chemistry paper 1
... Directions: Questions 16 to 18 refer to the following information. In an experiment to determine the concentration of sulphuric acid in a brand of toilet cleaner, 25.0 cm3 of the cleaner was first diluted to 250.0 cm3 with distilled water. Upon titration with 0.950 M sodium hydroxide solution using ...
... Directions: Questions 16 to 18 refer to the following information. In an experiment to determine the concentration of sulphuric acid in a brand of toilet cleaner, 25.0 cm3 of the cleaner was first diluted to 250.0 cm3 with distilled water. Upon titration with 0.950 M sodium hydroxide solution using ...
2.3 ThermoChemistry - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... Thermochemistry concerns the study of changes in energy which occur during chemical reactions. ...
... Thermochemistry concerns the study of changes in energy which occur during chemical reactions. ...
June Exam Review Material World
... June Exam Review Material World 18. The table below gives the chemical symbols of four elements and provides space to indicate the following characteristics: the number of valence electrons, the number of energy levels, chemical reactivity (none, low or high) and the family number. Using the periodi ...
... June Exam Review Material World 18. The table below gives the chemical symbols of four elements and provides space to indicate the following characteristics: the number of valence electrons, the number of energy levels, chemical reactivity (none, low or high) and the family number. Using the periodi ...
Ch 10 - Enrico Fermi High School
... 1. What effect (increase, decrease, no change) will a decrease in temperature have on K? 2. What effect (inc, dec, none) will removing H2 have on the equilibrium constant, K? 3. In which direction will the reaction shift if gaseous H2 is removed from the system? 4. Adding a catalyst (a gold surface) ...
... 1. What effect (increase, decrease, no change) will a decrease in temperature have on K? 2. What effect (inc, dec, none) will removing H2 have on the equilibrium constant, K? 3. In which direction will the reaction shift if gaseous H2 is removed from the system? 4. Adding a catalyst (a gold surface) ...
thermodynamics
... do not. Explain whether the following properties are extensive or intensive. Mass, internal energy, pressure, heat capacity, molar heat capacity, density, mole fraction, specific heat, temperature and molarity. 60. The lattice enthalpy of an ionic compound is the enthalpy when one mole of an ionic c ...
... do not. Explain whether the following properties are extensive or intensive. Mass, internal energy, pressure, heat capacity, molar heat capacity, density, mole fraction, specific heat, temperature and molarity. 60. The lattice enthalpy of an ionic compound is the enthalpy when one mole of an ionic c ...
REACTIONS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION
... sugar (sucrose) in a cup of water (! FIGURE 4.2). Both solutions are clear and colorless, but they possess very different electrical conductivities: the salt solution is a good conductor of electricity, whereas the sugar solution is not. In order for the bulb in the device of Figure 4.2 to light up, ...
... sugar (sucrose) in a cup of water (! FIGURE 4.2). Both solutions are clear and colorless, but they possess very different electrical conductivities: the salt solution is a good conductor of electricity, whereas the sugar solution is not. In order for the bulb in the device of Figure 4.2 to light up, ...
WRITING CHEMICAL FORMULAE
... some solvent (water) and some acid together. In any reactions of the acid, it is the HCl particles which are involved. The water is just a carrier for the acid, so when we measure out a volume of the solution, we want to know how much acid it contains. To do this, we need to define the CONCENTRATION ...
... some solvent (water) and some acid together. In any reactions of the acid, it is the HCl particles which are involved. The water is just a carrier for the acid, so when we measure out a volume of the solution, we want to know how much acid it contains. To do this, we need to define the CONCENTRATION ...
Q - PIMS
... 180 grams of glucose and 342 grams of sucrose have same number of molecules, but different number of atoms present in them. Justify it. Ans: 180 grams of glucose (C6H12O6), and 342 grams of sucrose (C12H22O11) are one mole of each. One mole of various substances contain equal number of molecules i.e ...
... 180 grams of glucose and 342 grams of sucrose have same number of molecules, but different number of atoms present in them. Justify it. Ans: 180 grams of glucose (C6H12O6), and 342 grams of sucrose (C12H22O11) are one mole of each. One mole of various substances contain equal number of molecules i.e ...
Core_Class_Science_Chemistry_for_the_web 838.3 KB
... called the nucleus. Protons are positively charged particles (P+). Electrons are negatively charged particles (E-) located on the outside of the nucleus. Electrons constantly move around the nucleus in energy levels. Today’s Objectives: Diagram the particles that make up an atom. Compare covalent an ...
... called the nucleus. Protons are positively charged particles (P+). Electrons are negatively charged particles (E-) located on the outside of the nucleus. Electrons constantly move around the nucleus in energy levels. Today’s Objectives: Diagram the particles that make up an atom. Compare covalent an ...
unit iii kinetics and mechanism of reactions in metal complexes
... [Pt(NH3)3Cl]+ changes only by a factor of 2 whereas the charge of the complex changes from -2 to +1. This suggests that both bond breaking and bond making are important, which is characteristic of an associative SN2 mechanism. 4. Nature of the entering ligand greatly affects the rate of substitution ...
