LECTURE NOTE ELECTRIC POTENTIAL
... Ev IS USEFUL TO STATE THE ENERGIES OF MOLECULES AND ELEMENTARY PARTICLES BUT IT IS NOT A PROPER SI UNIT. FPR CALCULATIONS Ev SHOULD BE CONTINUED TO JOULES EX: 5000 Ev = 8.0 x 10-16 j/1.6 x 10-19 Ev USING eV TO STATE ENERGY IS FINE BUT TO MAKE FURTHER CALCULATIONS THE CONVERSION MUST BE MADE. ELECTR ...
... Ev IS USEFUL TO STATE THE ENERGIES OF MOLECULES AND ELEMENTARY PARTICLES BUT IT IS NOT A PROPER SI UNIT. FPR CALCULATIONS Ev SHOULD BE CONTINUED TO JOULES EX: 5000 Ev = 8.0 x 10-16 j/1.6 x 10-19 Ev USING eV TO STATE ENERGY IS FINE BUT TO MAKE FURTHER CALCULATIONS THE CONVERSION MUST BE MADE. ELECTR ...
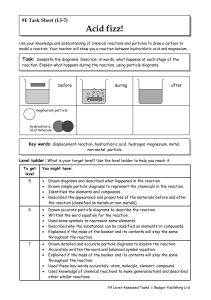
Precipitation Reactions
... The rules you just learned assume that the redox reaction is taking place under acidic conditions. (You are, after all, either producing or consuming H+ ions.) There are slightly different rules for basic conditions: 1. Balance the reaction (using your method of choice) as if it were under acidic co ...
... The rules you just learned assume that the redox reaction is taking place under acidic conditions. (You are, after all, either producing or consuming H+ ions.) There are slightly different rules for basic conditions: 1. Balance the reaction (using your method of choice) as if it were under acidic co ...
Nervous Systems - Western Washington University
... Describe the increasing complexity that likely reflects the stages in the evolution of nervous systems. Differentiate between inhibitory and excitatory postsynaptic potentials, and the generation of a grand synaptic potential Differentiate between synaptic potentials and action potentials ...
... Describe the increasing complexity that likely reflects the stages in the evolution of nervous systems. Differentiate between inhibitory and excitatory postsynaptic potentials, and the generation of a grand synaptic potential Differentiate between synaptic potentials and action potentials ...
Atoms and Elements Notes
... 1. Physical Change- A change in form that does not result in a new substance. Ex. Sugar dissolves in water or any state change. 2. Chemical Change- A change/reaction that creates a new substance. An indication this is happening is when you see a color change, heat, light, smoke/gas and a new byprodu ...
... 1. Physical Change- A change in form that does not result in a new substance. Ex. Sugar dissolves in water or any state change. 2. Chemical Change- A change/reaction that creates a new substance. An indication this is happening is when you see a color change, heat, light, smoke/gas and a new byprodu ...
Review Material
... The first bond between any two atoms is a strong sigma (σ) bond. To describe multiple (double and triple) bonding we must consider a second kind of bond that results from the overlap between two p orbitals oriented perpendicular to the inter-nuclear axis, as illustrated below: ...
... The first bond between any two atoms is a strong sigma (σ) bond. To describe multiple (double and triple) bonding we must consider a second kind of bond that results from the overlap between two p orbitals oriented perpendicular to the inter-nuclear axis, as illustrated below: ...
Introduction to Chemistry for Coach Keith`s Biology
... The force of attraction between molecules is so strong that the oxygen atom of one molecule can actually remove the hydrogen from other water molecules; called Dissociation H20-----GOES TO----- H+ + OHOH- called hydroxide ion; H+ called hydrogen ion Free H+ ion can react with another water molecule ...
... The force of attraction between molecules is so strong that the oxygen atom of one molecule can actually remove the hydrogen from other water molecules; called Dissociation H20-----GOES TO----- H+ + OHOH- called hydroxide ion; H+ called hydrogen ion Free H+ ion can react with another water molecule ...
