic compounds prevents them to evaporate easily. Hence, ionic compounds have no smell. 4. Solid ionic compounds don’t conduct electricity but they do when they are aqueous or molten. This is because in liquid/aqueous state the ions which conduct electricity are free to ...
Chapter 15 PPT
... Thermodynamics is the study of the changes in energy and transfers of energy that accompany chemical and physical processes. In this chapter we will address 3 fundamental questions. Will two (or more) substances react when they are mixed under specified conditions? If they do react, what energy chan ...
... Thermodynamics is the study of the changes in energy and transfers of energy that accompany chemical and physical processes. In this chapter we will address 3 fundamental questions. Will two (or more) substances react when they are mixed under specified conditions? If they do react, what energy chan ...
Redox
... to realize the role of oxygen in burning. Understanding the connection of corrosion (rusting, tarnishing, etc.) and burning is an even more recent development. Reactions of substances with oxygen, whether they were the explosive combustion of gunpowder, the burning of wood, or the slow corrosion of ...
... to realize the role of oxygen in burning. Understanding the connection of corrosion (rusting, tarnishing, etc.) and burning is an even more recent development. Reactions of substances with oxygen, whether they were the explosive combustion of gunpowder, the burning of wood, or the slow corrosion of ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
... FIGURE 2–16 Conjugate acid-base pairs consist of a proton donor and a proton acceptor. Some compounds, such as acetic acid and ammonium ion, are monoprotic; they can give up only one proton. Others are diprotic (H2CO3 (carbonic acid) and glycine) or triprotic ...
... FIGURE 2–16 Conjugate acid-base pairs consist of a proton donor and a proton acceptor. Some compounds, such as acetic acid and ammonium ion, are monoprotic; they can give up only one proton. Others are diprotic (H2CO3 (carbonic acid) and glycine) or triprotic ...
AP 2005 Chemistry Free-Response Questions
... Your responses to the rest of the questions in this part of the examination will be graded on the basis of the accuracy and relevance of the information cited. Explanations should be clear and well organized. Examples and equations may be included in your responses where appropriate. Specific answer ...
... Your responses to the rest of the questions in this part of the examination will be graded on the basis of the accuracy and relevance of the information cited. Explanations should be clear and well organized. Examples and equations may be included in your responses where appropriate. Specific answer ...
SCH4U Exam Review
... 14. A solution was made by dissolving 0.837 g Ba(OH)2 in 100 mL final volume. If Ba(OH)2 is fully broken up into its ions, what is the pOH and the pH of the solution? ANS: 1.01, 12.99 15. A soft drink was put on the market with [H+] = 1.4x10-5 mol/L. What is its pH? ...
... 14. A solution was made by dissolving 0.837 g Ba(OH)2 in 100 mL final volume. If Ba(OH)2 is fully broken up into its ions, what is the pOH and the pH of the solution? ANS: 1.01, 12.99 15. A soft drink was put on the market with [H+] = 1.4x10-5 mol/L. What is its pH? ...
CHEMISTRY SEC 06 SYLLABUS
... 4. Scheme of Assessment The examination will consist of two written papers, each of two hours’ duration, and an assessment of practical work in chemistry. Questions will be set in English and must be answered in English. The examination will be structured as follows: Paper I consists of a written pa ...
... 4. Scheme of Assessment The examination will consist of two written papers, each of two hours’ duration, and an assessment of practical work in chemistry. Questions will be set in English and must be answered in English. The examination will be structured as follows: Paper I consists of a written pa ...
aq - Byron High School
... HNO3 and HCHO2 , are acids. Nitric acid, HNO3 is a common strong acid, as shown in Table 4.2, and therefore is a strong electrolyte. Because most acids are weak acids, our best guess would be that HCHO2 is a weak acid (weak electrolyte). This is correct. The remaining molecular compound, C2H5OH is n ...
... HNO3 and HCHO2 , are acids. Nitric acid, HNO3 is a common strong acid, as shown in Table 4.2, and therefore is a strong electrolyte. Because most acids are weak acids, our best guess would be that HCHO2 is a weak acid (weak electrolyte). This is correct. The remaining molecular compound, C2H5OH is n ...
GCE Chemistry Question Paper Unit 05 - Energetics, Redox
... Use the graph to calculate a value for the slope (gradient) of the line. Give the units of this slope and the symbol for the thermodynamic quantity that this slope represents. Value of the slope ......................................................................................................... ...
... Use the graph to calculate a value for the slope (gradient) of the line. Give the units of this slope and the symbol for the thermodynamic quantity that this slope represents. Value of the slope ......................................................................................................... ...
