www.xtremepapers.net
... Choose the one you consider correct and record your choice in soft pencil on the separate answer sheet. Read the instructions on the answer sheet very carefully. Each correct answer will score one mark. A mark will not be deducted for a wrong answer. Any rough working should be done in this booklet. ...
... Choose the one you consider correct and record your choice in soft pencil on the separate answer sheet. Read the instructions on the answer sheet very carefully. Each correct answer will score one mark. A mark will not be deducted for a wrong answer. Any rough working should be done in this booklet. ...
File
... 55. Which pair of solutions forms a buffer when equal volumes of each are mixed? A) 0.20 M HCl and 0.20 M NaCl C) 0.20 M HCl and 0.20 M NH3 B) 0.40 M HC2H3O2 and 0.20 M NaOH D) 0.40 M HCl and 0.20 M NH3 56. A student is attempting to standardize a NaOH solution with a 0.500 molar solution of oxalic ...
... 55. Which pair of solutions forms a buffer when equal volumes of each are mixed? A) 0.20 M HCl and 0.20 M NaCl C) 0.20 M HCl and 0.20 M NH3 B) 0.40 M HC2H3O2 and 0.20 M NaOH D) 0.40 M HCl and 0.20 M NH3 56. A student is attempting to standardize a NaOH solution with a 0.500 molar solution of oxalic ...
Chemical Reactions - We can`t sign you in
... A halogen displacement reaction occurs when a halogen is added to a metal halide containing a less reactive halogen. The less reactive halogen is displaced from the compound and the more reactive halogen bonds with the metal to form a new metal halide. ...
... A halogen displacement reaction occurs when a halogen is added to a metal halide containing a less reactive halogen. The less reactive halogen is displaced from the compound and the more reactive halogen bonds with the metal to form a new metal halide. ...
C14_-_Organic_Chemistry
... Identify and draw the structures of methane, ethane, ethene, and ethanol. ...
... Identify and draw the structures of methane, ethane, ethene, and ethanol. ...
Reactions Flowchart
... • Metal Hydroxide Metal oxide + H2O Ca(OH)2 CaO + H2O • Metal Carbonate Metal oxide + CO2 Li2CO3 LiO + CO2 ...
... • Metal Hydroxide Metal oxide + H2O Ca(OH)2 CaO + H2O • Metal Carbonate Metal oxide + CO2 Li2CO3 LiO + CO2 ...
Grade 11 Chemistry E.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 23. Describe the different types of intermolecular forces. 24. Balance the following equations. a. CF4(l) → C(s) + F2(g) b. H2SO4(aq) + KOH(aq) → KHSO4(aq) + H2O(l) c. ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) → Zn(s) + HCl(aq) d. SO2(g) + H2O(l) + O2(g) → H2SO4(aq) e. Li(s) + H2O(l) → LiOH(aq) + H2(g) f. H2CO3(aq) → H2O(l ...
... 23. Describe the different types of intermolecular forces. 24. Balance the following equations. a. CF4(l) → C(s) + F2(g) b. H2SO4(aq) + KOH(aq) → KHSO4(aq) + H2O(l) c. ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) → Zn(s) + HCl(aq) d. SO2(g) + H2O(l) + O2(g) → H2SO4(aq) e. Li(s) + H2O(l) → LiOH(aq) + H2(g) f. H2CO3(aq) → H2O(l ...
Practice Writing AP Questions
... 7. An excess of nitric acid solution is added to a solution of tetraamminecopper(II) sulfate, Cu(NH3)42+. a. State the change in pH you would expect before and after this reaction. Explain. 8. Solid sodium oxide is added to water. a. If phenolphthalein were added to the water before the reaction, wh ...
... 7. An excess of nitric acid solution is added to a solution of tetraamminecopper(II) sulfate, Cu(NH3)42+. a. State the change in pH you would expect before and after this reaction. Explain. 8. Solid sodium oxide is added to water. a. If phenolphthalein were added to the water before the reaction, wh ...
Carboxylic Acids - BSAK Chemistry weebly
... • Benzoyl chloride has the formula C6H5COCl. • How does the reactivity of benzoyl chloride compare to that of ethanoyl chloride? Explain. • The -COCl group is attached directly to a benzene ring. It is much less reactive than simple acyl chlorides like ethanoyl chloride. ...
... • Benzoyl chloride has the formula C6H5COCl. • How does the reactivity of benzoyl chloride compare to that of ethanoyl chloride? Explain. • The -COCl group is attached directly to a benzene ring. It is much less reactive than simple acyl chlorides like ethanoyl chloride. ...
Chapter 4 - profpaz.com
... This relationship is valid because the product of molarity times volume on each side equals the moles of solute, which remains constant during dilution. Molarity and volume, however, are inversely proportional during the dilution process. ...
... This relationship is valid because the product of molarity times volume on each side equals the moles of solute, which remains constant during dilution. Molarity and volume, however, are inversely proportional during the dilution process. ...
Today Electrochemistry electrons moving about equilibrium with a
... The oxidation state of an atom in a neutral element is 0 Example: O2(g), H2(g), C(s), Na(s), Hg(l) why? monatomic have no charge If diatomic break up they will end up as neutral atoms ...
... The oxidation state of an atom in a neutral element is 0 Example: O2(g), H2(g), C(s), Na(s), Hg(l) why? monatomic have no charge If diatomic break up they will end up as neutral atoms ...
Today Electrochemistry electrons moving about equilibrium with a
... If diatomic break up they will end up as neutral atoms! ...
... If diatomic break up they will end up as neutral atoms! ...
makeup2
... (A) Atomic sizes decrease going down a Group or Family. (B) Atomic sizes increase going from Fr in Group I to F in Group VII. (C) Atomic sizes decrease going from left to right in a Period. (D) All atoms in the same Group have the same size. 16. In their stable compounds, alkaline earth metals norma ...
