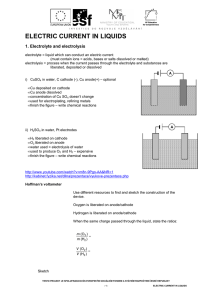
gallagher chapter 21 08
... of AgNO3 and beaker (b) was the solution of Zn(NO3)2 Because there is no outside source of electricity the only reaction that can occur is a spontaneous one – Cu is above Ag therefore spontaneous, Cu is below Zn, therefore a nonspontaneous reaction and would require an outside source of energy to fo ...
... of AgNO3 and beaker (b) was the solution of Zn(NO3)2 Because there is no outside source of electricity the only reaction that can occur is a spontaneous one – Cu is above Ag therefore spontaneous, Cu is below Zn, therefore a nonspontaneous reaction and would require an outside source of energy to fo ...
Biology Fall Semester Test 1 Study Guide
... Two products of cellular respiration are: In producers, chlorophyll and sunlight are necessary for the process of: The closing of its shell when a clam is removed from its watery environment is an example of how a clam maintains its: In a trophic pyramid, _______% of the energy from a source is pass ...
... Two products of cellular respiration are: In producers, chlorophyll and sunlight are necessary for the process of: The closing of its shell when a clam is removed from its watery environment is an example of how a clam maintains its: In a trophic pyramid, _______% of the energy from a source is pass ...
Unit 14.1 REDOX Reactions Objectives REDOX Reactions
... • Determine the oxidation number of an element on both the reactant and product side of the reaction. If the oxidation number increases, the atom was oxidized. Cu (s) + 2 AgNO3 (aq) --> Cu(NO3) 2 (aq) + 2 Ag (s) ...
... • Determine the oxidation number of an element on both the reactant and product side of the reaction. If the oxidation number increases, the atom was oxidized. Cu (s) + 2 AgNO3 (aq) --> Cu(NO3) 2 (aq) + 2 Ag (s) ...
Chap 9 Redox Review Q`s
... Which processes occur during the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride? I. Sodium and chloride ions move through the electrolyte. II. Electrons move through the external circuit. III. Oxidation takes place at the positive electrode (anode). ...
... Which processes occur during the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride? I. Sodium and chloride ions move through the electrolyte. II. Electrons move through the external circuit. III. Oxidation takes place at the positive electrode (anode). ...
Chemical Equations
... 2) The oxidation state of a monatomic ion is equal to its ionic charge. (ex. Na+, Cl-3) 3) H has an oxidation of +1 and oxygen has an oxidation state of -2 when they are present in most compounds. (Exceptions: Hydrogen is -1 in hydrides of metals such as LiH, and Oxygen is -1 in peroxides such as H2 ...
... 2) The oxidation state of a monatomic ion is equal to its ionic charge. (ex. Na+, Cl-3) 3) H has an oxidation of +1 and oxygen has an oxidation state of -2 when they are present in most compounds. (Exceptions: Hydrogen is -1 in hydrides of metals such as LiH, and Oxygen is -1 in peroxides such as H2 ...
Chapter 20b - U of L Class Index
... water in the paste dissolves some salt to make a saturated solution in which the ion concentrations do not significantly decrease until near the end of the cell’s usefulness. The solution also allows for ion migration (necessary for flow of charge). Dry Batteries (Zinc-Carbon Cell, or Leclenché Cell ...
... water in the paste dissolves some salt to make a saturated solution in which the ion concentrations do not significantly decrease until near the end of the cell’s usefulness. The solution also allows for ion migration (necessary for flow of charge). Dry Batteries (Zinc-Carbon Cell, or Leclenché Cell ...
CHEMISTRY 1000 - U of L Class Index
... When the Cu2(OH)2CO3 reacts with acid rain (dilute sulfuric acid), a second, more permanent green solid, Cu2(OH)2SO4 is produced: Cu2(OH)2CO3(s) + H2SO4(aq) Cu2(OH)2SO4(s) + H2CO3(aq) ...
... When the Cu2(OH)2CO3 reacts with acid rain (dilute sulfuric acid), a second, more permanent green solid, Cu2(OH)2SO4 is produced: Cu2(OH)2CO3(s) + H2SO4(aq) Cu2(OH)2SO4(s) + H2CO3(aq) ...
Name: 1) What is the oxidation number of sulfur in H SO ? A)
... 63) In an electrolytic cell, to which electrode will a positive ion migrate and undergo reduction? A) the cathode, which is negatively charged B) the anode, which is positively charged ...
... 63) In an electrolytic cell, to which electrode will a positive ion migrate and undergo reduction? A) the cathode, which is negatively charged B) the anode, which is positively charged ...
Vocabulary Terms
... Solar cells collect energy from the sun. Chemical energy comes from the reaction of two or more chemicals such as in a battery or in the human body. Battery: A device that creates electricity from chemical reactions. Conductor: A material that lets electricity flow through it (metal, water). Insulat ...
... Solar cells collect energy from the sun. Chemical energy comes from the reaction of two or more chemicals such as in a battery or in the human body. Battery: A device that creates electricity from chemical reactions. Conductor: A material that lets electricity flow through it (metal, water). Insulat ...
Chapter 21 Nonmetallic Elements and Their Compounds
... electrolysis of carbon tetrachloride. oxidation of chloride ion with F2(g). electrolysis of NaCl(aq). oxidation of chloride ion with Br2(aq). electrolysis of AlCl3(aq). ...
... electrolysis of carbon tetrachloride. oxidation of chloride ion with F2(g). electrolysis of NaCl(aq). oxidation of chloride ion with Br2(aq). electrolysis of AlCl3(aq). ...
Electrochemistry of Fuel Cell
... where R is the gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, F is the Faraday constant, aA is the activity of A, aB is the activity of B, and E° is the standard electrode potential when the activity is equal to unity. E° is a potential intrinsic to the redox reaction; it is a measure of the ease of i ...
... where R is the gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, F is the Faraday constant, aA is the activity of A, aB is the activity of B, and E° is the standard electrode potential when the activity is equal to unity. E° is a potential intrinsic to the redox reaction; it is a measure of the ease of i ...
Unit 4 - cloudfront.net
... an electric current. A. Voltaic Cells (Galvanic Cells): A redox reaction that occurs _________________________. ΔG = ____; EMF (_____________________________, cell potential) = ____ 1. These redox reactions can supply ___________ and are used to do _______. 2. The oxidation and reduction reactions a ...
... an electric current. A. Voltaic Cells (Galvanic Cells): A redox reaction that occurs _________________________. ΔG = ____; EMF (_____________________________, cell potential) = ____ 1. These redox reactions can supply ___________ and are used to do _______. 2. The oxidation and reduction reactions a ...
PPt3 - WordPress.com
... • In addition, the concentration of unknown solution can be determined by generating a calibration curve of current vs. concentration. ...
... • In addition, the concentration of unknown solution can be determined by generating a calibration curve of current vs. concentration. ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.