... [Pt(NH3)3Cl]+ changes only by a factor of 2 whereas the charge of the complex changes from -2 to +1. This suggests that both bond breaking and bond making are important, which is characteristic of an associative SN2 mechanism. 4. Nature of the entering ligand greatly affects the rate of substitution ...
Ex - Bosna Sema
... the substance which is totally consumed when the chemical reaction is complete. The amount of product formed is limited by this reagent since the reaction cannot proceed further without it. The other reagents may be present in excess of the quantities required to react with the limiting reagent. 4 c ...
... the substance which is totally consumed when the chemical reaction is complete. The amount of product formed is limited by this reagent since the reaction cannot proceed further without it. The other reagents may be present in excess of the quantities required to react with the limiting reagent. 4 c ...
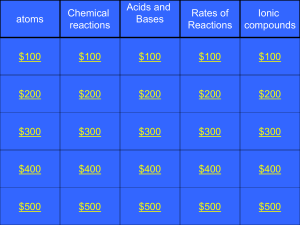
2P chem jeopardy 2011
... This NOT a chemical reaction. You can reverse it! (water vapour condenses to liquid water again). **Caution,bubbles DON’T ALWAYS mean a Chemical reaction! Category 2: $400: Q ...
... This NOT a chemical reaction. You can reverse it! (water vapour condenses to liquid water again). **Caution,bubbles DON’T ALWAYS mean a Chemical reaction! Category 2: $400: Q ...
Kinetics lecture
... Molecularity describes the number of reactant molecules (or ions , atoms) that react in an elementary step. It is rare to have an elementary step that involves three reactants (termolecular) ...
... Molecularity describes the number of reactant molecules (or ions , atoms) that react in an elementary step. It is rare to have an elementary step that involves three reactants (termolecular) ...
Praktikum in Allgemeiner Chemie für Biologen und Pharmazeuten
... The beginner’s course in inorganic and general chemistry is intended to teach the fundamental methods of laboratory work to students of biology and pharmaceutical sciences and to make them familiar with the important reaction types in inorganic chemistry. Restrictions in the availability of instrume ...
... The beginner’s course in inorganic and general chemistry is intended to teach the fundamental methods of laboratory work to students of biology and pharmaceutical sciences and to make them familiar with the important reaction types in inorganic chemistry. Restrictions in the availability of instrume ...
Chemical reaction
... How many moles of O2 are required to react completely with 5.6 moles C4H10? This question can be answered very easily based on the mole:mole ratios that are inherent in a balanced chemical equation. For example for the above equation 2 moles of C4H10 will react with every 13 moles of O2. This can al ...
... How many moles of O2 are required to react completely with 5.6 moles C4H10? This question can be answered very easily based on the mole:mole ratios that are inherent in a balanced chemical equation. For example for the above equation 2 moles of C4H10 will react with every 13 moles of O2. This can al ...
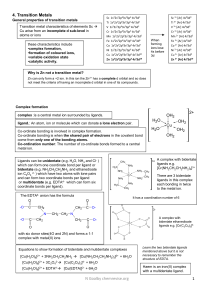
mod-5-revision-guide-4-transition-metals
... The acid is needed to supply the 8H+ ions. Some acids are not suitable as they set up alternative redox reactions and hence make the titration readings inaccurate. Only use dilute sulphuric acid for manganate titrations. Insufficient volumes of sulphuric acid will mean the solution is not acidic eno ...
... The acid is needed to supply the 8H+ ions. Some acids are not suitable as they set up alternative redox reactions and hence make the titration readings inaccurate. Only use dilute sulphuric acid for manganate titrations. Insufficient volumes of sulphuric acid will mean the solution is not acidic eno ...
Philicities, Fugalities, and Equilibrium Constants
... basicities relative to OH− (KAR, eq 4) by multiplication of the tabulated Brønsted basicities KA with the equilibrium constants KHARA defined by eq 3. KA R ...
... basicities relative to OH− (KAR, eq 4) by multiplication of the tabulated Brønsted basicities KA with the equilibrium constants KHARA defined by eq 3. KA R ...
3 - LPS
... dropped at the same time from the same height. The iron ball and wood fall at the same rate. The large mass of Earth causes it to exert the same gravitational attraction on any object, regardless of the object’s composition. ...
... dropped at the same time from the same height. The iron ball and wood fall at the same rate. The large mass of Earth causes it to exert the same gravitational attraction on any object, regardless of the object’s composition. ...
Solubility Product Constants We have been looking at how
... We have been looking at how equilibrium constants can be used in chemical reactions. The concept of equilibrium also applies to saturated solutions of ionic solids. A saturated solution is one that is holding the maximum amount of solute possible at a given temperature. Even though a solution is sat ...
... We have been looking at how equilibrium constants can be used in chemical reactions. The concept of equilibrium also applies to saturated solutions of ionic solids. A saturated solution is one that is holding the maximum amount of solute possible at a given temperature. Even though a solution is sat ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.