Cl -1
... Oxidation Numbers 1. The oxidation number of any uncombined element is 0. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the charge on the ion. 3. The more-electronegative element in a binary compound is assigned the number equal to the charge it would have if it were an ion. 4. The oxidation num ...
... Oxidation Numbers 1. The oxidation number of any uncombined element is 0. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the charge on the ion. 3. The more-electronegative element in a binary compound is assigned the number equal to the charge it would have if it were an ion. 4. The oxidation num ...
2015 Academic Challenge CHEMISTRY TEST – STATE
... B. 0.40 M MgCl2 C. 0.30 M AlCl3 D. 0.20 M CaCl2 E. All of these solutions have the same concentration of chloride ions. ...
... B. 0.40 M MgCl2 C. 0.30 M AlCl3 D. 0.20 M CaCl2 E. All of these solutions have the same concentration of chloride ions. ...
Chapter 8 - Chemical Equations
... ____ 9. ___ CaCO3 ___ CaO + ___ CO2 ____ 10. ___ Mg + ___HCl ___ MgCl2 + ___ H2 ____ 11. ___ Mg(OH)2 + ___ HCl ___ MgCl2 + ___ H2O ____ 12. ___ Na2SO4 + ___ BaCl2 ___ BaSO4 + ___ NaCl ____ 13. ___ C2H2 + ___O2 ___ CO2 + ___ H2O ____ 14. ___ CaI2 + ___ F2 ___ CaF2 + ___ I2 ____ 15. ___ Na ...
... ____ 9. ___ CaCO3 ___ CaO + ___ CO2 ____ 10. ___ Mg + ___HCl ___ MgCl2 + ___ H2 ____ 11. ___ Mg(OH)2 + ___ HCl ___ MgCl2 + ___ H2O ____ 12. ___ Na2SO4 + ___ BaCl2 ___ BaSO4 + ___ NaCl ____ 13. ___ C2H2 + ___O2 ___ CO2 + ___ H2O ____ 14. ___ CaI2 + ___ F2 ___ CaF2 + ___ I2 ____ 15. ___ Na ...
Unit F335/01
... (c) One type of intermolecular bonding in esters E and G is instantaneous dipole–induced dipole. (i) ...
... (c) One type of intermolecular bonding in esters E and G is instantaneous dipole–induced dipole. (i) ...
Class Notes
... are put in front of the chemical formulas to make the number and types of atoms in the reactants equal to the number and types of atoms in the products. You can never change the subscripts in the compound’s formula; you can only change the coefficient. Also, the coefficient affects the entire compou ...
... are put in front of the chemical formulas to make the number and types of atoms in the reactants equal to the number and types of atoms in the products. You can never change the subscripts in the compound’s formula; you can only change the coefficient. Also, the coefficient affects the entire compou ...
PPT: Chemical Reactions Review
... Temperature at which reaction is carried out, in this case 0 oC ...
... Temperature at which reaction is carried out, in this case 0 oC ...
Chapter 4 (additional powerpoint)
... • The amounts of product calculated in the last three examples are not the amounts that would be produced if the reactions were actually done in the laboratory. • In each case, less product would be obtained than was calculated. There are numerous causes. Some materials are lost during transfers fro ...
... • The amounts of product calculated in the last three examples are not the amounts that would be produced if the reactions were actually done in the laboratory. • In each case, less product would be obtained than was calculated. There are numerous causes. Some materials are lost during transfers fro ...
200 ways to pass the regents
... 157. Carbon ALWAYS makes four bonds in molecules. 158. Saturated hydrocarbons have all single bonds within them (alkanes). 159. Unsaturated hydrocarbons have double or triple bonds in them (alkenes & alkynes). ...
... 157. Carbon ALWAYS makes four bonds in molecules. 158. Saturated hydrocarbons have all single bonds within them (alkanes). 159. Unsaturated hydrocarbons have double or triple bonds in them (alkenes & alkynes). ...
Thermochemistry 2 Matching Match each item with the correct
... Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. heat of reaction d. heat of fusion b. heat of formation e. heat of solution c. Hess's law of heat summation ____ ...
... Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. heat of reaction d. heat of fusion b. heat of formation e. heat of solution c. Hess's law of heat summation ____ ...
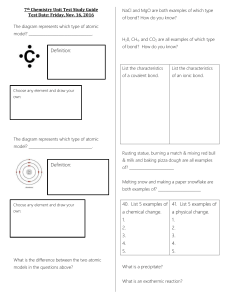
7th Chemistry Unit Test Study Guide Test Date: Friday, Nov. 16
... What mathematical function should take place between subscripts and coefficients to properly balance a chemical equation? ...
... What mathematical function should take place between subscripts and coefficients to properly balance a chemical equation? ...
Ionic bonding
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
C2 Revision Quick Questions FT
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
C2 Revision Quick Questions FT
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
Advanced Placement (AP) Chemistry 2012 – 2013 Ramsay High
... descriptive facts, including the chemistry involved in environmental and societal issues, should not be isolated from the principles being studied but should be taught throughout the course to illustrate and illuminate the principles. The following areas should be covered: 1. Chemical reactivity and ...