... (A) Atomic sizes decrease going down a Group or Family. (B) Atomic sizes increase going from Fr in Group I to F in Group VII. (C) Atomic sizes decrease going from left to right in a Period. (D) All atoms in the same Group have the same size. 16. In their stable compounds, alkaline earth metals norma ...
Stoichiometry Worksheet #4
... 1. Silver sulfide (Ag2S) is the common tarnish on silver objects. What weight of silver sulfide can be made from 1.23 g of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) obtained from a rotten egg? The reaction of formation of silver sulfide is given below: Ag(s) + H2S(g) + O2(g) Ag2S(s) + H2O(l) (Equation must first be b ...
... 1. Silver sulfide (Ag2S) is the common tarnish on silver objects. What weight of silver sulfide can be made from 1.23 g of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) obtained from a rotten egg? The reaction of formation of silver sulfide is given below: Ag(s) + H2S(g) + O2(g) Ag2S(s) + H2O(l) (Equation must first be b ...
Chemical Reactions Unit Pupils` Learning Outcomes
... Chemical Changes Pupils’ Learning Outcomes ...
... Chemical Changes Pupils’ Learning Outcomes ...
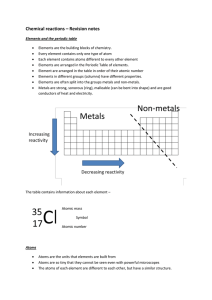
Chemical reactions revision
... oxygen. ‘Oxygen’ does not show up in the name; the ‘ate’ is the only clue it is there You should be able to give the name of the compound formed when different elements combine and tell which elements are present in any simple compound ...
... oxygen. ‘Oxygen’ does not show up in the name; the ‘ate’ is the only clue it is there You should be able to give the name of the compound formed when different elements combine and tell which elements are present in any simple compound ...
Honors Chapter 11 Reactions
... HCH3COO (aq) + Mg(HCO3)2 (aq) H2O(l) + CO2 (g) + Mg(CH3COO)2 (aq) 2HCH3COO (aq) + Mg(HCO3)2 (aq) 2H2O(l) + 2CO2 (g) + Mg(CH3COO)2 (aq) ...
... HCH3COO (aq) + Mg(HCO3)2 (aq) H2O(l) + CO2 (g) + Mg(CH3COO)2 (aq) 2HCH3COO (aq) + Mg(HCO3)2 (aq) 2H2O(l) + 2CO2 (g) + Mg(CH3COO)2 (aq) ...
Organic Chemical Reactions
... Figure 4: Energy vs reaction profiles for one- and two-step reactions. In those reactions where two or more different products may be formed from the same reactants, each process has its own energy/reaction profile. In general, the product with the lower energy is associated to the transition state ...
... Figure 4: Energy vs reaction profiles for one- and two-step reactions. In those reactions where two or more different products may be formed from the same reactants, each process has its own energy/reaction profile. In general, the product with the lower energy is associated to the transition state ...
FREE Sample Here
... 11) Ionic bonds are formed when A) atoms share electrons. B) two or more atoms lose electrons at the same time. C) electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another. D) hydrogen forms bonds with negatively charged atoms in the same or different molecule. E) a pair of electrons is shared ...
... 11) Ionic bonds are formed when A) atoms share electrons. B) two or more atoms lose electrons at the same time. C) electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another. D) hydrogen forms bonds with negatively charged atoms in the same or different molecule. E) a pair of electrons is shared ...
2012 C13 Exam answers
... 21 All but one of the following molecules are isomers. Which one is not an isomer of the others? ...
... 21 All but one of the following molecules are isomers. Which one is not an isomer of the others? ...
Chemistry I Final Exam Review Problems 2016
... b. F d. I ____ 65. At constant temperature and pressure, gas volume is directly proportional to the a. molar mass of the gas. c. density of the gas at STP. b. number of moles of gas. d. pressure of the gas ____ 66. Calculate the approximate temperature of a 0.50 mol sample of gas at 750 mm Hg and a ...
... b. F d. I ____ 65. At constant temperature and pressure, gas volume is directly proportional to the a. molar mass of the gas. c. density of the gas at STP. b. number of moles of gas. d. pressure of the gas ____ 66. Calculate the approximate temperature of a 0.50 mol sample of gas at 750 mm Hg and a ...
Oxidation And Degradation Products Of Common Oxygen Scavengers
... and metal passivators. The reactions are frequently very complex. This article is an attempt to explain the oxidation and degradation reactions of the more common oxygen scavengers in current use. In each case, the material will react with oxygen, and with metal oxides. The efficiency of the reactio ...
... and metal passivators. The reactions are frequently very complex. This article is an attempt to explain the oxidation and degradation reactions of the more common oxygen scavengers in current use. In each case, the material will react with oxygen, and with metal oxides. The efficiency of the reactio ...
document
... When compounds containing polyatomic ions dissociate, the polyatomic group stays together as one ion. ...
... When compounds containing polyatomic ions dissociate, the polyatomic group stays together as one ion. ...
Chapter 4 - Colby College Wiki
... solution to turn the indicator (phenolphthalein) slightly pink, what is the concentration of the hydrobromic acid solution? • The above process is known as a titration – the careful addition of one solution to another until one component has exactly consumed another (at the Equivalence Point) • An i ...
... solution to turn the indicator (phenolphthalein) slightly pink, what is the concentration of the hydrobromic acid solution? • The above process is known as a titration – the careful addition of one solution to another until one component has exactly consumed another (at the Equivalence Point) • An i ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.