DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY, CFS, IIUM
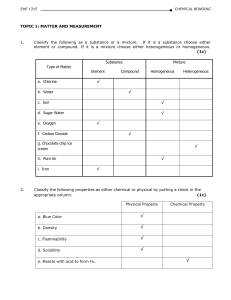
... the amount of matter is called an intensive property. A characteristic that can be observed without producing new kinds of matter is called a physical property. A characteristic that depends on how a kind of matter changes suring interactions with other kinds of matter is called chemical property. M ...
... the amount of matter is called an intensive property. A characteristic that can be observed without producing new kinds of matter is called a physical property. A characteristic that depends on how a kind of matter changes suring interactions with other kinds of matter is called chemical property. M ...
Course : Chem 312F
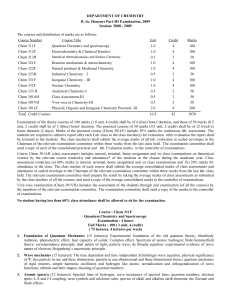
... Examination of the theory courses of 100 marks (1.0 unit, 4 credit) shall be of 4 (four) hours' duration, and those of 50 marks (0.5 unit, 2 credit) shall be of 3 (three) hours' duration. The practical courses of 50 marks (0.5 unit, 2 credit) shall be of 12 (twelve) hours duration (2 days). Marks of ...
... Examination of the theory courses of 100 marks (1.0 unit, 4 credit) shall be of 4 (four) hours' duration, and those of 50 marks (0.5 unit, 2 credit) shall be of 3 (three) hours' duration. The practical courses of 50 marks (0.5 unit, 2 credit) shall be of 12 (twelve) hours duration (2 days). Marks of ...
tro2_ppt_lecture_04 - Louisiana Tech University
... • If all 5.40 g Al were used, then 10.2 g of Al2O3 would be produced. 10.2 g < 17.2 g • The limiting reactant is Al. • Theoretical yield is 10.2 g Al2O3. To determine the percent yield of the reaction: (4.50 g/10.2) x 100 = 44.1% 44.1% is the percent yield for this reaction. © 2013 Pearson Education ...
... • If all 5.40 g Al were used, then 10.2 g of Al2O3 would be produced. 10.2 g < 17.2 g • The limiting reactant is Al. • Theoretical yield is 10.2 g Al2O3. To determine the percent yield of the reaction: (4.50 g/10.2) x 100 = 44.1% 44.1% is the percent yield for this reaction. © 2013 Pearson Education ...
Lesson Plan
... Strength of a base: indication of the extent that the base molecules break apart to release hydroxide ions. (=Degree of ionization) Strong bases: almost all the molecules break apart to release hydroxide ions. Ex) NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH)2… Weak acid: Only part of the molecules break apart to produce fewer ...
... Strength of a base: indication of the extent that the base molecules break apart to release hydroxide ions. (=Degree of ionization) Strong bases: almost all the molecules break apart to release hydroxide ions. Ex) NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH)2… Weak acid: Only part of the molecules break apart to produce fewer ...
Chapter 20 Thermodynamics
... is the same even though they took very different paths to get to the mountain top. This is the power of all the state functions in thermodynamics---we only need to now the start and the finish bulk parameters. ...
... is the same even though they took very different paths to get to the mountain top. This is the power of all the state functions in thermodynamics---we only need to now the start and the finish bulk parameters. ...
Sample Exercise 19.1 Identifying Spontaneous Processes
... Plan: In part (a) we can make this prediction by determining the sign of ΔS° for the reaction and then using that information to analyze Equation 19.12. In part (b) we need to calculate ΔH° and ΔS° for the reaction by using the data in Appendix C. We can then use Equation 19.12 to calculate ΔG°. Sol ...
... Plan: In part (a) we can make this prediction by determining the sign of ΔS° for the reaction and then using that information to analyze Equation 19.12. In part (b) we need to calculate ΔH° and ΔS° for the reaction by using the data in Appendix C. We can then use Equation 19.12 to calculate ΔG°. Sol ...
Shake_TJ_T_2014 - VTechWorks
... coupling the electric field through a thin passivation layer and avoiding their direct contact with the solution. The DEP force is achieved by insulating structures like iDEP, but avoids large heat buildup by applying the electric field only in the trapping region. The device consists of columns of ...
... coupling the electric field through a thin passivation layer and avoiding their direct contact with the solution. The DEP force is achieved by insulating structures like iDEP, but avoids large heat buildup by applying the electric field only in the trapping region. The device consists of columns of ...
5.1 questions - DrBravoChemistry
... Write an expression showing the relationship between free-energy change, ∆G, enthalpy change, ∆H, and entropy change, ∆S. ...
... Write an expression showing the relationship between free-energy change, ∆G, enthalpy change, ∆H, and entropy change, ∆S. ...
Chemistry 2 Higher revision mark scheme
... forms an oxide that reacts with alkalis with chlorine forms a molecular chloride 1 of these for 1 mark semi-conductor suggests in between this, or any other for 1further mark [NB Maximum of 2 for arguing metal/non-metal only] Under each head 1 wrong reason → maximum of 1 available 2 wrong reasons → ...
