Review - The University of Texas at Dallas
... Reduction half-cell (cathode) – Consumes same number of electrons supplied Salt Bridge – Permits charge rebalance by transporting counterions Spontaneous e– flow if voltage E > 0 ...
... Reduction half-cell (cathode) – Consumes same number of electrons supplied Salt Bridge – Permits charge rebalance by transporting counterions Spontaneous e– flow if voltage E > 0 ...
Chemistry (Theory)
... When aldol condensation is carried out between two different aldehydes and / or ketones, it is called cross aldol condensation. If both of them contain α-hydrogen atoms, it gives a mixture of four products. ...
... When aldol condensation is carried out between two different aldehydes and / or ketones, it is called cross aldol condensation. If both of them contain α-hydrogen atoms, it gives a mixture of four products. ...
Oxidation Number Rules
... c. Hydrogen usually has an oxidation number of +1 except in metallic hydrides where it then has an oxidation number of -1 Examples: HCl, hydrogen is +1; NaH, hydrogen is -1. d. The halogens, unless bonded to an element with a higher electronegativity, have an oxidation number of -1. Examples: NaCl, ...
... c. Hydrogen usually has an oxidation number of +1 except in metallic hydrides where it then has an oxidation number of -1 Examples: HCl, hydrogen is +1; NaH, hydrogen is -1. d. The halogens, unless bonded to an element with a higher electronegativity, have an oxidation number of -1. Examples: NaCl, ...
A-level Paper 1 Practice Paper 8 - A
... An ethanol–oxygen fuel cell may be an alternative to a hydrogen–oxygen fuel cell. When the cell operates, all of the carbon atoms in the ethanol molecules are converted into carbon dioxide. (i) ...
... An ethanol–oxygen fuel cell may be an alternative to a hydrogen–oxygen fuel cell. When the cell operates, all of the carbon atoms in the ethanol molecules are converted into carbon dioxide. (i) ...
Discussion 9, Mahaffy et al., Chapter 15
... a. Oxidation is loss of electrons (acts as a reducing agent) b.Reduction is gain of electrons (acts as a oxidizing agent) Assigning Oxidation numbers c. Oxidation number is 0 for atoms in an element. d.The sum of all oxidation numbers in a molecule or ion must add up to the total charge. e. In compo ...
... a. Oxidation is loss of electrons (acts as a reducing agent) b.Reduction is gain of electrons (acts as a oxidizing agent) Assigning Oxidation numbers c. Oxidation number is 0 for atoms in an element. d.The sum of all oxidation numbers in a molecule or ion must add up to the total charge. e. In compo ...
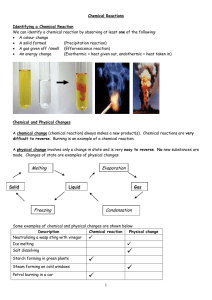
Chemical Reactions
... – When they absorb energy, it is known as an endothermic reaction – When they release heat it is called an exothermic reaction • Photosynthesis (when plants make sugar using carbon dioxide and water) is endothermic – it absorbs energy from the sun. • A campfire burning is exothermic – it releases en ...
... – When they absorb energy, it is known as an endothermic reaction – When they release heat it is called an exothermic reaction • Photosynthesis (when plants make sugar using carbon dioxide and water) is endothermic – it absorbs energy from the sun. • A campfire burning is exothermic – it releases en ...
Ionic Equations
... (MUCH more on this later!) • A reaction in which electrons are transferred from one atom to another is called an ____________________ reaction. ...
... (MUCH more on this later!) • A reaction in which electrons are transferred from one atom to another is called an ____________________ reaction. ...
Electrochem 1 - GCG-42
... To extrapolate the linear part of m ~ C1/2 at low concentration to C = 0, m can be ...
... To extrapolate the linear part of m ~ C1/2 at low concentration to C = 0, m can be ...
Electrochemistry - Menihek Home Page
... 8NO2(g) + ClO4-(aq) + 4 H2O Cl-(aq) + 8NO3-(aq) + 8 H+ To balance redox equations under basic conditions: Follow the same steps as under acidic conditions, but, there is an extra step.....balance out the H+ ions by adding OH- ... this will leave OH- in your overall redox reaction, which is expecte ...
