Irreversible Changes
... school, but it is not always obvious that a chemical reaction has taken place. Changes that take place in cooking, some heating, mixing some materials, such as vinegar and bicarbonate of soda, and burning are all chemical reactions. As children experience these activities it is worth discussing this ...
... school, but it is not always obvious that a chemical reaction has taken place. Changes that take place in cooking, some heating, mixing some materials, such as vinegar and bicarbonate of soda, and burning are all chemical reactions. As children experience these activities it is worth discussing this ...
Review Packet
... Given the following reactants predict the products. Add if the reactions are classified as Acid-Base in addition to the other classifications. ...
... Given the following reactants predict the products. Add if the reactions are classified as Acid-Base in addition to the other classifications. ...
Packet
... Given the following reactants predict the products. Add if the reactions are classified as Acid-Base in addition to the other classifications. ...
... Given the following reactants predict the products. Add if the reactions are classified as Acid-Base in addition to the other classifications. ...
Writing Chemical Equations
... • Chemical change does not result in destruction or creation of atoms. Thus all atoms in the reactants must also be present in the products. • 2Al(s) + 3Br2(l) → 2AlBr3(s) • In the above equation there are 2 Al atoms and 6 Br atoms, thus matter is conserved. ...
... • Chemical change does not result in destruction or creation of atoms. Thus all atoms in the reactants must also be present in the products. • 2Al(s) + 3Br2(l) → 2AlBr3(s) • In the above equation there are 2 Al atoms and 6 Br atoms, thus matter is conserved. ...
part 3 - instructor version
... Oxidizing Agent = oxidizes something else while being reduced (Cu 2+ Cu0) ...
... Oxidizing Agent = oxidizes something else while being reduced (Cu 2+ Cu0) ...
Notes
... When two different metals are attached, electrons always flow from the metal higher in the series to the lower metal. The further apart the two metals are in the ECS the larger the cell voltage is. A more complex electrochemical cell can be made by joining two half cells with an ion bridge. By dippi ...
... When two different metals are attached, electrons always flow from the metal higher in the series to the lower metal. The further apart the two metals are in the ECS the larger the cell voltage is. A more complex electrochemical cell can be made by joining two half cells with an ion bridge. By dippi ...
X CHEMISTRY-1-2006 TIME-1½ MARKS 80 SECTION
... Calculate the volume of methane (ctlu) measured at S.T.P released from 14.48 of aluminum carbide by excess of water (Al-27, C=12, H=1). E. a. What a kind of particles will be found in a liquid compound which is a non- electrolyte? c. If HX is a weak acid, what particles will be preseut in its dilute ...
... Calculate the volume of methane (ctlu) measured at S.T.P released from 14.48 of aluminum carbide by excess of water (Al-27, C=12, H=1). E. a. What a kind of particles will be found in a liquid compound which is a non- electrolyte? c. If HX is a weak acid, what particles will be preseut in its dilute ...
Notes
... Key Questions: • Identify the three subatomic particles found in atoms. • Explain how all of the isotopes of an element are similar and how they are different. • Explain how compounds are different from their component elements. • Describe the two main types of chemical bonds ...
... Key Questions: • Identify the three subatomic particles found in atoms. • Explain how all of the isotopes of an element are similar and how they are different. • Explain how compounds are different from their component elements. • Describe the two main types of chemical bonds ...
Review AGº = -RTlnKº Calculate the equilibrium constant Kc at 25 ºC
... ΔG°rxn = ΔG°rxn1 + ΔG°rxn2 + … = ΣnΔG°rxns ΔS°rxn = ΔS°rxn1 + ΔS°rxn2 + … = ΣnΔS°rxns ΔH°rxn = ΔH°rxn1 + ΔH°rxn2 + … = ΣnΔH°rxns ...
... ΔG°rxn = ΔG°rxn1 + ΔG°rxn2 + … = ΣnΔG°rxns ΔS°rxn = ΔS°rxn1 + ΔS°rxn2 + … = ΣnΔS°rxns ΔH°rxn = ΔH°rxn1 + ΔH°rxn2 + … = ΣnΔH°rxns ...
