Chemistry 30
... reduction are the basis of batteries of all kinds and fuel cells, among other things. Oxidation and reduction are the reactions involved in both photosynthesis and respiration. Oxidation and reduction involve the exchange of electrons (acid-base reactions involve protons). Oxidation is the loss of a ...
... reduction are the basis of batteries of all kinds and fuel cells, among other things. Oxidation and reduction are the reactions involved in both photosynthesis and respiration. Oxidation and reduction involve the exchange of electrons (acid-base reactions involve protons). Oxidation is the loss of a ...
Chemistry -- Oxidation
... How could you get the electrons that Zn loses to Cu to create a current? You’d have to connect them! ...
... How could you get the electrons that Zn loses to Cu to create a current? You’d have to connect them! ...
Document
... The cell potential (voltage of the cell) depends on the chemicals used. For example, the chemicals in dry-cells (batteries) are such that the potential is always about 1.5 V. This has become a standard and is now a limiting factor in deciding which chemicals can be used to create a battery. The cell ...
... The cell potential (voltage of the cell) depends on the chemicals used. For example, the chemicals in dry-cells (batteries) are such that the potential is always about 1.5 V. This has become a standard and is now a limiting factor in deciding which chemicals can be used to create a battery. The cell ...
Big Idea #3
... Electrolysis & Understanding Electrolytic Cells: •When a non-spontaneous redox reaction is made to occur by putting electrical energy into the system. •The battery (energy source) acts as a “pump” pushing electrons into the cathode and removing electrons from the anode. •To maintain electrical neut ...
... Electrolysis & Understanding Electrolytic Cells: •When a non-spontaneous redox reaction is made to occur by putting electrical energy into the system. •The battery (energy source) acts as a “pump” pushing electrons into the cathode and removing electrons from the anode. •To maintain electrical neut ...
Red-ox reactions Electochemistry
... complete transfer of electrons to form ionic bond or only a partial transfer or shift of electrons to form ...
... complete transfer of electrons to form ionic bond or only a partial transfer or shift of electrons to form ...
Section A oxide in molten cryolite?
... cathode and bromine at the anode. Write half-equations for the two electrode reactions that take place during this electrolysis. anode ............................................................................................................................... cathode ............................. ...
... cathode and bromine at the anode. Write half-equations for the two electrode reactions that take place during this electrolysis. anode ............................................................................................................................... cathode ............................. ...
Red-ox reactions Electochemistry
... complete transfer of electrons to form ionic bond or only a partial transfer or shift of electrons to form ...
... complete transfer of electrons to form ionic bond or only a partial transfer or shift of electrons to form ...
Tutorial 7
... c) In the electrolysis : no. of moles of Mn2+ produced = It/nF =2.6 X 18 X 60/2 X 96500 =0.01455mol Total moles of [Mn2+] = 0.0250 + 0.01455 = conc. Of [Mn2+] = 0.0396 moles in 1 Liter = 0.0396 M ...
... c) In the electrolysis : no. of moles of Mn2+ produced = It/nF =2.6 X 18 X 60/2 X 96500 =0.01455mol Total moles of [Mn2+] = 0.0250 + 0.01455 = conc. Of [Mn2+] = 0.0396 moles in 1 Liter = 0.0396 M ...
General Chemistry 1412
... The Cu electrode is therefore being reduced and is the cathode. We can expect to see a gain in the mass of the electrode as the Cu2+ in solution is reduced to Cu and plates onto the electrode. The flow through the wire is then from anode to cathode, as in all electrochemical cells. In all voltaic ce ...
... The Cu electrode is therefore being reduced and is the cathode. We can expect to see a gain in the mass of the electrode as the Cu2+ in solution is reduced to Cu and plates onto the electrode. The flow through the wire is then from anode to cathode, as in all electrochemical cells. In all voltaic ce ...
Corrosion - iMechanica
... behaves entirely as a cathode and hence corrosion is averted. This can be achieved in two ways: a. Impressed Voltage: As shown in the figure 1a, an external dc power supply is connected to the metal to be protected. The negative terminal of the power supply is connected to the metal and the positive ...
... behaves entirely as a cathode and hence corrosion is averted. This can be achieved in two ways: a. Impressed Voltage: As shown in the figure 1a, an external dc power supply is connected to the metal to be protected. The negative terminal of the power supply is connected to the metal and the positive ...
AP Chapter Five Outline
... ions, or ions that are present in the reaction but to not undergo any change are ignored. ...
... ions, or ions that are present in the reaction but to not undergo any change are ignored. ...
TECHNICAL REPORT Modeling of faradaic reactions in
... The CV dependencies of the whole electrochemical cell are characterized by exponential current growth for small potential differences. When the system becomes limited by the transport, the exponential growth is suppressed. For high potential differences, the limiting current is reached. The shift of ...
... The CV dependencies of the whole electrochemical cell are characterized by exponential current growth for small potential differences. When the system becomes limited by the transport, the exponential growth is suppressed. For high potential differences, the limiting current is reached. The shift of ...
ch_24_poss_elmo
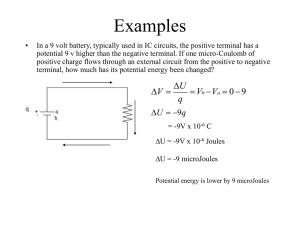
... Examples A proton is placed in an electric field of E=105 V/m and released. After going 10 cm, what is its speed? Use conservation of energy. a ...
... Examples A proton is placed in an electric field of E=105 V/m and released. After going 10 cm, what is its speed? Use conservation of energy. a ...
Redox - Plusnet
... In water Add oxygen in H2O to balance.... Giving MnO4-(aq) Mn2+(aq) + 4H2O(l) Assume an acidic solution to balance H.... Giving MnO4-(aq) + 8H+ Mn2+(aq) + 4H2O(l) Sort-out electrons for charge and redox.... MnO4-(aq) + 8H+ + 5e- Mn2+(aq) + 4H2O(l) ...
... In water Add oxygen in H2O to balance.... Giving MnO4-(aq) Mn2+(aq) + 4H2O(l) Assume an acidic solution to balance H.... Giving MnO4-(aq) + 8H+ Mn2+(aq) + 4H2O(l) Sort-out electrons for charge and redox.... MnO4-(aq) + 8H+ + 5e- Mn2+(aq) + 4H2O(l) ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.