chemical reaction equation - parmod cobra insititution.
... Types of chemical reaction:- Chemical reaction occurs as a result of breaking and making of bonds resulting in surface. The ribbons is before burning to remove the layer of these compounds so that reactions are classified in different types. They are – (1) Combination reaction or synthesis reaction ...
... Types of chemical reaction:- Chemical reaction occurs as a result of breaking and making of bonds resulting in surface. The ribbons is before burning to remove the layer of these compounds so that reactions are classified in different types. They are – (1) Combination reaction or synthesis reaction ...
Ceramics for catalysis
... “non-traditional” ceramics applications and is now a burgeoning topic of research. In this Review, the principles of heterogeneous catalysis are presented and discussed in terms of surface reactivity and catalyst structure in general. Catalytic selectivity, rate enhancement and catalyst deactivation ...
... “non-traditional” ceramics applications and is now a burgeoning topic of research. In this Review, the principles of heterogeneous catalysis are presented and discussed in terms of surface reactivity and catalyst structure in general. Catalytic selectivity, rate enhancement and catalyst deactivation ...
BIOC203W1_Lecture Slides_Enzymes
... Consider, a molecule has 2 hydrogen atoms Xa and Xb, a group Y and another group Z bonded tetrahedrally to a carbon atom. Now suppose the enzyme binds 3 groups of this substrate i.e. Xa, Y and Z at 3 complimentary sites. In contrast the other combination Xb, Y and Z cannot be bonded to this ac ...
... Consider, a molecule has 2 hydrogen atoms Xa and Xb, a group Y and another group Z bonded tetrahedrally to a carbon atom. Now suppose the enzyme binds 3 groups of this substrate i.e. Xa, Y and Z at 3 complimentary sites. In contrast the other combination Xb, Y and Z cannot be bonded to this ac ...
Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
... Oxidizing Agent – a chemical substance that oxidizes (removes electrons from) other substances in a chemical reaction. In the process of oxidizing something, the oxidant becomes reduced; it’s oxidation state decreases. Reducing Agent – a chemical substance that reduces (loses electrons to) other sub ...
... Oxidizing Agent – a chemical substance that oxidizes (removes electrons from) other substances in a chemical reaction. In the process of oxidizing something, the oxidant becomes reduced; it’s oxidation state decreases. Reducing Agent – a chemical substance that reduces (loses electrons to) other sub ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... the instructions from the proctor for completing the student information on your answer sheet. Record your answers to the Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice questions on this separate answer sheet. Record your answers for the questions in Part B–2 and Part C in your separate answer booklet. Be sure ...
... the instructions from the proctor for completing the student information on your answer sheet. Record your answers to the Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice questions on this separate answer sheet. Record your answers for the questions in Part B–2 and Part C in your separate answer booklet. Be sure ...
Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Solids 21 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
... to the Langmuir method may be performed at considerably lower pressures. The Langmuir Method is often applied in order to increase the rate of the weight loss (especially suitable for substances with high sublimation energies). Examples: Fig. 3.5.: shows the resulting activities of Cu - Ge alloys. ...
... to the Langmuir method may be performed at considerably lower pressures. The Langmuir Method is often applied in order to increase the rate of the weight loss (especially suitable for substances with high sublimation energies). Examples: Fig. 3.5.: shows the resulting activities of Cu - Ge alloys. ...
Unit 6 Study Guide - Dorman High School
... B) A metal-nonmetal reaction can always be assumed to be an oxidation-reduction reaction. C) Two nonmetals can undergo an oxidation-reduction reaction. D) When two nonmetals react, the compound formed is ionic. E) A metal-nonmetal reaction involves electron transfer. ...
... B) A metal-nonmetal reaction can always be assumed to be an oxidation-reduction reaction. C) Two nonmetals can undergo an oxidation-reduction reaction. D) When two nonmetals react, the compound formed is ionic. E) A metal-nonmetal reaction involves electron transfer. ...
MASS-INDEPENDENT ISOTOPE FRACTIONATION OF CHROMIUM
... Introduction: Recently, the classic theory of stable isotope fractionation of the Bigeleisen-Mayer equation [1] has been expanded by the original author to include the mass-independent term named the nuclear field shift effect [2]. The improved theory successfully explained the observed non-linear i ...
... Introduction: Recently, the classic theory of stable isotope fractionation of the Bigeleisen-Mayer equation [1] has been expanded by the original author to include the mass-independent term named the nuclear field shift effect [2]. The improved theory successfully explained the observed non-linear i ...
Chapter 18: The Representative Elements The Representative
... Chlorine is more soluble in water than fluorine. As a result even though there is more F present in the Earth’s crust the oceans are salty with chlorides rather than fluorides. Cl is one of the most heavily manufactured chemicals. It is a strong oxidizing agent. Chapter 18: The Representative Elemen ...
... Chlorine is more soluble in water than fluorine. As a result even though there is more F present in the Earth’s crust the oceans are salty with chlorides rather than fluorides. Cl is one of the most heavily manufactured chemicals. It is a strong oxidizing agent. Chapter 18: The Representative Elemen ...