Reactions In Aqueous Solution
... What is the oxidation number of phosphorus in sodium phosphate, Na3PO4? In the dihydrogen phosphate ion, H2PO4-1? ...
... What is the oxidation number of phosphorus in sodium phosphate, Na3PO4? In the dihydrogen phosphate ion, H2PO4-1? ...
Year 8 Science Assessment Point 2
... 3. Limiting reactants: A reactant that is used up in a chemical reaction and stops it from continuing 4. Chromatography: A technique where a mixture is separated For example: • Magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid. • When the reaction is over: Magnesium is the limiting reactant if it is all gone ...
... 3. Limiting reactants: A reactant that is used up in a chemical reaction and stops it from continuing 4. Chromatography: A technique where a mixture is separated For example: • Magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid. • When the reaction is over: Magnesium is the limiting reactant if it is all gone ...
2. Chemistry of Living Things Outline
... The simplest carbohydrates are called ___________________ or simple sugars. They are called the “_____________________” of carbohydrates. A common monosaccharide is ______________ (C6H12O6). o Glucose is formed during _____________________. When two simple sugars combine, they form a _____________ o ...
... The simplest carbohydrates are called ___________________ or simple sugars. They are called the “_____________________” of carbohydrates. A common monosaccharide is ______________ (C6H12O6). o Glucose is formed during _____________________. When two simple sugars combine, they form a _____________ o ...
Chemistry of Living Things Outline
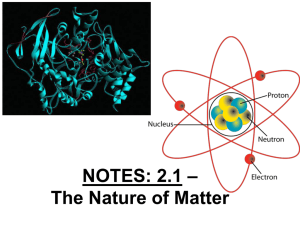
... Living and nonliving things are made up of tiny units called ________. The center core is called the _____________. The nucleus is made up of particles called __________ and ___________ _____________ have a positive charge (+1) and _____________ have no electrical charge (0). Negatively charged pa ...
... Living and nonliving things are made up of tiny units called ________. The center core is called the _____________. The nucleus is made up of particles called __________ and ___________ _____________ have a positive charge (+1) and _____________ have no electrical charge (0). Negatively charged pa ...
electrochemistry - einstein classes
... redox reactions, i.e, the oxidation and reduction reactions takes place in different container. The electrochemical cells (galvanic or voltaic) consists of two half cells connected with each other by means of an electric wire to allow an indirect redox reaction. Although the solutions of two half ce ...
... redox reactions, i.e, the oxidation and reduction reactions takes place in different container. The electrochemical cells (galvanic or voltaic) consists of two half cells connected with each other by means of an electric wire to allow an indirect redox reaction. Although the solutions of two half ce ...
Chapter 2 Chemical Reactions
... Describes a reaction Must be balanced in order to follow the Law of Conservation of Mass Can only be balanced by changing the coefficients. Has special symbols to indicate the physical state, if a catalyst or energy is ...
... Describes a reaction Must be balanced in order to follow the Law of Conservation of Mass Can only be balanced by changing the coefficients. Has special symbols to indicate the physical state, if a catalyst or energy is ...
Review-Semester Final (Part I)
... 13. List the 4 signs of a chemical change (i.e. chemical reaction) ...
... 13. List the 4 signs of a chemical change (i.e. chemical reaction) ...
review sheet
... 3. The oxidation number of a free element is always ____________________. 4.The most active reducing agent among the elements is ____________________. 5. For each of the following equation s determine whether oxidation or reduction is happening. K K+ + eS + 2e- S-2 6. What is the difference betw ...
... 3. The oxidation number of a free element is always ____________________. 4.The most active reducing agent among the elements is ____________________. 5. For each of the following equation s determine whether oxidation or reduction is happening. K K+ + eS + 2e- S-2 6. What is the difference betw ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.