AP Chem Summer Assign Gen Chem Rev Problems
... t. sodium chloride reacts with fluorine to produce sodium fluoride and chlorine in a single replacement reaction. u. hydrogen and oxygen combine to form water. v. silver nitrate and magnesium chloride react to produce silver chloride and magnesium nitrate. w. aluminum bromide reacts with potassium s ...
... t. sodium chloride reacts with fluorine to produce sodium fluoride and chlorine in a single replacement reaction. u. hydrogen and oxygen combine to form water. v. silver nitrate and magnesium chloride react to produce silver chloride and magnesium nitrate. w. aluminum bromide reacts with potassium s ...
Chem 173: Final Exam Review Short Answer and Problems 1
... Limestone is composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) as well as other compounds. In an analysis, a chemist takes a sample of limestone which has a mass of 413 mg and treats it with oxalic acid (H2C 2O4). A chemical reaction occurs between the calcium carbonate and the acid producing calcium oxalate an ...
... Limestone is composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) as well as other compounds. In an analysis, a chemist takes a sample of limestone which has a mass of 413 mg and treats it with oxalic acid (H2C 2O4). A chemical reaction occurs between the calcium carbonate and the acid producing calcium oxalate an ...
2C - Edexcel
... 4 A student investigated the neutralisation of acids by measuring the temperature changes when alkalis were added to acids of known concentrations. He used this apparatus to add different volumes of sodium hydroxide solution to a fixed volume of dilute nitric acid. ...
... 4 A student investigated the neutralisation of acids by measuring the temperature changes when alkalis were added to acids of known concentrations. He used this apparatus to add different volumes of sodium hydroxide solution to a fixed volume of dilute nitric acid. ...
A Classification of AP Chemistry Reactions
... Hydrogen gas, H2, is an effective reducing agent for some metal oxides. - Hydrogen gas is passed over hot copper (II) oxide. CuO + H2 Cu + H2O Electron Transfer Reactions The first general type of redox reactions are simple electron-transfer equations. These do not involve oxygen or oxyanions. The ...
... Hydrogen gas, H2, is an effective reducing agent for some metal oxides. - Hydrogen gas is passed over hot copper (II) oxide. CuO + H2 Cu + H2O Electron Transfer Reactions The first general type of redox reactions are simple electron-transfer equations. These do not involve oxygen or oxyanions. The ...
do not
... Enzymes are Catalysts Catalysts: speed up chemical reactions but do not change as a result of the reaction ...
... Enzymes are Catalysts Catalysts: speed up chemical reactions but do not change as a result of the reaction ...
Net Ionic Prep Session NMSI INSTRUCTOR
... WRITE ALL WEAK ACIDS AND BASES AS MOLECULES—be on the look out for BF3 and its cousins BCl3, etc. They are classic Lewis acids and when reacting with ammonia (a classic weak Lewis base), the product is F3BNH3 (just smash everything together) since nitrogen donated its unshared electron pair to boron ...
... WRITE ALL WEAK ACIDS AND BASES AS MOLECULES—be on the look out for BF3 and its cousins BCl3, etc. They are classic Lewis acids and when reacting with ammonia (a classic weak Lewis base), the product is F3BNH3 (just smash everything together) since nitrogen donated its unshared electron pair to boron ...
do not - wwphs
... Enzymes are Catalysts Catalysts: speed up chemical reactions but do not change as a result of the reaction ...
... Enzymes are Catalysts Catalysts: speed up chemical reactions but do not change as a result of the reaction ...
Balancing and Predicting Chemical Reactions:
... Use the activity series for metals to explain why copper metal is used in plumbing where the water might contain compounds of many different metals. ...
... Use the activity series for metals to explain why copper metal is used in plumbing where the water might contain compounds of many different metals. ...
Equilibrium (Sheet 1)
... Section III La Chatelier's principle states that if a stress such as a change in concentration, pressure or temperature is applied to a system in equilibrium, the equilibrium will shift in a way that tends to undo the effect of the stress. For example: H2O + CO H2 + CO2 + heat. If no stress is intro ...
... Section III La Chatelier's principle states that if a stress such as a change in concentration, pressure or temperature is applied to a system in equilibrium, the equilibrium will shift in a way that tends to undo the effect of the stress. For example: H2O + CO H2 + CO2 + heat. If no stress is intro ...
Chemical Reactions Chemical Arithmetic
... reaction in which the oxidation numbers of elements change because of a loss or gain of electrons • Oxidation Number- A number that indicates the charge that an atom in a molecule or polyatomic ion would have if all bonds were ionic. – Fictitious- No actual charge of this magnitude actually exists w ...
... reaction in which the oxidation numbers of elements change because of a loss or gain of electrons • Oxidation Number- A number that indicates the charge that an atom in a molecule or polyatomic ion would have if all bonds were ionic. – Fictitious- No actual charge of this magnitude actually exists w ...
Cl Cl and
... Too much energy is needed to remove 4 electrons from an atom. Too much energy is needed to insert 4 electrons into an atom in order to overcome the repulsive forces between like charges. 28. Why do elements of groups 6 and 7 form ions of charge –2 and –1 respectively? By gaining electrons they achie ...
... Too much energy is needed to remove 4 electrons from an atom. Too much energy is needed to insert 4 electrons into an atom in order to overcome the repulsive forces between like charges. 28. Why do elements of groups 6 and 7 form ions of charge –2 and –1 respectively? By gaining electrons they achie ...