RES6_chem_stretch_challenge
... reagents for the reaction. You must also write the correct equations and products. Stretch and Challenge questions often allow you to demonstrate knowledge and understanding from different parts of the specification. Again, you first need to identify the functional groups present in the molecule and ...
... reagents for the reaction. You must also write the correct equations and products. Stretch and Challenge questions often allow you to demonstrate knowledge and understanding from different parts of the specification. Again, you first need to identify the functional groups present in the molecule and ...
Course Pack3 Phase Diagrams
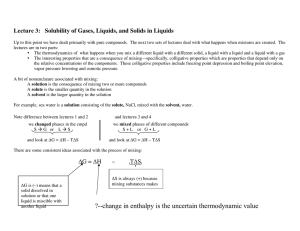
... ∆Hsoln is (+) for NaCl in H2O ∆Hsoln is (–) for Na2SO4 in H2O ∆Hsoln is (–) for O2 in H2O Consider the case that ∆Hmix is negative: since ∆Smix is positive then ∆Gsoln will have to be negative and the reaction happens. Now consider the case that ∆Hmix is positive: in this case the spontaneity of the ...
... ∆Hsoln is (+) for NaCl in H2O ∆Hsoln is (–) for Na2SO4 in H2O ∆Hsoln is (–) for O2 in H2O Consider the case that ∆Hmix is negative: since ∆Smix is positive then ∆Gsoln will have to be negative and the reaction happens. Now consider the case that ∆Hmix is positive: in this case the spontaneity of the ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... Convert the fractional ratios for each element into whole numbers by multiplying all the ratios by the same number. The resulting numbers are the subscripts for the each element in the empirical formula. ...
... Convert the fractional ratios for each element into whole numbers by multiplying all the ratios by the same number. The resulting numbers are the subscripts for the each element in the empirical formula. ...
Enzymes - WordPress.com
... animals, and prokaryotes all depend on enzymes to break down large molecules or build new ones. ENZYMES are proteins that act as catalysts and help chemical reactions occur. In order for these chemical reactions to occur energy is needed. The amount of energy needed to start a chemical reaction is c ...
... animals, and prokaryotes all depend on enzymes to break down large molecules or build new ones. ENZYMES are proteins that act as catalysts and help chemical reactions occur. In order for these chemical reactions to occur energy is needed. The amount of energy needed to start a chemical reaction is c ...
vsepr_lite_oct_2011 - chemistry11crescentsummer
... The lone pair of electrons on the central atom, N in this case, has the same spatial requirements as a pair of electrons involved in a chemical bond. This means that the overall, or electronic geometry of ammonia will also be tetrahedral. If we look only at the chemical bonds—and not at the lone pa ...
... The lone pair of electrons on the central atom, N in this case, has the same spatial requirements as a pair of electrons involved in a chemical bond. This means that the overall, or electronic geometry of ammonia will also be tetrahedral. If we look only at the chemical bonds—and not at the lone pa ...
GROUP 13 ELEMENTS -THE BORON FAMILY -
... important because it forms gallium arsenide (GaAs), which can convert light directly into electricity. Also due to thermite reaction, aluminum can extract oxygen from water and hydrogen is released. However, as mentioned above, aluminum forms a protective coat in the presence of water. By combining ...
... important because it forms gallium arsenide (GaAs), which can convert light directly into electricity. Also due to thermite reaction, aluminum can extract oxygen from water and hydrogen is released. However, as mentioned above, aluminum forms a protective coat in the presence of water. By combining ...
Chemistry - Higher tier - Paper 2 - Sample assessment material
... In 1879, Thomas Edison discovered that using a carbon filament in a glass bulb filled with argon improved the design of the original bulbs. He found that this bulb lasted 40 hours. ...
... In 1879, Thomas Edison discovered that using a carbon filament in a glass bulb filled with argon improved the design of the original bulbs. He found that this bulb lasted 40 hours. ...
03 Inorg. drugs with acid-base prop. IOC of С,Al, Ba,Ag
... carbonization white precipitate on the filter Sulphates A. (BrPh, SPU). Reaction with barium chloride solution in the hydrochloricacid medium. Dissolve about 45 mg of the substance to be examined in 5 ml of water R or use 5 ml of the prescribed solution. Add 1 ml of dilute hydrochloric acid R and 1 ...
... carbonization white precipitate on the filter Sulphates A. (BrPh, SPU). Reaction with barium chloride solution in the hydrochloricacid medium. Dissolve about 45 mg of the substance to be examined in 5 ml of water R or use 5 ml of the prescribed solution. Add 1 ml of dilute hydrochloric acid R and 1 ...
GCE Getting Started - Edexcel
... Carry out research to produce a timeline of events in the development of our current understanding of the structure of the atom. Build a model to represent Geiger and Muller’s experiment to confirm most of an atom is ...
... Carry out research to produce a timeline of events in the development of our current understanding of the structure of the atom. Build a model to represent Geiger and Muller’s experiment to confirm most of an atom is ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.