AP Chemistry Lab Manual
... your error, and continue. It is expected that some errors will occur. A lab notebook is a working document, not a perfect, error-free, polished product. Errors should be corrected by drawing one line through the mistake, and then proceeding with the new data. 6. Do not use the first person or includ ...
... your error, and continue. It is expected that some errors will occur. A lab notebook is a working document, not a perfect, error-free, polished product. Errors should be corrected by drawing one line through the mistake, and then proceeding with the new data. 6. Do not use the first person or includ ...
Modification of the surface electronic and chemical properties of Pt
... plane wave energy cutoff was used. The calculated adsorption energies on Pt changed by less than 0.05 eV with higher cutoff energies. Maximum symmetry constraints were applied in all cases. In previous work on Ni–Pt systems, it was found that including spin polarization in the calculations did not a ...
... plane wave energy cutoff was used. The calculated adsorption energies on Pt changed by less than 0.05 eV with higher cutoff energies. Maximum symmetry constraints were applied in all cases. In previous work on Ni–Pt systems, it was found that including spin polarization in the calculations did not a ...
AP Chemistry - Freehold Regional High School District
... 1. There are six main types of chemical reactions; 2. The products of a chemical reaction can be predicted using a set of rules. 3. Stoichiometry is a method of problem solving using balanced equations. Solution concentration can be expressed in several ways. Chemical compounds can be acids, bases o ...
... 1. There are six main types of chemical reactions; 2. The products of a chemical reaction can be predicted using a set of rules. 3. Stoichiometry is a method of problem solving using balanced equations. Solution concentration can be expressed in several ways. Chemical compounds can be acids, bases o ...
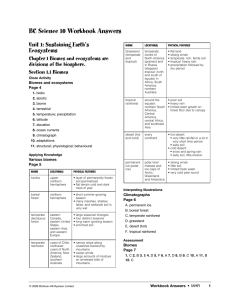
BC Science 10 Workbook Answers
... 1. PCBs are synthetic chemicals. Their full chemical name is polychlorinated biphenyl. 2. PCBs were used for industrial products, such as heat exchange fluids, paints, plastics, and lubricants for electrical transformers. 3. PCBs stay in the environment for a long time. Aquatic ecosystems and specie ...
... 1. PCBs are synthetic chemicals. Their full chemical name is polychlorinated biphenyl. 2. PCBs were used for industrial products, such as heat exchange fluids, paints, plastics, and lubricants for electrical transformers. 3. PCBs stay in the environment for a long time. Aquatic ecosystems and specie ...
Grade 11 review answers
... c) Why is methane gas not ideal at very low temperatures and high pressures? London forces are able to attract gas molecules together at low temperatures and high pressure. ...
... c) Why is methane gas not ideal at very low temperatures and high pressures? London forces are able to attract gas molecules together at low temperatures and high pressure. ...
Complexometric Titration
... Molecule or ion with at least 1 pair of unshared electron can form covalent bond with metal ion = ligands The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs Eg of ligands = ammonia, cyanide ions, halide ions, water (neutral/-ve charg ...
... Molecule or ion with at least 1 pair of unshared electron can form covalent bond with metal ion = ligands The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs Eg of ligands = ammonia, cyanide ions, halide ions, water (neutral/-ve charg ...
Chemistry 30 - SharpSchool
... an acid/base reaction is a chemical reaction in which _____________ is transferred from an _________ to a ___________ forming a ________________________ and a _______________________ ...
... an acid/base reaction is a chemical reaction in which _____________ is transferred from an _________ to a ___________ forming a ________________________ and a _______________________ ...
111 Exam III OUTLINE TRO 1-3-11
... 1. The forward reaction (⇀ ) and reverse (↽ ) reactions are occurring simultaneously. 2. The rate for the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction and a dynamic equilibrium is achieved. 3. The ratio of the concentrations of the products to reactants is constant. B. THE EQUILIBRI ...
... 1. The forward reaction (⇀ ) and reverse (↽ ) reactions are occurring simultaneously. 2. The rate for the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction and a dynamic equilibrium is achieved. 3. The ratio of the concentrations of the products to reactants is constant. B. THE EQUILIBRI ...
Chemistry Transition Information
... Calcium atoms each lose two electrons to form calcium ions. Chlorine atoms each gain one electron to form chloride ions. This means that calcium atoms react with chlorine atoms in the ratio of one calcium atom for every two chlorine atoms. Complete the following diagram to show the electronic struct ...
... Calcium atoms each lose two electrons to form calcium ions. Chlorine atoms each gain one electron to form chloride ions. This means that calcium atoms react with chlorine atoms in the ratio of one calcium atom for every two chlorine atoms. Complete the following diagram to show the electronic struct ...