... forms an oxide that reacts with alkalis with chlorine forms a molecular chloride 1 of these for 1 mark semi-conductor suggests in between this, or any other for 1further mark [NB Maximum of 2 for arguing metal/non-metal only] Under each head 1 wrong reason → maximum of 1 available 2 wrong reasons → ...
Chemistry 8.2
... burning charcoal are the products of a combustion reaction. Combustion is one of the five general types of chemical reactions. If you can recognize a reaction as being a particular type, you may be able to predict the products of the reaction. ...
... burning charcoal are the products of a combustion reaction. Combustion is one of the five general types of chemical reactions. If you can recognize a reaction as being a particular type, you may be able to predict the products of the reaction. ...
19 BROWN Chemical Thermodynamics PPTSExercise
... Plan: In part (a) we can make this prediction by determining the sign of ΔS° for the reaction and then using that information to analyze Equation 19.12. In part (b) we need to calculate ΔH° and ΔS° for the reaction by using the data in Appendix C. We can then use Equation 19.12 to calculate ΔG°. Sol ...
... Plan: In part (a) we can make this prediction by determining the sign of ΔS° for the reaction and then using that information to analyze Equation 19.12. In part (b) we need to calculate ΔH° and ΔS° for the reaction by using the data in Appendix C. We can then use Equation 19.12 to calculate ΔG°. Sol ...
Slide 1
... Plan: In part (a) we can make this prediction by determining the sign of ΔS° for the reaction and then using that information to analyze Equation 19.12. In part (b) we need to calculate ΔH° and ΔS° for the reaction by using the data in Appendix C. We can then use Equation 19.12 to calculate ΔG°. Sol ...
... Plan: In part (a) we can make this prediction by determining the sign of ΔS° for the reaction and then using that information to analyze Equation 19.12. In part (b) we need to calculate ΔH° and ΔS° for the reaction by using the data in Appendix C. We can then use Equation 19.12 to calculate ΔG°. Sol ...
UNIVERSITY OF TARTU THE GIFTED AND
... water. In one beaker, the amount of water displaced by the gas was two times the amount displaced in the other beaker. a) Write the equations for the half-reactions for both the anode and cathode. Write the equation for the overall reaction. b) Calculate: i) the masses of the substances formed durin ...
... water. In one beaker, the amount of water displaced by the gas was two times the amount displaced in the other beaker. a) Write the equations for the half-reactions for both the anode and cathode. Write the equation for the overall reaction. b) Calculate: i) the masses of the substances formed durin ...
support material
... definite proportion by mass, which could be split by suitable chemical methods. Characteristics of compound Compounds always contain a definite proportion of the same elements by mass. The properties of compounds are totally different from the elements from which they are formed. Compounds are homog ...
... definite proportion by mass, which could be split by suitable chemical methods. Characteristics of compound Compounds always contain a definite proportion of the same elements by mass. The properties of compounds are totally different from the elements from which they are formed. Compounds are homog ...
ESO - ENCIGA
... order to be able to predict its behaviour and understand its history. Science is based on systematic experimentation and on observation of natural phenomena to discover facts about them and to formulate laws and principles based on these facts. The organized knowledge that is derived from scientific ...
... order to be able to predict its behaviour and understand its history. Science is based on systematic experimentation and on observation of natural phenomena to discover facts about them and to formulate laws and principles based on these facts. The organized knowledge that is derived from scientific ...
Document
... brought into same phase. However they do not dissolve glass, polyethylene, or Teflon. High solubility usually implies small reactor volumes in the final process. They are immiscible with a number of organic solvents and provide a non-aqueous, polar alternative for two phase systems, this has been us ...
... brought into same phase. However they do not dissolve glass, polyethylene, or Teflon. High solubility usually implies small reactor volumes in the final process. They are immiscible with a number of organic solvents and provide a non-aqueous, polar alternative for two phase systems, this has been us ...
Lessons 9
... Exothermic: A chemical system that releases energy from its surroundings Endothermic: A chemical system that absorbs energy from its surroundings Temperature: A measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a sample In early work, the energy required to raise the temperature of one gram ...
... Exothermic: A chemical system that releases energy from its surroundings Endothermic: A chemical system that absorbs energy from its surroundings Temperature: A measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a sample In early work, the energy required to raise the temperature of one gram ...
Chapter 23 + Practice Problems - Bloomsburg Area School District
... have a large amount of saturated fatty acids, fats are solids at room temperature. Oils have more unsaturated fatty acids than fats, and are liquids. Like other animals, humans make fat, which is stored in adipose tissue until it is needed as an energy source. Fat has about twice as much energy per ...
... have a large amount of saturated fatty acids, fats are solids at room temperature. Oils have more unsaturated fatty acids than fats, and are liquids. Like other animals, humans make fat, which is stored in adipose tissue until it is needed as an energy source. Fat has about twice as much energy per ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.