... 8NO2(g) + ClO4-(aq) + 4 H2O Cl-(aq) + 8NO3-(aq) + 8 H+ To balance redox equations under basic conditions: Follow the same steps as under acidic conditions, but, there is an extra step.....balance out the H+ ions by adding OH- ... this will leave OH- in your overall redox reaction, which is expecte ...
PChem Experiment No. 1
... 100cm3 of 0.2M potassium ferricyanide solution was prepared. The zinc electrode was rinsed in dilute nitric acid solution and then rinsed with deionized water. The cell was assembled and was then placed in a two liter beaker filled with water at room temperature. 10cm3 of 1M ZnSO4 was added to the z ...
... 100cm3 of 0.2M potassium ferricyanide solution was prepared. The zinc electrode was rinsed in dilute nitric acid solution and then rinsed with deionized water. The cell was assembled and was then placed in a two liter beaker filled with water at room temperature. 10cm3 of 1M ZnSO4 was added to the z ...
Equilibrium - Cobb Learning
... Strike a match and it erupts instantaneously. Coal made from dead plants takes millions of years ...
... Strike a match and it erupts instantaneously. Coal made from dead plants takes millions of years ...
Ch 5.1 The Nature of Chemical Reactions
... Objectives For this Chapter • Understand parts to a chemical equation (reactants, products, yeild sign, double arrow) • Conservation of matter is expressed through balancing chemical equations • Describe difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions ...
... Objectives For this Chapter • Understand parts to a chemical equation (reactants, products, yeild sign, double arrow) • Conservation of matter is expressed through balancing chemical equations • Describe difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions ...
Oxidation-Reduction and Electrochemistry
... our present expression, enters: it is the negative extremity of the decomposing body; is where oxygen, chlorine, acids, etc., are evolved; and is against or opposite the positive electrode. The cathode is that surface at which the current leaves the decomposing body, and is its positive extremit ...
... our present expression, enters: it is the negative extremity of the decomposing body; is where oxygen, chlorine, acids, etc., are evolved; and is against or opposite the positive electrode. The cathode is that surface at which the current leaves the decomposing body, and is its positive extremit ...
Hebden V.2 – Oxidation Numbers
... Electrode – conductor at which a half-reaction occurs Anode – conductor at which oxidation occurs - receives electrons from substance being oxidized - electrode towards which anions travel Cathode – conductor at which reduction occurs - gives electrons away to a substance being reduced - electrode t ...
... Electrode – conductor at which a half-reaction occurs Anode – conductor at which oxidation occurs - receives electrons from substance being oxidized - electrode towards which anions travel Cathode – conductor at which reduction occurs - gives electrons away to a substance being reduced - electrode t ...
Electric Charges & Current
... Similar to potential energy (lifting something higher against the force of gravity gives it greater potential to do work, increasing its potential energy.) When given the opportunity, objects will move from higher potential energy to an area of lower potential energy Electrical potential is related ...
... Similar to potential energy (lifting something higher against the force of gravity gives it greater potential to do work, increasing its potential energy.) When given the opportunity, objects will move from higher potential energy to an area of lower potential energy Electrical potential is related ...
Uddingston Grammar School
... What effect would rusting have on the strength of an iron bridge? 1KU State one method that could be used to protect the iron bridge from rusting. 1KU The rate of rusting increases if an iron bridge comes into contact with sea water. Why does this happen? 1KU ...
... What effect would rusting have on the strength of an iron bridge? 1KU State one method that could be used to protect the iron bridge from rusting. 1KU The rate of rusting increases if an iron bridge comes into contact with sea water. Why does this happen? 1KU ...
Final Review: L17-25
... When we balance a chemical equation, the number of each type of atom must be the same on both the product and reactant sides of the equation. We use coefficients in front of compounds to balance chemical reactions. ...
... When we balance a chemical equation, the number of each type of atom must be the same on both the product and reactant sides of the equation. We use coefficients in front of compounds to balance chemical reactions. ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.