Chemistry - RESONANCE PCCP IDEAL for NTSE, IJSO, Olympiads
... In Latin, mole means heap or collection or pile. A mole of atoms is a collection of atoms whose total mass is the number of grams equal to the atomic mass in magnitude. Since an equal number of moles of different elements contain an equal number of atoms, it becomes convenient to express the amounts ...
... In Latin, mole means heap or collection or pile. A mole of atoms is a collection of atoms whose total mass is the number of grams equal to the atomic mass in magnitude. Since an equal number of moles of different elements contain an equal number of atoms, it becomes convenient to express the amounts ...
1.24 calculations and chemical reactions
... 4.1) An acid, H2A, reacts with sodium hydroxide as shown in the equation below. H2A(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) 2Na+(aq) + X2– (aq) + 2H2O(l) A solution of this acid was prepared by dissolving 2.02 g of H2A in water and making the volume up to 250 cm3 in a volumetric flask. A 25.0 cm3 sample of this solution re ...
... 4.1) An acid, H2A, reacts with sodium hydroxide as shown in the equation below. H2A(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) 2Na+(aq) + X2– (aq) + 2H2O(l) A solution of this acid was prepared by dissolving 2.02 g of H2A in water and making the volume up to 250 cm3 in a volumetric flask. A 25.0 cm3 sample of this solution re ...
- Lancaster EPrints
... theorists alike. Complexes of the f-elements typically exhibit strong relativistic effects, substantial dynamical electron correlation and weak crystal fields. These phenomena result in highly complicated electronic structures and, as such, theoretical measures of covalency based on different premis ...
... theorists alike. Complexes of the f-elements typically exhibit strong relativistic effects, substantial dynamical electron correlation and weak crystal fields. These phenomena result in highly complicated electronic structures and, as such, theoretical measures of covalency based on different premis ...
File - Chem with Appleby
... Questions: An Exothermic Equilibrium-36 The ________________________ for producing ammonia from the elements is exothermic. • One would think that cooling down the reactants would result in more product. • However, the activation energy for this reaction is _______________! • This is the _______ in ...
... Questions: An Exothermic Equilibrium-36 The ________________________ for producing ammonia from the elements is exothermic. • One would think that cooling down the reactants would result in more product. • However, the activation energy for this reaction is _______________! • This is the _______ in ...
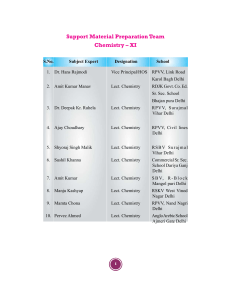
Support Material
... neither be created nor be destroyed. Law of De®nite Proportions (Joseph Proust) : A given compound Some Basic Concepts Of Chemistry ...
... neither be created nor be destroyed. Law of De®nite Proportions (Joseph Proust) : A given compound Some Basic Concepts Of Chemistry ...
09_Lecture
... • The equilibrium constant, K, defines the extent of a chemical reaction as a ratio of the concentration of the products to the concentration of the reactants. • If a chemical reaction at equilibrium is disturbed, the reaction can regain its equilibrium according to Le Châtelier’s principle by shift ...
... • The equilibrium constant, K, defines the extent of a chemical reaction as a ratio of the concentration of the products to the concentration of the reactants. • If a chemical reaction at equilibrium is disturbed, the reaction can regain its equilibrium according to Le Châtelier’s principle by shift ...
Study Material - Class- XI- Chemistry
... properties. *Atoms of different elements are different in all respects. *Atom is the smallest unit that takes part in chemical reactions. *Atoms combine with each other in simple whole number ratios to form molecules. *Atoms cannot be created, divided or destroyed during any chemical or physical cha ...
... properties. *Atoms of different elements are different in all respects. *Atom is the smallest unit that takes part in chemical reactions. *Atoms combine with each other in simple whole number ratios to form molecules. *Atoms cannot be created, divided or destroyed during any chemical or physical cha ...
equilibrium questions - Southington Public Schools
... Answer the following questions that relate to solubility of salts of lead and barium. (a) A saturated solution is prepared by adding excess PbI2(s) to distilled water to form 1.0 L of solution at 25˚C. The concentration of Pb2+(aq) in the saturated solution is found to be 1.3 10–3 M. The chemical ...
... Answer the following questions that relate to solubility of salts of lead and barium. (a) A saturated solution is prepared by adding excess PbI2(s) to distilled water to form 1.0 L of solution at 25˚C. The concentration of Pb2+(aq) in the saturated solution is found to be 1.3 10–3 M. The chemical ...
Science - The King`s School, Canterbury
... (c) Another group of students did experiments that gave several anomalous results. The teacher discussed possible errors that could have caused these anomalous results. ...
... (c) Another group of students did experiments that gave several anomalous results. The teacher discussed possible errors that could have caused these anomalous results. ...