FINAL EXAM Review Sheet / Study Guide Honors Chemistry
... 33) Write the name of each of the following compounds. a) ________________________ AgNO3 ...
... 33) Write the name of each of the following compounds. a) ________________________ AgNO3 ...
Miami-Dade College
... e. Calculating the concentration of ions needed to initiate precipitation. f. Predicting if precipitation will occur if solutions of known ionic concentration are mixed. g. Listing several ways to dissolve “insoluble” substances. [OPTIONAL] h. Solving appropriate [OPTIONAL] ...
... e. Calculating the concentration of ions needed to initiate precipitation. f. Predicting if precipitation will occur if solutions of known ionic concentration are mixed. g. Listing several ways to dissolve “insoluble” substances. [OPTIONAL] h. Solving appropriate [OPTIONAL] ...
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Oxidation-Reduction
... The concept of oxidation numbers is a simple way of keeping track of electrons in a reaction. The oxidation number (or oxidation state) of an atom in a substance is the actual charge of the atom if it exists as a monatomic ion. Alternatively, it is hypothetical charge assigned to the atom in the sub ...
... The concept of oxidation numbers is a simple way of keeping track of electrons in a reaction. The oxidation number (or oxidation state) of an atom in a substance is the actual charge of the atom if it exists as a monatomic ion. Alternatively, it is hypothetical charge assigned to the atom in the sub ...
Web Supplement 7.2
... In the preceding equations, the dissolved copper and zinc species are shown as ions having a +2 charge, i.e., Cu2+ (aq) and Zn2+ (aq). Chemists have extended this concept of charge to chemically bound atoms by assigning its atom an oxidation number. The rules for determining the oxidation number of ...
... In the preceding equations, the dissolved copper and zinc species are shown as ions having a +2 charge, i.e., Cu2+ (aq) and Zn2+ (aq). Chemists have extended this concept of charge to chemically bound atoms by assigning its atom an oxidation number. The rules for determining the oxidation number of ...
Chemistry Review: Unit2 - Menno Simons Christian School
... 6) Name 5 observations that indicate a chemical change. Heat is produced or absorbed, starting material is used up, there is a change in colour, a material with new properties is formed, gas bubbles form in a liquid, a precipitate forms in a liquid and the change is difficult to reverse. 7) In the t ...
... 6) Name 5 observations that indicate a chemical change. Heat is produced or absorbed, starting material is used up, there is a change in colour, a material with new properties is formed, gas bubbles form in a liquid, a precipitate forms in a liquid and the change is difficult to reverse. 7) In the t ...
Honors Chemistry- Chapter 16 Homework Packet Reaction Energy
... 4) 2.5 kJ of heat energy is added to a 75 gram sample of copper metal. If the metal starts at a temperature of 45°C, what will the final temperature of the copper metal be? (Cp (Cu) = 0.385 J/g°C). ...
... 4) 2.5 kJ of heat energy is added to a 75 gram sample of copper metal. If the metal starts at a temperature of 45°C, what will the final temperature of the copper metal be? (Cp (Cu) = 0.385 J/g°C). ...
Writing Chemical Formulas
... Practice Writing Chemical Formulas: Write the formulas for the compounds formed when these elements combine. Do not look at the answers before you have written all the formulas. If one of your formulas differs from the answer, try to find out why. If you have questions, ask your ...
... Practice Writing Chemical Formulas: Write the formulas for the compounds formed when these elements combine. Do not look at the answers before you have written all the formulas. If one of your formulas differs from the answer, try to find out why. If you have questions, ask your ...
Review Sheet for Chemistry* First Semester Final
... Chemical reactions can often be classified as one of five types. Write the general form for each type of reaction. Direct Combination (or synthesis): ...
... Chemical reactions can often be classified as one of five types. Write the general form for each type of reaction. Direct Combination (or synthesis): ...
the mechanical universe - Binghamton City School District
... What famous royal figure attended a formal lecture given by Michael Faraday in the lat 1700’s at the Royal Institute? ...
... What famous royal figure attended a formal lecture given by Michael Faraday in the lat 1700’s at the Royal Institute? ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.