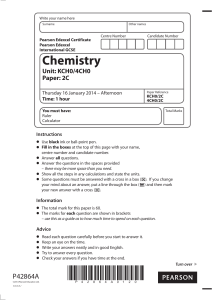
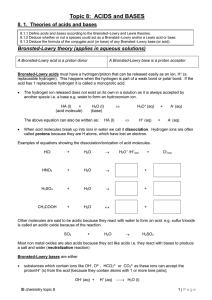
Topic 8: ACIDS and BASES
... positive ions like the H+ which never exists on its own and either reacts with water to form H3O+ or with a another base to form water. Other examples include CH3+ and Br+ (Hal+) which you will study in organic chemistry. molecules containing positive centres (mostly organic molecules) as a res ...
... positive ions like the H+ which never exists on its own and either reacts with water to form H3O+ or with a another base to form water. Other examples include CH3+ and Br+ (Hal+) which you will study in organic chemistry. molecules containing positive centres (mostly organic molecules) as a res ...
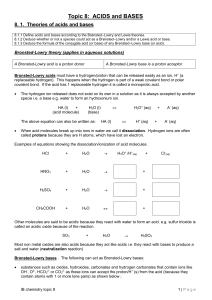
Topic 8: ACIDS and BASES
... positive ions like the H+ which never exists on its own and either reacts with water to form H3O+ or with a another base to form water. Other examples include CH3+ and Br+ (Hal+) which you will study in organic chemistry. molecules containing positive centres (mostly organic molecules) as a res ...
... positive ions like the H+ which never exists on its own and either reacts with water to form H3O+ or with a another base to form water. Other examples include CH3+ and Br+ (Hal+) which you will study in organic chemistry. molecules containing positive centres (mostly organic molecules) as a res ...
50 Frequently Forgotten Facts
... 39) In Le Chatelier’s Principle, if a system is at equilibrium, if something is added, then the equilibrium will shift away from the side it is on. If something is removed, then the equilibrium will shift towards that side. After the shift, whatever is being shifted towards will increase in concentr ...
... 39) In Le Chatelier’s Principle, if a system is at equilibrium, if something is added, then the equilibrium will shift away from the side it is on. If something is removed, then the equilibrium will shift towards that side. After the shift, whatever is being shifted towards will increase in concentr ...
chp0-Intro
... Molecules are comprised of atoms bound together by chemical bonds: e.g. CO2 and CCl2F2 H2O2 and NO HO• ...
... Molecules are comprised of atoms bound together by chemical bonds: e.g. CO2 and CCl2F2 H2O2 and NO HO• ...
Chapters 14
... 10. Consider the quilibrium N2(g) + 3H2(g) ↔ 2NH3(g) at a certain temperature. An equilibrium mixture in a 4.00 liter vessel contains 1.60 moles NH3, 0.800 moles N2, and 1.20 moles H2. What is the value of K? ...
... 10. Consider the quilibrium N2(g) + 3H2(g) ↔ 2NH3(g) at a certain temperature. An equilibrium mixture in a 4.00 liter vessel contains 1.60 moles NH3, 0.800 moles N2, and 1.20 moles H2. What is the value of K? ...
Notes for Matter Packet- Balancing equations (PDF
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
FREQUENTLY FORGOTTEN FACTS
... 39) In Le Chatelier’s Principle, if a system is at equilibrium, if something is added, then the equilibrium will shift away from the side it is on. If something is removed, then the equilibrium will shift towards that side. After the shift, whatever is being shifted towards will increase in concentr ...
... 39) In Le Chatelier’s Principle, if a system is at equilibrium, if something is added, then the equilibrium will shift away from the side it is on. If something is removed, then the equilibrium will shift towards that side. After the shift, whatever is being shifted towards will increase in concentr ...
George Facer`s A level Chemistry
... The reaction between a halogenoalkane and ammonia produces an amine. Ammonia is a gas that is soluble in water. However, a solution cannot be heated under reflux because ammonia gas would be liberated. This would then escape because it would not be condensed by the reflux condenser. The halogenoalka ...
... The reaction between a halogenoalkane and ammonia produces an amine. Ammonia is a gas that is soluble in water. However, a solution cannot be heated under reflux because ammonia gas would be liberated. This would then escape because it would not be condensed by the reflux condenser. The halogenoalka ...
11.2 Types of Chemical Reactions
... These equations describe two examples of single-replacement reactions. A single-replacement reaction is a chemical change in which one element replaces a second element in a compound. You can identify a singlereplacement reaction by noting that both the reactants and the products consist of an eleme ...
... These equations describe two examples of single-replacement reactions. A single-replacement reaction is a chemical change in which one element replaces a second element in a compound. You can identify a singlereplacement reaction by noting that both the reactants and the products consist of an eleme ...
Lecture 4
... 1. For an atom in its elemental form, the oxidation number is always zero. 2. For any monatomic ion, the oxidation number equals the charge on the ion. 3. Nonmetals usually have negative oxidation numbers, although they can sometimes be positive. a. The oxidation number of oxygen is usually –2 in bo ...
... 1. For an atom in its elemental form, the oxidation number is always zero. 2. For any monatomic ion, the oxidation number equals the charge on the ion. 3. Nonmetals usually have negative oxidation numbers, although they can sometimes be positive. a. The oxidation number of oxygen is usually –2 in bo ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.