C:\Documents and Settings\mrh70950\My Documents
... Chapter 1. Electrons, Bonds, and Molecular Properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 Chapter 2. Molecular Representations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17 Chapter 3. Acids and Bases . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
... Chapter 1. Electrons, Bonds, and Molecular Properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 Chapter 2. Molecular Representations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17 Chapter 3. Acids and Bases . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
API III User Training
... A syringe pump with air-tight “Sample-Lock” syringe can be used for air-sensitive analyses ...
... A syringe pump with air-tight “Sample-Lock” syringe can be used for air-sensitive analyses ...
Chapter 15a
... There are three types of problems encountered with weak acids or bases: dissociation, buffers or hydrolysis. We'll look at each type in detail. Dissociation of a Weak Acid In this type of problem, you will be asked to find the hydronium ion concentration and/or the pH of a weak acid whose initial co ...
... There are three types of problems encountered with weak acids or bases: dissociation, buffers or hydrolysis. We'll look at each type in detail. Dissociation of a Weak Acid In this type of problem, you will be asked to find the hydronium ion concentration and/or the pH of a weak acid whose initial co ...
CHE 1400 Lab Manual - Al Akhawayn University
... melting point and boiling point. Additional physical properties such as conductivity, malleability, etc. can also be determined. 1. Solubility The solubility of a substance is most accurately defined as the maximum mass (expressed in grams) of the test substance that dissolves in a known mass (usual ...
... melting point and boiling point. Additional physical properties such as conductivity, malleability, etc. can also be determined. 1. Solubility The solubility of a substance is most accurately defined as the maximum mass (expressed in grams) of the test substance that dissolves in a known mass (usual ...
Solutions - ChemConnections
... hydrogen in HCl is +1. To be reduced, the oxidation state of H must decrease. The obvious choice for the hydrogen product is H2(g), where hydrogen has a zero oxidation state. The balanced reaction is Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g). Mg goes from the 0 to the +2 oxidation state by losing two ele ...
... hydrogen in HCl is +1. To be reduced, the oxidation state of H must decrease. The obvious choice for the hydrogen product is H2(g), where hydrogen has a zero oxidation state. The balanced reaction is Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g). Mg goes from the 0 to the +2 oxidation state by losing two ele ...
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 120(15)
... Abstract: In contrast to porphyrins and chlorins, the direct metalation of bacteriochlorins is difficult. Nevertheless, Cu2+ and Zn2+ can be introduced into bacteriopheophytin in acetic acid, whereas Cd2+ can be inserted in dimethylformamide. The former reactions depend on the substituents of the is ...
... Abstract: In contrast to porphyrins and chlorins, the direct metalation of bacteriochlorins is difficult. Nevertheless, Cu2+ and Zn2+ can be introduced into bacteriopheophytin in acetic acid, whereas Cd2+ can be inserted in dimethylformamide. The former reactions depend on the substituents of the is ...
regents chemistry midterm - irondequoit 2014_entire exam w key
... Midterm Test 17. An element that is malleable and a good conductor of heat and electricity could have an atomic number of ...
... Midterm Test 17. An element that is malleable and a good conductor of heat and electricity could have an atomic number of ...
V. Diffusion
... Law for the relevant boundary and initial conditions. In specific cases where the jet component is stationary, ie constant during the process, the diffusion coefficient D can also be determined from the first Fick's law. Such a method of determining the values of D are called phones and the methods ...
... Law for the relevant boundary and initial conditions. In specific cases where the jet component is stationary, ie constant during the process, the diffusion coefficient D can also be determined from the first Fick's law. Such a method of determining the values of D are called phones and the methods ...
PDF document
... mination of acetylsalicylic acid. However, as far we know, there is no kinetic-spectrophotometric method for the determination of acetylsalicylic acid in the literature. Spectrophotometry is the technique of choice even today due to its inherent simplicity. It is frequently used in the laboratories ...
... mination of acetylsalicylic acid. However, as far we know, there is no kinetic-spectrophotometric method for the determination of acetylsalicylic acid in the literature. Spectrophotometry is the technique of choice even today due to its inherent simplicity. It is frequently used in the laboratories ...
silbchp4
... A, In forming the ionic compound MgO, each Mg atom transfers two electrons to each O atom. (Note that atoms become smaller when they lose electrons and larger when they gain electrons.) The resulting Mg 2+ and O2- ions aggregate with many others to form an ionic solid. B, In the reactants H2 and Cl2 ...
... A, In forming the ionic compound MgO, each Mg atom transfers two electrons to each O atom. (Note that atoms become smaller when they lose electrons and larger when they gain electrons.) The resulting Mg 2+ and O2- ions aggregate with many others to form an ionic solid. B, In the reactants H2 and Cl2 ...
chemistry notes on the mole - lessons
... quantity of sugar, fat, or vitamins and minerals between different brands as well. The quantitative information helps us decide which product to select to suit our needs. Quantities in chemical formulas offer the same kind of important information about the composition and properties of compounds in ...
... quantity of sugar, fat, or vitamins and minerals between different brands as well. The quantitative information helps us decide which product to select to suit our needs. Quantities in chemical formulas offer the same kind of important information about the composition and properties of compounds in ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.