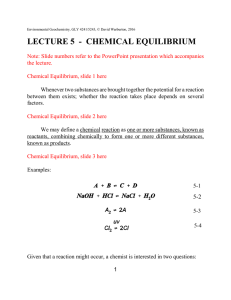
LECTURE 5 - CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
... equilibrium. Rather, it is said to be metastable. A metastable system is one that changes so slowly that it appears stable. Metastable systems are not at equilibrium but may persist for very long times. The reason that metastable systems exist is the presence of a significant kinetic barrier. Kineti ...
... equilibrium. Rather, it is said to be metastable. A metastable system is one that changes so slowly that it appears stable. Metastable systems are not at equilibrium but may persist for very long times. The reason that metastable systems exist is the presence of a significant kinetic barrier. Kineti ...
An Introduction to Redox
... Description of Lesson: The purpose of this lesson is to introduce students to chemical reactions that involved the simultaneous processes of oxidation and reduction as electrons are transferred from one chemical species to another. Students are placed in cooperative groups to process through t ...
... Description of Lesson: The purpose of this lesson is to introduce students to chemical reactions that involved the simultaneous processes of oxidation and reduction as electrons are transferred from one chemical species to another. Students are placed in cooperative groups to process through t ...
CHEMISTRY SEC 06 SYLLABUS
... 4. Scheme of Assessment The examination will consist of two written papers, each of two hours’ duration, and an assessment of practical work in chemistry. Questions will be set in English and must be answered in English. The examination will be structured as follows: Paper I consists of a written pa ...
... 4. Scheme of Assessment The examination will consist of two written papers, each of two hours’ duration, and an assessment of practical work in chemistry. Questions will be set in English and must be answered in English. The examination will be structured as follows: Paper I consists of a written pa ...
CHEMISTRY SEC 06 SYLLABUS
... 4. Scheme of Assessment The examination will consist of two written papers, each of two hours’ duration, and an assessment of practical work in chemistry. Questions will be set in English and must be answered in English. The examination will be structured as follows: Paper I consists of a written pa ...
... 4. Scheme of Assessment The examination will consist of two written papers, each of two hours’ duration, and an assessment of practical work in chemistry. Questions will be set in English and must be answered in English. The examination will be structured as follows: Paper I consists of a written pa ...
CHEMISTRY SEC 06 SYLLABUS
... 4. Scheme of Assessment The examination will consist of two written papers, each of two hours’ duration, and an assessment of practical work in chemistry. Questions will be set in English and must be answered in English. The examination will be structured as follows: Paper I consists of a written pa ...
... 4. Scheme of Assessment The examination will consist of two written papers, each of two hours’ duration, and an assessment of practical work in chemistry. Questions will be set in English and must be answered in English. The examination will be structured as follows: Paper I consists of a written pa ...
Analyze
... (b) Because two moles of CO are produced from CO 2 (which is not an element) and C, this reaction does not represent H f° . (c) Because two substances are produced and one of the reactants (CO 2) is not an element, this reaction does not represent H f° . (d) One mole of CH4 is produced from elemen ...
... (b) Because two moles of CO are produced from CO 2 (which is not an element) and C, this reaction does not represent H f° . (c) Because two substances are produced and one of the reactants (CO 2) is not an element, this reaction does not represent H f° . (d) One mole of CH4 is produced from elemen ...
- skv institute
... (iii) Contact surface area of molecule. 2. State the types of van der Waal’s forces. (i) Dispersion forces or London forces ...
... (iii) Contact surface area of molecule. 2. State the types of van der Waal’s forces. (i) Dispersion forces or London forces ...
`A` LEVEL H2 CHEMISTRY ORGANIC REACTIONS SUMMARY By
... Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: (a) identify and describe protons, neutrons and electrons in terms of their relative charges and relative masses (b) deduce the behaviour of beams of protons, neutrons and electrons in an electric field (c) describe the distribution of mass and charges ...
... Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: (a) identify and describe protons, neutrons and electrons in terms of their relative charges and relative masses (b) deduce the behaviour of beams of protons, neutrons and electrons in an electric field (c) describe the distribution of mass and charges ...
2009 U. S. NATIONAL CHEMISTRY OLYMPIAD
... c. Explain why all elements and compounds have positive S˚ values at 25˚C. d. Give an example of a chemical species that does not have a positive S˚ value at 25 ˚C and explain why its standard entropy is not positive. a. ΔGo values refer to standard conditions including 1 M concentrations. Reactions ...
... c. Explain why all elements and compounds have positive S˚ values at 25˚C. d. Give an example of a chemical species that does not have a positive S˚ value at 25 ˚C and explain why its standard entropy is not positive. a. ΔGo values refer to standard conditions including 1 M concentrations. Reactions ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.