... descriptive facts, including the chemistry involved in environmental and societal issues, should not be isolated from the principles being studied but should be taught throughout the course to illustrate and illuminate the principles. The following areas should be covered: 1. Chemical reactivity and ...
Balancing ANY chemical Equation
... • Electrolytes: Substances that form ions when dissolved in solution. Electrolytes can be weak or strong. • Strong Electrolytes: Substances that completely separate into their component ions when dissolved. (All soluble ionic compounds and strong acids are strong electrolytes.) • Weak Electrolytes: ...
... • Electrolytes: Substances that form ions when dissolved in solution. Electrolytes can be weak or strong. • Strong Electrolytes: Substances that completely separate into their component ions when dissolved. (All soluble ionic compounds and strong acids are strong electrolytes.) • Weak Electrolytes: ...
C2 revision slides V3 + questions + MS – F
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
10 IB Chemistry Assessment Statements 2009 Revised
... Although skeletal formulas are used for more complex structures in the Chemistry data booklet, such formulas will not be accepted in examination ...
... Although skeletal formulas are used for more complex structures in the Chemistry data booklet, such formulas will not be accepted in examination ...
Chapter 10 Chemical Reactions
... Activity Series: Relative order of metal elements and hydrogen arranged by their ability to undergo reaction. Li > K > Ba > Sr > Ca > Na > Mg > Al > Mn > Zn > Fe > Cd > Co > Ni > Sn > Pb > (H) > Cu > Ag > Au Note: The Activity Series will be given to you on quizzes and exams Most active (closes ...
... Activity Series: Relative order of metal elements and hydrogen arranged by their ability to undergo reaction. Li > K > Ba > Sr > Ca > Na > Mg > Al > Mn > Zn > Fe > Cd > Co > Ni > Sn > Pb > (H) > Cu > Ag > Au Note: The Activity Series will be given to you on quizzes and exams Most active (closes ...
1999 U. S. NATIONAL CHEMISTRY OLYMPIAD
... A periodic table and other useful information are provided on page 2 for student reference. Students should be permitted to use nonprogrammable calculators. DIRECTIONS TO THE EXAMINEE–PART I DO NOT TURN THE PAGE UNTIL DIRECTED TO DO SO. Answers to questions in Part I must be entered on a Scantron an ...
... A periodic table and other useful information are provided on page 2 for student reference. Students should be permitted to use nonprogrammable calculators. DIRECTIONS TO THE EXAMINEE–PART I DO NOT TURN THE PAGE UNTIL DIRECTED TO DO SO. Answers to questions in Part I must be entered on a Scantron an ...
ch8 - Otterville R-VI School District
... BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) NaCl(aq) + BaSO4(s) iron sulfide and hydrochloric acid FeS(aq) + HCl(aq) FeCl2(aq) + H2S(g) hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide HCl(aq) + NaOH NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) potassium iodide and lead (II) nitrate KI(aq) + Pb(NO3)2 KNO3(aq) + PbI2(s) ...
... BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) NaCl(aq) + BaSO4(s) iron sulfide and hydrochloric acid FeS(aq) + HCl(aq) FeCl2(aq) + H2S(g) hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide HCl(aq) + NaOH NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) potassium iodide and lead (II) nitrate KI(aq) + Pb(NO3)2 KNO3(aq) + PbI2(s) ...
Review 3
... 2. Calculate the equilibrium constant for a given 3. Know the factors that affect reaction rate, and be able to apply them to a specific reaction. ...
... 2. Calculate the equilibrium constant for a given 3. Know the factors that affect reaction rate, and be able to apply them to a specific reaction. ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
... 11) Ionic bonds are formed when A) atoms share electrons. B) two or more atoms lose electrons at the same time. C) electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another. D) hydrogen forms bonds with negatively charged atoms in the same or different molecule. E) a pair of electrons is shared ...
... 11) Ionic bonds are formed when A) atoms share electrons. B) two or more atoms lose electrons at the same time. C) electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another. D) hydrogen forms bonds with negatively charged atoms in the same or different molecule. E) a pair of electrons is shared ...
Enthalpy - Mr. Rowley
... This would be an “endothermic” process as energy needs to be put in to ...
... This would be an “endothermic” process as energy needs to be put in to ...
CHEM 1211 and CHEM 1212 National ACS Exams About the Exam
... As the published ACS Study Guide articulates, chemistry knowledge should be more than sets of formulas and techniques. Rather, it is a coherent set of knowledge that enables comprehension of the submicroscopic (chemical) world. As such, the ACS tests seek to uncover such genuine understanding. ...
... As the published ACS Study Guide articulates, chemistry knowledge should be more than sets of formulas and techniques. Rather, it is a coherent set of knowledge that enables comprehension of the submicroscopic (chemical) world. As such, the ACS tests seek to uncover such genuine understanding. ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.