ElEctricity
... Magnetism Electricity and magnetism, although they seem quite different, are actually two forms of the same force. An electric current produces magnetism. To put it another way, whenever electricity moves, magnetism is produced. And whenever a magnetic force field changes, electricity is produced. W ...
... Magnetism Electricity and magnetism, although they seem quite different, are actually two forms of the same force. An electric current produces magnetism. To put it another way, whenever electricity moves, magnetism is produced. And whenever a magnetic force field changes, electricity is produced. W ...
PPT
... Parallel Plate: C = e0A/d Capacitors in parallel: Ceq = C1+C2 Capacitors in series: 1/Ceq = 1/C1+1/C2 Batteries provide fixed potential difference ...
... Parallel Plate: C = e0A/d Capacitors in parallel: Ceq = C1+C2 Capacitors in series: 1/Ceq = 1/C1+1/C2 Batteries provide fixed potential difference ...
LABORATORY MANUAL FOR GENERAL CHEMISTRY I
... 4. Consider all chemicals to be hazardous unless you are instructed otherwise. Dispose of chemicals as instructed by your instructor. Follow the explicit instructions given in the experiments. 5 If chemicals come into contact with your skin or eyes, wash immediately with copious amounts of water and ...
... 4. Consider all chemicals to be hazardous unless you are instructed otherwise. Dispose of chemicals as instructed by your instructor. Follow the explicit instructions given in the experiments. 5 If chemicals come into contact with your skin or eyes, wash immediately with copious amounts of water and ...
Curriculum Vitae - Université Paris-Sud
... and small clusters of a metal, even a noble metal, may exhibit much stronger reducing properties than the bulk metal, and may be spontaneously corroded by the solvent with simultaneous hydrogen evolution. It also implied that for a given metal the thermodynamics depended on the particle nuclearity ( ...
... and small clusters of a metal, even a noble metal, may exhibit much stronger reducing properties than the bulk metal, and may be spontaneously corroded by the solvent with simultaneous hydrogen evolution. It also implied that for a given metal the thermodynamics depended on the particle nuclearity ( ...
word - My eCoach
... When certain ionic solids crystallize from aqueous solutions, a definite number of molecules of water remain attached to the crystal. Ionic solids that contain a definite amount of water are called hydrates or hydrated salts and the water in the crystal structure is called water of hydration. The wa ...
... When certain ionic solids crystallize from aqueous solutions, a definite number of molecules of water remain attached to the crystal. Ionic solids that contain a definite amount of water are called hydrates or hydrated salts and the water in the crystal structure is called water of hydration. The wa ...
Holt Modern Chemistry Workbook
... whose simplest units are molecules. In other words, a single molecule of any molecular compound is an individual unit that is capable of existing on its own. A molecule may contain two or more atoms of the same element, as in oxygen. Or, a molecule may consist of two or more atoms of different eleme ...
... whose simplest units are molecules. In other words, a single molecule of any molecular compound is an individual unit that is capable of existing on its own. A molecule may contain two or more atoms of the same element, as in oxygen. Or, a molecule may consist of two or more atoms of different eleme ...
visual problems - Western Oregon University
... decomposition of stratospheric ozone. Trichlorofluoromethane (CCl3F) boils at 23.8°C and its molar heat of vaporization is 24.8 kJ/mol. What is the molar entropy of evaporation of CCl 3F(ℓ)? 12.72. Methane-Producing Bacteria Methanogenic bacteria convert liquid acetic acid (CH3COOH) into CO2(g) and ...
... decomposition of stratospheric ozone. Trichlorofluoromethane (CCl3F) boils at 23.8°C and its molar heat of vaporization is 24.8 kJ/mol. What is the molar entropy of evaporation of CCl 3F(ℓ)? 12.72. Methane-Producing Bacteria Methanogenic bacteria convert liquid acetic acid (CH3COOH) into CO2(g) and ...
379 - FTP
... are 1.63V and –0.13V, respectively. A saturated solution of chlorine at 25°C consists of about 33% hypochlorous acid. The acid is unstable in water. It reacts with hypochlorite ion forming chlorate: 2HOCl + OCl¯ → ClO3̄ + 2H+ + 2Cl¯, dissociation constant 3.4 x 10–8. Hypochlorous acid is a strong ox ...
... are 1.63V and –0.13V, respectively. A saturated solution of chlorine at 25°C consists of about 33% hypochlorous acid. The acid is unstable in water. It reacts with hypochlorite ion forming chlorate: 2HOCl + OCl¯ → ClO3̄ + 2H+ + 2Cl¯, dissociation constant 3.4 x 10–8. Hypochlorous acid is a strong ox ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.